What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a disorder of central nervous system or a neurological disorder characterised by abnormal brain activity that leads to seizures and sometimes loss of awareness.
Causes & risk factors of Epilepsy
Symptoms of Epilepsy
- Temporary confusion
- A brief seizure, usually less than 15 seconds, also known as staring spell.
- Uncontrollable & jerking movements of the arms and legs.
- Loss of awareness.
- Fear, anxiety
Types of Seizures
Doctors generally classify seizures either focal or generalized, based on how the abnormal brain activity begins.
Focal Seizures
Focal Seizures occur when there abnormal activity in just one area of brain.
These seizures are of two types:
- Focal seizures without loss of consciousness – They may change the way things look, smell, feel, taste or sound & may also result in involuntary jerking of a body part, such as an arm or leg but don’t cause a loss of consciousness. They were once called simple partial seizures.
- Focal seizures with impaired awareness – These seizures involve a change or loss of consciousness or awareness. & were once called complex partial seizures.
Generalized seizures
Generalized seizures involve all areas of the brain.
Types of Generalized seizures.
- Absence seizures also known as petit mal seizures – They usually occur in children and involve subtle body movements such as eye blinking or lip smacking.
- Tonic seizures – These usually affect muscles in your back, arms and legs.
- Atonic seizures – Also known as drop seizures, atonic seizures can cause a loss of muscle control, which may cause sudden collapse.
- Clonic seizures – Clonic seizures involve repeated or rhythmic, jerking muscle movements.
- Myoclonic seizures – These usually involve sudden brief jerks.
- Tonic-clonic seizures – These were previously known as grand mal seizures, can cause an abrupt loss of consciousness, body stiffening and shaking, and sometimes loss of bladder control or biting the tongue
Diagnosis of Epilepsy
Neurological exam
Blood tests
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
CT scan
MRI
SPECT
Treatment of Epilepsy
Medicines
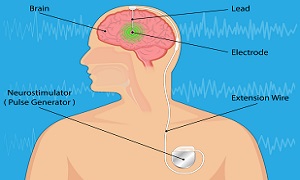
Surgeries
When medications fail to provide adequate control over seizures, surgery may be an option. Surgery is generally considered when:
- Seizures originate in a small and well-defined region of the brain
- The said area doesn’t control any vital function of the body like vision, hearing, speech etc.
The surgical options for the treatment of Epilepsy are as follows:
Resective surgery
Resective surgery is the most common surgery used for the treatment of Epilepsy. This surgery involves removal of brain tissues in the area of the brain where seizures originate.
Corpus Callostomy
Corpus callosotomy is the surgery of bundle of nerves that connects the right and left sides of the brain & is usually used in children.
Hemispherectomy
Hemispherectomy involves removal of one side (hemisphere) of the folded gray matter of the brain.
Functional Hemispherectomy
Functional hemispherectomy, is primarily used in children & involves the undercutting of the seizure-inducing hemisphere.
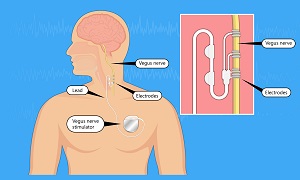
Therapies
Apart from medications and surgery, the following therapies can offer an alternative for treating epilepsy.