Bladder Prolapse
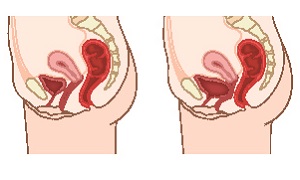
In women, the bladder is normally held in place by a hammock of supportive pelvic floor muscles as well as tissue. When these tissues are stretched or get weak, the bladder may drop or bulge through this layer and into the vagina. This can lead to bladder prolapse, which is also termed a cystocele. The prolapsed bladder may appear at the opening of the vagina as well, in severe cases. Sometimes it might even protrude through the vaginal opening.
Bladder prolapse is a common condition among women. The symptoms can be bothersome, but they are treatable. A prolapsed bladder is rarely a life-threatening condition, and in most cases, it is treatable without surgery. Sometimes even severe prolapsed bladders can be corrected without any form of surgery.
Symptoms
The first symptom that women with a prolapsed bladder might notice is the presence of tissue in the vagina that many women can describe as something that can feel like a ball.
A prolapsed bladder can have several other symptoms which can include the following:
- Difficulty while urinating
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvis
- Tissue protruding from the vagina
- A feelings that the bladder is not empty immediately following urination
- Stress
- Incontinence
- More frequent infections in the bladder
- Lower back pain
- Painful intercourse
Some women might not experience or notice symptoms if their condition is mild.
However, women who notice symptoms of a prolapsed bladder should see a doctor immediately. A prolapsed bladder can also be associated with prolapses of other organs within a woman’s pelvis. Timely medical care is important to evaluate for as well as prevent any problematic symptoms as well as complications caused by weakening tissue as well as muscle in the vagina. Prolapsed organs are unable to heal themselves, and may worsen over time. Several treatments are available to correct a prolapsed bladder.
Causes
The most common factors associated with a prolapsed bladder include the following-
Childbirth: This is known as the most common cause of a prolapsed bladder. The delivery process is stressful on the vaginal tissues as well as muscles, which support the bladder.
Straining: Lifting objects that are too heavy or straining during a bowel movement, or having a long-term condition that causes coughing, or having long-term constipation can also damage the muscles of the pelvic floor.
Estrogen: Estrogen is a hormone that helps to maintain the strength as well as the health of muscles in the vagina. This hormone is not produced after menopause. This can lead to a prolapsed bladder as well.
Diagnosis
Bladder prolapse can be easily detected with a clinical history and a pelvic exam. The exam can be performed while a patient is lying down, straining or pushing, or even standing. Your doctor or healthcare worker might need to measure how serious the prolapse is and which parts of the vagina are falling.
Few other tests and imaging studies might also be required to check the pelvic floor, such as:
- Urodynamics
- X-rays
- Cystoscopy
- Ultrasound
- MRI
Treatment
If the condition is mild and does not produce any pain or discomfort, then you might not require any medical or surgical treatment. A patient having a mild prolapsed bladder should, however, refrain from heavy lifting or straining, and this might be recommended by your doctor.
If your case is more serious, then various factors will be taken into account by your doctor, such as the patient’s health, treatment preference, and most importantly, the severity of the condition.
Non-surgical treatments
Pessary
A pessary is a tool placed within the vagina to help in holding the bladder in place. Pessaries require removal and cleaning at regular intervals to prevent any infection. Some pessaries allow the woman to do this themselves. However, for other types, a doctor will need to remove and clean them. Estrogen cream is also used commonly with this tool to help prevent infection as well as erosion of the vaginal wall.
Estrogen replacement therapy
This therapy has proven to be beneficial for many women with prolapsed bladders. Estrogen helps in strengthening as well as maintaining muscles in the vagina.
For mild-to-moderate cases of prolapsed bladder, the doctor might recommend moderating a few activities such as avoiding heavy lifting or straining. The doctor may also recommend certain exercises, which can help in tightening the muscles of the pelvic floor.
Medications for Prolapsed Bladder
Estrogen replacement therapy might also be considered by your doctor for a prolapsed bladder. This therapy can help the body strengthen the tissues in as well as around the vagina. Estrogen replacement therapy can’t be used by everyone, which includes people with certain types of cancer. Women’s bodies stop creating as much estrogen naturally after menopause, which causes weakening of the muscles of the vagina. In mild cases of prolapsed bladder, estrogen may be prescribed in an attempt to reverse bladder symptoms of the prolapse, such as vaginal weakening and incontinence. However, when the prolapsed is severe, estrogen replacement therapy might be considered along with other types of treatment.
Estrogen can be administered orally as a pill or even as a patch or cream.
Surgery
Surgery is considered for severely prolapsed bladders that cannot be managed with a pessary or medications. Prolapsed bladder surgery is generally performed through the vagina, and the goal of this procedure is to secure the bladder in its proper position. The bladder is repaired with an incision created in the vaginal wall.
Depending on the procedure, regional, general, or local anesthesia might be used. For smaller surgeries, patients are generally able to go home the same day.
After surgery, it might take around six weeks for a woman to return to a normal level of activity. Surgeons might however recommend reducing or eliminating activities that can cause straining for at least six months.
Prevention
A high-fiber diet as well as a daily intake of plenty of fluids should reduce the risk of developing constipation, which can reduce the risk of bladder prolapse. Straining should also be avoided during bowel movements, if possible. If you are suffering from long-term constipation, then it is best to seek a medical condition to lessen the chance of developing a prolapsed bladder.
Heavy lifting is also associated with a prolapsed bladder and it should be avoided if possible. Obesity is also a risk factor for developing a prolapsed bladder. Weight control might help prevent this condition from developing.