Papilledema
Papilledema is a condition in which there is a swelling in your optic nerve, connecting the eye and the brain. This swelling is caused by a reaction to a buildup of pressure in or around the brain that can be caused by various reasons.
Generally, it is a warning sign of a serious medical condition requiring an immediate attention, like a brain tumor or hemorrhage. However, sometimes the pressure and swelling are untraceable to the specific problem. In such cases, there are other ways to ease the swelling.
If left untreated, Papilledema can cause vision loss as well.
Symptoms
In the early stage of papilledema, you might not have any symptoms. Your doctor might discover the condition when they see optic nerve swelling during a routine eye exam.
As the condition progresses, you are likely to have few vision problems, usually in both eyes. It is also common to have blurred or double vision and you might even lose your vision for a few seconds at a time. You might also experience symptoms such as queasiness, headache, or vomiting.
You could even get a headache every day on either or both sides of the head. Although the headaches might not be of the same intensity, they do get worse as you keep on getting them. You might even hear throbbing in your head.
Untreated Papilledema may lead to several serious eye problems, which can include the loss of your peripheral or side vision. In later stages, your vision might even become completely blurred. Sometimes people might go blind in one or both the eyes.
Causes
The optic nerve is a bundle of fibers that helps transmit visual information between your retina and your brain. The optic disc is the area where the optic nerve enters the back of the eyeball.
The brain and optic nerve are surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid which helps in keeping them stable. It also protects them from damage from sudden movements.
Papilledema may occur when there is increased pressure from the brain and cerebrospinal fluid, on the optic nerve.
This leads to swelling in the nerve as it enters the eyeball at the optic disc.
There are certain serious medical conditions that can lead to this increased pressure to develop.Some of these conditions include the following:
- Head trauma
- Inflammation of the brain or surrounding tissue
- Severely high blood pressure, known as a hypertensive crisis
- Blockages of blood or cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
- Infection in the brain
- Brain tumor
- Bleeding in the brain
- Abnormalities of the skull
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is a rare condition where the body produces excess cerebrospinal fluid, which can also cause increased pressure in the brain. Symptoms of this condition generally include headaches, visual disturbances, and ringing in the ears.
However, the exact cause of this condition is not yet known and is also not related to any brain disease or injury. It generally affects younger, obese females. It can also be associated with certain medications.
Diagnosis
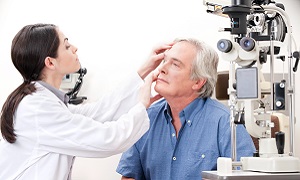
Ophthalmoscope
Next, he/she will likely use a tool which is termed an ophthalmoscope, which is an instrument resembling a pen with a lighted wheel at the tip. This tool is used to inspect the back portion of the eye through the pupil, though this will require a dilated eye. Drops will need to be placed in the eye, in order to force the pupil to become larger.
Then the doctor will assess the optic disc for any abnormalities. Certain changes might indicate that the optic nerve is swollen.
In severe cases, there might be spots of blood which can appear on the retina. Tests may be done to assess any changes in color vision, vision loss, or double vision, along with assessment for visual accuracy.
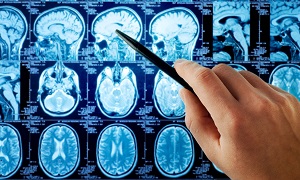
Brain imaging scans
If any sign of Papilledema are detected, then brain-imaging scans are going to be needed. These can include magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, or computed tomography.
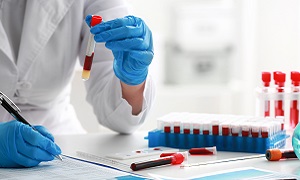
Blood test
In all instances, it is very important to determine the cause of the increase in pressure that affects the brain.
Treatment
If another medical problem is detected during the tests, then treating it should also cure the Papilledema. Otherwise, your treatment will likely be guided by your symptoms. With slight Papilledema without any symptoms, your doctor might keep doing regular checks to see if he/she spots any kind of vision problems.
If your doctors rule out a life-threatening cause for your Papilledema, then they might be recommending weight loss and a diuretic.
You might also receive a few other medications including a pain reliever for your headaches.
Often, removing some of the spinal fluid also eases the pressure and symptoms. If your vision continues to get worsen despite all of these treatments, then your doctor might consider various types of brain surgery to relieve pressure and protect the optic nerve.
It is also noteworthy that unless your doctor finds a specific cause and treats it successfully, the condition can return.