What is Brain Aneurysm?
Brain Aneurysm is a condition in which there is ballooning or bulging of a blood vessel of your brain. It may rupture or leak which may result in bleeding in the brain. This is termed as a hemorrhagic stroke.
The space between the thin tissues that cover the brain and the brain is the most common spot for the occurrence of a ruptured Brain Aneurysm. It is often referred to as subarachnoid hemorrhage.
A ruptured aneurysm may prove to be life-threatening, thereby requiring an urgent need for medical treatment. While most of the aneurysms don’t rupture, they may cause symptoms and create health problems.
Types of Brain Aneurysm
There are different types of Brain Aneurysms.
- Saccular Aneurysm: It is the most common type of aneurysm of the brain that bulges out from the main artery in a dome shape. These aneurysms connect with the main artery through a narrow neck.
- Fusiform Aneurysm: This is the uncommon type of aneurysm that doesn’t take up the dome shape. Unlike a saccular aneurysm, it makes a large speck within the blood vessel.
Causes of Brain Aneurysm
Common in people over the age of 40 years, Brain Aneurysm may occur at any age. Some may also have a defect in the blood vessels by birth. You may observe a significant female predilection. The sections where the blood vessels branch off are weaker. Brain Aneurysms are common at these places and mostly occur in the base of the brain. There are some factors responsible for the rupture of an already existing Brain Aneurysm. They may be:
- Excess straining during bowel movements
- Startling
- Excessive exercise
- Intense anger
- Coffee consumption
Damage to the structure of the arteries may result in weakness and cause Brain Aneurysms. If a serious infection in the body damages the arteries, it may lead to a Brain Aneurysm. Sometimes, chronic high blood pressure and smoking are also possible causes for brain aneurysms.
Brain Aneurysm in children
Although rare, children below 18 years of age sometimes develop a brain aneurysm. In children, boys have a higher tendency of developing the same rather than girls. Around 20% of the total cases of children are of large aneurysms that are more than 2.5 cms in size. The cause behind aneurysms in children hasn’t been found but it might be one of the following:
- Infection
- Trauma to the head
- Family history
- Connective tissue diseases
- Generic disorder
Risk factors
There are a plethora of factors contributing to the weaker vessel wall thereby increasing the risk of aneurysm development or its rupture. Risk factors may either be present by birth or may develop with time.
- Risk factors by birth: There are several conditions present by birth that increase the risk of developing an aneurysm. These may be:
- Coarctation of the aorta: Abnormal narrowing of the aorta which is responsible for circulating oxygenated blood from the heart to other body organs.
- Inherited connective tissue disorders: This may make the blood vessels weak.
- Genetic passing: The first-degree relatives with an aneurysm can pass the same to future generations.
- Polycystic kidney disease: This involves fluid-filled sacs within the kidneys that can raise blood pressure.
- Brain AVM: A malformation between the brain’s veins and arteries responsible for blocking normal blood circulation.
- Risk factors developing with time: A few risk factors develop with the time that includes:
- Hypertension or high blood pressure
- Old age
- Alcohol consumption
- Cigarette smoking
- Drug abuse
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysm
Unruptured Aneurysm: You may not notice any symptoms for an unruptured Brain Aneurysm, especially if it is a small one. However, the larger ones may press the nerves and tissues of the brain. Ultimately it may result in-
- Double vision or change in vision
- Pain above one eye
- Numbness on a side of the face
- Dilated pupil
Leaking Aneurysm: Sometimes, an aneurysm may leak some amount of blood that is called sentinel bleeding. This leaking may result in an extremely severe and sudden headache.
Ruptured Aneurysm: One of the chief symptoms of a ruptured Brain Aneurysm is a severe sudden headache. It is sometimes referred to as the worst headache that you will experience. Some other symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm include:
- Nausea
- Double vision or blurred vision
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
- Stiff neck
- Drooping eyelids
- Vomiting
- Sensitivity to light
- Confusion
Hereditary correlation
When it comes to first-degree relatives like parents or siblings, it is always better for the rest of the members to undergo tests if anybody has a brain aneurysm. There is a high possibility of developing an aneurysm amongst the first-degree relatives. For example, if your father has been detected with an aneurysm, you and your siblings must go for the tests. However, this should be done after having a word with your doctor or healthcare provider. Around 15%-20% of cases have a hereditary correlation.
Causes of bleeding aneurysm
To simply put, anything that raises your blood pressure can cause the aneurysm to bleed. If the blood pressure is higher, it pushes the blood against the vessel walls. The causes may be:
- Working hard to lift any kind of heavy object like furniture.
- The sudden burst of emotions or stress for a long time.
- People with high blood pressure and not under medications for the same.
When to see the doctor?
If you are experiencing a severe headache suddenly, you must visit your doctor. When the artery walls start thinning, a brain aneurysm develops. Usually located at the artery branches, they may develop anywhere in the brain. They are common in the weaker sections of the arteries that are present in the region of the base of the brain.
Complications
The bleeding caused by brain aneurysm rupture may last for a couple of seconds but may cause damage to the nearby cells. It can also kill these cells or raise the pressure within the skull. Ultimately, the oxygen and blood supply to the brain may be obstructed with elevated pressure. This may either result in losing consciousness or prove fatal for the person. Some other complications are:
- Hydrocephalus: Sometimes, the aneurysm ruptures between the brain and its neighboring tissues. This causes bleeding resulting in subarachnoid hemorrhage that may block the fluid flow to the spinal cord and brain. Further, the condition may progress towards increased CSF or cerebrospinal fluid that expands the pressure on the damaged tissues. This condition where the brain experiences increased pressure is called hydrocephalus.
- Recurrent bleeding: A leaked or ruptured aneurysm can cause recurrent bleeding which results in damaged brain cells.
- Hyponatremia: Subarachnoid hemorrhage can imbalance the sodium in the blood due to a damaged hypothalamus. Hypothalamus is the region near the base of your brain. This decline in the sodium level is hyponatremia that causes swelling and permanent damage to the brain cells.
- Vasospasm: Blood vessels get narrow when the aneurysm ruptures which is termed vasospasm. This may cause ischemic stroke that hampers the flow of blood to the brain with additional loss and/or cell damage.
- Permanent brain damage and coma are two other complications of the condition.
Diagnosis of Brain Aneurysm
The presence of a severe headache suddenly indicates a ruptured aneurysm. In such a situation, you need to undergo a few tests to rule out the possibility of subarachnoid hemorrhage or any other kind of stroke. If you are experiencing pain behind your eyes or can witness alterations in your vision, you might need to get tested for locating the aneurysm.
There are several tests and different types of scans that help in determining whether you have a Brain Aneurysm or not.
MRI
During MRI, your doctor will ask you to lie on a table that will slide into a scanner. It uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create detailed images of your blood vessels and brain. It has the ability to detect Brain Aneurysms that are larger than 5 millimeters. Alternatively, your doctor may perform MRI angiography for the assessment of arteries and detecting the aneurysm.
CT Scans
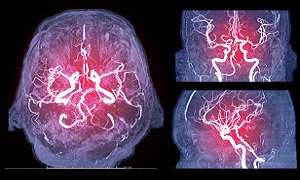
Angiogram
CSF test
Screening for Brain Aneurysm
You must always discuss the benefits of a screening test for a brain aneurysm with your doctor if:
- you have any kind of congenital condition that may increase the risk of developing an aneurysm.
- there is a history of brain aneurysms within your family members.
Preparing for the visit
In a majority of the cases, patients detect the presence of an aneurysm after it ruptures and requires medical attention. In other cases, it might get detected after undergoing imaging tests for some other ailment. If there is the presence of a brain aneurysm, you need to discuss everything with a neurosurgeon or a neuroradiologist.
Questions to ask
To ensure that you collect relevant information regarding your condition from your doctor, you must ask some questions from him or her.
- What is the location and size of the brain aneurysm?
- What can be done to lower the chances of an aneurysm rupture?
- Will the imaging tests reveal the chances of its rupture?
- Can I wait before getting operated on for the aneurysm?
- What is the condition of the aneurysm?
- What is the best treatment for the condition of my brain aneurysm?
- Do I need to come for follow-ups if I am waiting for observation?
Informing the doctor
Your doctor might need sufficient information from your side before he or she discusses your treatment. You must inform your doctor if you smoke or drink alcohol. If one of your family members gives a history of a brain aneurysm, you must inform the same. Also, inform him or her about any medications that you take, recreational drugs (if you consume), or medications for any ailment like hypertension and increased cholesterol levels.
A detailed medical history will provide your doctor with an insight into your condition and help him or her plan everything. If you have a history of atherosclerosis, polycystic kidney diseases, or connective tissue disorders, you must tell about the same. Furthermore, you must add about any kind of tumor in your head & neck as well as abnormalities present by birth.
Treatment options for Brain Aneurysm
For Unruptured Brain Aneurysm
There may not be a need for the treatment of small and unruptured aneurysms. Some lifestyle changes can help you prevent the leaking of the aneurysm like:
- Avoid stimulant drugs or cocaine
- Take a proper diet and exercise regularly to lower your blood pressure
- Avoid lifting heavy objects to avoid a rise in your blood pressure
- Stop smoking
- Restrict the consumption of caffeine because it may cause your blood pressure to elevate.
For Ruptured Brain Aneurysm
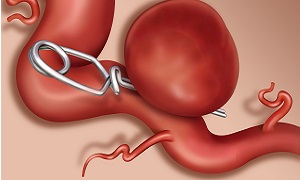
Surgical clipping
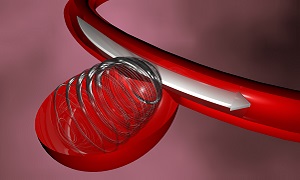
Endovascular coiling
This is a minimally invasive procedure in comparison to surgical clipping.
Your doctor will insert a flexible tube called a catheter into the groin region of your body to reach the affected blood vessels. This will help to locate the aneurysm. He or she will then send platinum coils through the flexible tube and place them inside the aneurysm. The coils stop the blood flow to the aneurysm and seal it off from the artery of the brain.
Flow diverter surgery
Other treatments
These types of treatments aim to manage any kind of complications and/or relieve the symptoms of a brain aneurysm.
- Preventing stroke: Your doctor may give intravenous injections of vasopressor. The drug raises the blood pressure to a level that it withstands the obstruction from weaker blood vessels.
- Pain relievers: They help to treat the pain from severe headaches.
- Ventricular draining catheters: Lumbar catheters or ventricular draining catheters followed by surgery help decrease the pressure on the brain due to hydrocephalus. The catheter is placed within the ventricles to drain the CSF. Your doctor might introduce a shunt, a silicone rubber tube, with a valve.
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications prevent calcium from entering the blood vessels. They also act on vasospasm that may worsen the aneurysm.
- Anti-seizure medications: These medications help treat seizures caused by a brain aneurysm. The medication may be phenytoin, valproic acid, etc.
- Rehabilitative therapy: You may need speech and physical therapy if there is damage to the brain due to subarachnoid hemorrhage. Alternatively, you might also require occupational therapy that will help you learn skills again.
Palliative therapy
Lifestyle changes
You must adopt a healthy lifestyle and take a sound sleep. Some changes in your lifestyle can surely make a huge difference and help you deal better with the condition. When you stress less and keep yourself busy, your body will cope better. You must avoid the use of any type of stimulant drug or cocaine. Also, try to avoid strenuous activities like lifting heavy objects or consumption of caffeine that might raise your blood pressure.
- Regular exercise: Exercising regularly can lower your blood pressure that will ensure good blood circulation. You can talk to your doctor or physical therapist about the exercises that will help you.
- Quitting smoking: You must discuss with your doctor the recreational changes to help you quit smoking. Your doctor will advise you of a program or strategy for the treatment.
- Managing the blood pressure and cholesterol level: You must monitor your blood pressure by checking it regularly. If you are hypertensive, you must take the medicines on time. Also, try avoiding foods that are rich in cholesterol so that the cholesterol levels are maintained.
- Eating a balanced diet of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and low-fat dairy products can further help in maintaining a healthy and fit body.
These small lifestyle changes may help significantly to manage Brain Aneurysms.
Prevention of new aneurysm
A brain aneurysm cannot resolve on its own when detected. However, you can prevent the growth or change of an aneurysm. Also, it is possible to prevent new aneurysm formation and eliminate the chances of its rupture. You can:
- Have a balanced diet
- Avoid smoking
- Control your blood pressure through medications
- Perform light exercises and physical therapy daily
- Get the right treatment for withdrawal of alcohol and drug abuse.
Prognosis
Many people are completely unaware of their aneurysm throughout their lives as it remains unruptured. However, there is an equal risk of an aneurysm rupture that depends on certain factors. These factors may be the appearance, size, and location of the aneurysm. A ruptured aneurysm may cause hemorrhagic stroke requiring urgent medical treatment. If unattended, the aneurysm may increase the chances of death.
People with a ruptured aneurysm live for more than 24 hours in about 70% of the cases. Some others may experience serious complications for 6 months before they die. The best way out is to get treatment immediately for a ruptured aneurysm to have a better prognosis.