Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a problem that occurs with the heart’s electrical activity leading to irregular and rapid heart rate, which can increase one’s risk of strokes, heart failure or other complications.
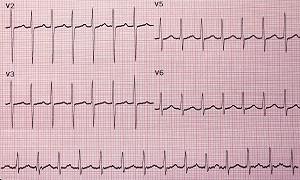
During this problem, the heart’s two upper chambers beat chaotically as well as irregularly out of coordination with the two lower chambers of the heart. Symptoms of atrial fibrillation usually include heart palpitations, shortness of breath and weakness. One major concern with this ailment is the potential to develop blood clots within the upper chambers of the heart, which can circulate to other organs, leading to blocked blood flow which is termed as ischemia.
Treatments for atrial fibrillation often include medications as well as other interventions to attempt to alter the heart’s electrical system.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
Some people who have from atrial fibrillation show no symptoms and are unaware of their conditions until they discover it during a physical examination. Other people with this ailment can show symptoms such as :
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the chest
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation can be of multiple types:
- Occasional- In this case, you can have symptoms from time to time which can last from a minute to an hour. Sometimes the symptoms can show for as long as one week, but it might go away on their own without treatment.
- Persistent- In this case, your heart rhythm doesn’t go back to normal on its own. When your atrial fibrillation becomes persistent, you will require treatment such as shock or medications to help you restore your heart rhythm.
- Long-standing persistent- In this case, the atrial fibrillation becomes continuous and lasts longer than 12 months.
- Permanent- In this type of atrial fibrillation, you can’t restore the abnormal heart rhythm, and you will need to keep taking medications to control your heart rate and to prevent blood clots.
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
The heart has four chambers- two upper and two lower. Within the upper right chamber of your heart, there is a group of cells termed as the sinus node. This is the natural pacemaker of the heart. The signal that starts each heart back is produced by the sinus node.
This signal normally travels through the two upper heart chambers and then through a connecting pathway which lies between the upper and the lower chambers called the atrioventricular node. The movement of this signal can cause the heart to squeeze which sends blood to your heart and body.
During Atrial fibrillation, the signals in the upper chambers of one’s heart are chaotic; this causes them to quiver. This causes the AV node to be bombarded with impulses trying to get through to the ventricles. The ventricles beat rapidly as well, though not as much as the atria and not all the impulses get through.
Damage or abnormalities in the structure are the most common causes of this condition. Some possible causes that lead to atrial fibrillation are:
- Heart attack
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal heart valves
- Coronary artery disease
- An overactive thyroid gland or other metabolic imbalance
- Heart defends that come with birth
- Too much exposure to stimulants such as medications, caffeine, alcohol and tobacco
- Lung diseases
- Viral infection
- Previous heart surgery
- Stress caused by surgery or illnesses such as pneumonia
- Sleep apnea
However, some people have atrial fibrillation but don’t have any heart defects or damage, a condition called lone atrial fibrillation. In this condition, the cause is often unclear and serious complications are rare. Some factors that might reduce the risk of atrial fibrillation include:
- Age- As you get older, your risk of developing atrial fibrillation increases.
- Heart disease- Anyone with heart diseases such as congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, a history of heart attack or heart surgery also has an increased risk of atrial fibrillation.
- Drinking- Too much drinking can also trigger atrial fibrillation, for some people.
- High blood pressure- If you have high blood pressure, it puts you at risk, especially if you are not controlling it with lifestyle changes or medication.
- Family history- Some families show an increased risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
- Obesity- Obese people are at a higher risk as well.
- Chronic conditions- People who suffer from certain chronic conditions like sleep apnea, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, thyroid problems, chronic kidney or lung disease also have a greater chance of having atrial fibrillation.
Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation
For diagnosing this condition, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, after which a physical examination will be conducted. Some of the tests the doctor may order include:
Electrocardiogram
Event Recorder
Holter Monitor
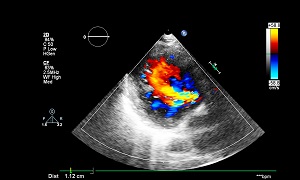
Echocardiogram
Blood tests
Stress test
Chest X-ray
Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
Initially, your doctor will give you medicines that can help in preventing clots and strokes as well as control the heart rhythm.
Blood thinners are a type of medication that thins your blood to lower your risk of having such problems. However, they can increase your risk of bleeding, which is why you might need to cut back on some activities that lead to injuries. You’ll also need to visit your doctor at least once every month in order to make sure that the medication is working and you are on the right dosage.
Heart rate medicines are another form of treatment that is used to treat atrial fibrillation. These can help in slowing your rapid heart rate so that your heart can pump better. You might also need some other drugs called beta-blockers, such as Atenolol, Metoprolol and Timolol.
Your doctor might also prescribe heart rhythm medicines, which can slow the electrical signals in order to bring your heartbeat into what we call a normal sinus rhythm. Sometimes this kind of treatment is called chemical cardioversion.
If medicines fail to work or they cause side effects, your doctor might recommend one of two procedures which are called cardioversion or ablation. These can treat without surgery.
Electrical cardioversion
The doctor will give your heart a shock to regulate your heartbeat, after which he will use paddles or stick patches called electrodes onto your chest. You’ll be initially given medicine that will make you fall asleep. Then your doctor will be putting the paddles on your chest and sometimes on your back. This can give you a mild electrical shock in order to get your heart’s rhythm back to normal.
Most people need only one shock and since you’re sedated, you probably won’t remember being shocked and you should be able to return home the same day. Sometimes your skin might be irritated where the paddles touched it. Your doctor can recommend a lotion to ease pain or itching.
Cardiac ablation
This includes two major options-
Catheter ablation
Also termed as radiofrequency or pulmonary vein ablation, this is a less invasion option as compared to surgery. Your doctor will put a thin and flexible tube into a blood vessel in your leg or your neck. It will be guided to the heart. When it reaches the area that is causing the arrhythmia, it will be sending out electrical signals which will destroy these cells, and after this, the treated tissue will help your heartbeat get to regular again.
There are also main types of catheter ablation which include:
- Radiofrequency ablation– In this method, the doctor will be using catheters to send radiofrequency energy which will create circular scars around each vein or group of veins.
- Cryoablation- A single catheter sends a balloon-tipped with a substance that will be able to freeze the tissues, causing a scar.
Surgical ablation
This involves involve cutting into your chest and it is of different types:
- Maze procedure- This procedure is usually performed while you are having open-heart surgery for another problem such as a bypass or a valve replacement. The surgeon will then make small cuts in the upper part of the heart, which will be stitched together eventually in order to form the scar tissue which will help to stop abnormal signals.
- Mini Maze- Most people who suffer from atrial fibrillation usually don’t need open-heart surgery and that’s where this less invasion option’s effectiveness can be seen. The doctor will make several small cuts between your ribs, after which he will use a camera to guide catheters for cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation. There are also some hospitals that are known to offer robot-assisted surgery, which uses smaller cuts allowing more precision. Your doctor will next put a video camera or tiny robot into your chest, which will guide the creation of scar tissue, in order to help keep your heartbeat at the right place.
Convergent Procedure
This procedure pairs catheter ablation with a mini maze. The doctor uses radiofrequency ablation in the pulmonary vein, after which a surgeon will make a small cut under your breastbone in order to use radiofrequency energy on the outside of the heart.
AV node ablation
This procedure can be recommended if your medications don’t work or you are unable to take them due to side effects. If you aren’t a good candidate for the other procedures, this one is considered as the last option. In this procedure, your doctor will be inserting a catheter into a vein in your groin and slide it up the AV node, a nerve that conducts electrical impulses between the top as well as bottom chambers of the heart. Your doctor will also send radiofrequency energy through your ventricle and then will implant a pacemaker into your chest. It will deliver electric pulses that will make your heartbeat.
Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation
There are also steps that you can take to prevent atrial fibrillation and there’s nothing more important than living a lifestyle that will help to reduce your risk of heart disease. A healthy lifestyle should include:
- A diet which is healthy for the heart
- Increasing your physical activity
- Not smoking
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting or restricting caffeine and alcohol
- Reducing stress, as intense stress and anger might lead to heart rhythm problems.