Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is an opening or hole in the wall that separates the two upper chambers of the heart.
The hole causes oxygen-rich blood to leak from the left side of the heart to the right side. This causes extra work for the right side of the heart, since more blood than necessary is flowing through the right ventricle to the lungs. Surgery or device closure may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects so as to prevent complications.
Signs & symptoms of ASD
Many babies do not have any signs & symptoms for ASD, they are shown in adults if ASD is left untreated.
The common signs & symptoms are:
- Frequent respiratory or lung infections
- Difficulty in breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Skipped heartbeats
- A heart murmur, it is a whooshing sound that can be heard with a stethoscope
- Swollen legs, feet, or abdomen
Types of ASD
- Secundum: It involves the middle of the wall between the atrial septum and is the most common type of ASD.
- Primum: It involves the lower part of atrial septum.
- Sinus venosus: It involves the upper part of the atrial septum and occurs very rarely.
- Coronary sinus: It involves the wall between the coronary sinus and the left atrium
Causes & risk factors of ASD
- Consumption of drug, tobacco or alcohol.
- Exposure to certain substances like heavy metals and environmental toxins.
- Rubella infection.
- Diabetes & obesity.
- Genetic problems like Down’s syndrome.
Diagnosis of ASD
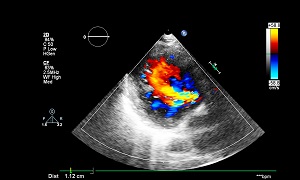
Echocardiogram
Chest X-ray
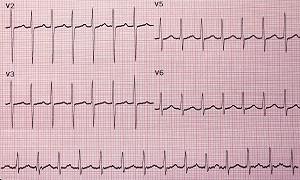
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Cardiac catheterization
Computerized tomography (CT) scan

Computerized tomography (CT) scan creates detailed images of your heart to diagnose an ASD.
Treatment Options for ASD
Medications
Interventions
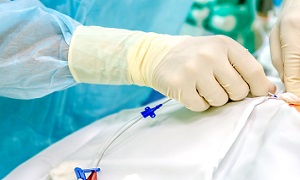
Cardiac catheterization
In Cardiac catheterization procedure, a thin tube known as catheter is inserted into a blood vessel through the groin and advanced into the heart with the help of imaging techniques. Through the catheter, doctors set a mesh patch or plug into is placed close the hole. The heart tissue grows around the mesh that seals the hole permanently.
Open-heart surgery
During Open-heart surgery, the patient is given general anaesthesia and a heart-lung machine is also required. Through an incision in the chest, patches are placed to close the hole. This procedure is the preferred for certain types of atrial septal defects.
FAQs
Can ASD close its own?
- The child’s (patient) cardiologist will check periodically whether ASD is closing on its own or not. If an ASD is not closing then it is repaired or surgically closed.
How long does it take to recover from ASD closure surgery?
- It takes up to 6 weeks to recover from ASD closure surgery.
Can ASD defect be cured?
- ASD can be cured by two surgeries: Cardiac catheterization & Open-heart surgery