Cataracts
When a clouding is formed over the clear lens of the eyes, it is called a Cataract. People suffering from this ailment feel like seeing through a frosty or fogged-up window when they see through their cloudy lenses. It causes difficulty in several day-to-day activities, such as reading, driving or even seeing somebody’s face clearly.
Although most cataracts develop slowly, your eyesight doesn’t get disturbed early on. However, over time, it eventually starts interfering with your vision. Sometimes cataracts also make the colors appear less vibrant and yellowed, similar to a sepia-toned photo. Though it is known as the most common cause of vision loss worldwide, it is treatable.
Initially, stronger lighting and eyeglass can help people who are suffering from cataracts. However, if it continues to interfere with daily activities, cataract surgery might be the best option. Cataract surgery is generally safe as well as effective.
Cataracts usually result when people get older, and usually after the age of forty. This happens as the proteins that make up the lens start to clump together, causing the clouding.
Symptoms of Cataracts
The signs and symptoms of cataracts can include:
- Clouded, dim or blurred vision
- Difficulty in vision, especially at night
- Light sensitivity
- Visual halos around bright lights
- Double vision
- Requiring brighter light for reading or any such activity.
An outside viewer will see that the pupil of the cataract patient will appear light gray rather than black when it reaches an advanced stage.
Common types of Cataracts
There are different types of Cataracts:
- Nuclear cataracts- A nuclear cataract forms in the center of the lens of the eyes, and usually causes nearsightedness or even an improvement in one’s reading vision, temporarily. However, over time, it gradually worsens and affects the vision, turning it densely yellow, and further clouding it.
- Cortical Cataracts- A cortical cataract is a type of cataract that affects the edges of the lens. It begins as a whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the lens cortex’s outer edge. When it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center which causes interference with the light that passes through the center of the lens.
- Posterior subcapsular cataracts- This kind of cataract develops along the back of the lens, and unfortunately, compared to the others, it develops much more quickly. It can interfere with your reading vision, reduce your vision in bright light, and also cause halos around lights at night.
- Congenital cataracts- Some people have cataracts since birth, or develop them in early childhood. This kind of cataracts can be genetic, or even associated with an intrauterine infection or trauma.
Causes of Cataracts
Most Cataracts develop due to aging, or when an injury changes the tissue that makes up the eye lens. Sometimes inherited genetic disorders that cause health problems can also increase one’s risk of cataracts. Medical conditions such as diabetes, or past eye surgery can also sometimes contribute to cataracts. Using steroid medications for a long time can also cause it to develop.
How Cataracts form:
The lens, where the cataracts form, is positioned behind the iris, the colored part of the eye. The lens focuses the light which is passed into your eye, producing a clear and sharp image on the retina. However, when you age, the flexibility of your lenses decreases, and they also cause the lens to break down and clump together, which causes clouding in small areas within the lens.
As the cataract continues to develop, the clouding becomes denser and involves a bigger part of the lens during this period of time. The cataract scatters as well as blocks the light when it tries to pass through the lens, and due to this, the sharply defined image is unable to reach the retina. This causes the vision to become blurry.
Risk Factors of Cataracts
The risk factors of Cataracts are:
- Excessive UV radiation
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Excessive Alcohol Intake
- Eye Injury
- Previous Eye Surgery
- Eye Inflammation
- Family History of Cataracts.
Preventing Cataracts
There is nothing that can guarantee to stop cataracts from developing, as they simply appear as we age. However, there are still some preventive measures that we can take to limit the risk factors.
- Wearing sunglasses during the daytime can help ones’ eyes from being exposed to the sun’s UV radiation.
- Quitting smoking can also help in the prevention of cataracts.
- Eating a healthy diet is also very important, and maintaining an exercise regiment, even if it is just light physical activity such as walking.
- Managing and reducing the effects of coexisting conditions such as diabetes or hypertension can help as well.
- One can consider getting eye exams done frequently in order to ensure that if cataracts are developing, they are diagnosed quite early.
- If you have other health problems, such as diabetes, which can increase the risk of cataracts, it is important that you follow your treatment plan properly.
Diagnosis of Cataracts
When you want to determine whether you are having cataracts, your doctor will need to review your medical history and look for symptoms. An eye examination will also need to be performed. Your doctor may perform several tests, which can include the following:
Visual Acuity Test
Visual acuity test uses eye charts in order to measure how well you are able to read a series of letters. One eye is tested one at a time, while the other remains covered. With the help of the chart, the eye doctor is able to determine if you have 20/20 vision, or if the eye is showing signs of impairment.
Slit-lamp examination
Retinal exam
Surgery for Cataracts
Surgery is the only effective treatment for cataracts when the prescription glasses can no longer give you the clear vision that you want.
First, you need to consult with your eye doctor, whether surgery is right for you. Eye doctors usually suggest surgery only when one’s quality of life is affected and you are unable to perform your day-to-day activities.
However, the decision remains up to you once the doctor has made the decision. Most people don’t rush to remove their cataracts as, despite the difficulties, it doesn’t really harm their eyes. However, it is important to note that for people with diabetes, cataracts can worsen quite fast.
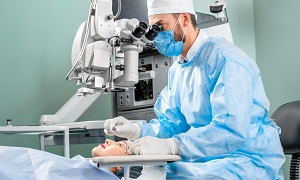
The surgery is done on an outpatient basis, which means that you are able to go home right after the surgery. The surgery involves the surgeon removing your natural lens and replacing it with an artificial one. It has a high success rate, and 96 percent of people claim that they see better afterwards.
If you delay the procedure, it won’t affect much how well your vision recovers if you later make the decision to go through cataract surgery. Take time to consider the benefits as well as the risks of the surgery with your specialist.