Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a condition of irregular heartbeat, where a person’s heart may beat too fast, too slowly or with an irregular rhythm. This problem occurs when the electrical signals that coordinate heartbeats don’t work properly. An irregular heartbeat might feel like a racing heart. Sometimes, doctors use the word ‘dysrhythmia’ to describe this condition, but the words ‘dysrhythmia’ and ‘arrhythmia’ actually means the same.
Many heart arrhythmias are harmless. However, if they become highly irregular or result from a weak or damaged heart, it can cause severe and potentially fatal symptoms as well as complications.
Types of Arrhythmia
There are different categories of arrhythmia, which includes:
- Bradycardia, a slow heartbeat
- Tachycardia, a fast heartbeat
- Irregular heartbeat also called flutter or fibrillation
- Early heartbeat, also called as a premature contraction
The majority of arrhythmias are not severe and they don’t cause complications. However, there are some, which can increase the risk of stroke or cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias might not cause any signs or symptoms. It is usually found by your doctor while having a routine examination. It is also important to note that having a few signs and symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean that your condition is serious.
Some of the noticeable symptoms of arrhythmia include:
- A fluttering in your chest
- A slow heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breathe
- A racing heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Sweating
- Fainting
- Lightheadedness
If you are experiencing these problems on a regular basis, you might consider seeking urgent medical care. Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia that can be deadly. It occurs when your heart beats with rapid, erratic and electrical impulses. This can cause the lower chambers of your heart to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood. Without a proper and effective heartbeat, blood pressure plummets and it cuts off blood supply to the vital organs.
A person suffering from ventricular fibrillation can collapse within a few seconds and soon won’t be breathing or having a pulse. If this happens, you need to call the emergency number in your area. If you find no one who is trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation, try to provide hands-only CPR. Also, see if an automated external defibrillator is available nearby. They might be available in several places, such as airplanes, police cars or shopping malls.
Causes of Arrhythmia
Several causes leading to arrhythmia is there, such as
- Alcohol abuse
- Diabetes
- Drinking a lot of coffee
- High Blood Pressure
- Hyperthyroidism
- Stress
- Scarring of the heart, often due to a heart attack
- Substance abuse
- Certain medications or supplements
- Smoking
- Structural changes in the heart
A person having a healthy heart won’t ever experience long-term arrhythmia, unless they receive an external trigger, such as an electrical shock.
Diagnosis of Arrhythmia
For diagnosis of a heart arrhythmia your doctor will review your symptoms as well as your medical history, after which a physical examination will be conducted. Your doctor might ask you about conditions that can trigger your arrhythmia, such as heart disease or a problem with the thyroid gland. Your doctor might also perform heart-monitoring tests specific to arrhythmias. These can include:
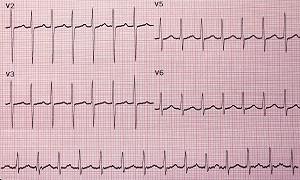
Electrocardiogram
Holter monitor
Event recorder
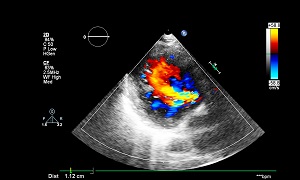
Echocardiogram
Implantable loop recorder
Stress test
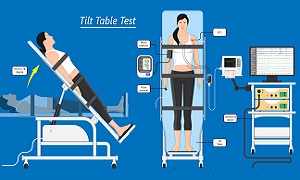
Tilt Table Test
Your doctor might recommend tilt table test if you’ve had fainting spells. Your heart rate and blood pressure are monitored as you lie flat on the doctor’s table. Then the table is tilted as if you were standing up. This can help your doctor observe how your heart and the nervous system which controls it respond to the change in angle.
Electrophysiological testing and mapping
Treatment options for Arrhythmia
Treating slow heartbeats
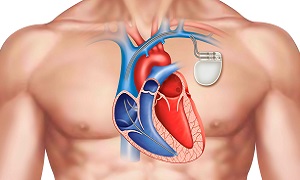
If slow heartbeats don’t have a cause that can be corrected, then doctors usually treat them with a pacemaker because there are no medications that are known to reliably speed up the heart.
Pacemaker is a small device that is usually implanted near your collarbone. Multiple electrode-tipped wires run from the device through your blood vessels to the inner portion of your heart. If your heart rate is too slow or if it stops, the pacemaker will be sending out electrical impulses which will be stimulating your heart to beat at a steady rate.
Treating fast heartbeats
Vagal maneuvers
It is possible to stop arrhythmia which begins above the lower half of the heart with the use of particular maneuvers which can include holding your breath and straining or dunking your face in ice water or coughing.
Your nervous system is affected by these maneuvers. Therefore this method can control your heartbeat and often causes your heart rate to slow. However, this technique doesn’t work for all kinds of arrhythmia.
Medications
For various types of tachycardia, your doctor will prescribe you medication to control your heart rate or restoring a normal heart rhythm. It is quite important to take any anti-arrhythmic medication as your doctor has directed. If you are having atrial fibrillation, your doctor might prescribe blood-thinning medications to help in keeping dangerous blood clots from forming.
Cardioversion
If you are having a certain type of arrhythmia like atrial fibrillation, your doctor might use cardioversion which can be conducted as a procedure or through medications.
Catheter ablation
During catheter ablation, your doctor threads one or more catheters through the blood vessels to your heart. Electrodes that are at the catheter tips can use heat, extreme cold or even radiofrequency energy to damage a small spot of heart tissue. It will then create an electrical block along the pathway that’s causing your arrhythmia.
Sometimes a pacemaker or defibrillator can also be implanted to help in treating heart arrhythmias. When a pacemaker detects an abnormal heart rate, it will emit electrical impulses which can stimulate the heart to beat at a normal rate. A defibrillator can also detect abnormal heart rhythm and send out low or high-energy shocks for resetting the heart to a normal rhythm. However, this device will not be able to prevent the abnormal rhythm from occurring.
Surgery
Surgery is also recommended in some cases for treating heart arrhythmias:
Maze procedure
In maze procedure, a surgeon will make a series of surgical incisions in your heart tissue in the upper half of the heart. Since scar tissue will not conduct electricity, it will interfere with stray electrical impulses that can cause some types of arrhythmia.
Though this procedure is effective, it is only reserved for the people who have not responded well to other treatments.
Coronary bypass surgery
Lifestyle changes
Prevention of Arrhythmia
In order to prevent heart arrhythmia, living a healthy lifestyle is quite important to reduce the risk of a heart ailment. A heart-healthy lifestyle can include:
- Eating a diet healthy for your heart
- Staying active physically and maintaining your weight
- Avoiding smoking or inhaling smoke
- Limiting the use of caffeine and alcohol
- Reducing stress, because intense stress and anger can lead to problems in the rhythm of the heart
- Using over-the-counter medications, with caution, as some cold and cough medications contain stimulants which can trigger a rapid heartbeat.