Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Types
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease may vary, depending on the severity of inflammation as well as where it occurs.
You are likely to have periods of active illness which is followed by periods of remission. Some of the signs and symptoms include:
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Blood in your stool
- Reduced appetite
- Unintended weight loss
- Abdominal pain and cramping
The signs and symptoms are common to both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
You should see your doctor if you are experiencing a persistent change in your bowel habits, or if you experience any of the signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn’t fatal, it’s a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
Causes & risk factors
The exact cause of this condition is still unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected, but now most doctors know that these factors aggravate but are not the exact causes of inflammatory bowel disease.
An immune system malfunction is a possible cause. When your immune system tries to fight off an invading virus or bacteria, an autoimmune response makes the immune system attack cells in the digestive tract as well. Heredity may play a role as well since inflammatory bowel disease is more common among people where there are family members having the disease.
Some of the risk factors include the following:
Age- Most people who develop this condition are diagnosed before the age of 30. Though some people don’t develop it until their 50s or 60s.
Cigarette smoking- Cigarette smoking is also a significant risk factor for developing Crohn’s disease.
Race or ethnicity- White or Caucasian people generally are at the highest risk of the disease, though it can occur in any race.
Family history- If you have a family member or close relative with this disease, then your risk increases.
Diagnosis
To diagnose inflammatory bowel disease, your doctor will first need to ask you questions about you and your family’s medical history, as well as your bowel movements.
A physical exam might be followed by one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
Computerized tomography (CT) scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Stool sample and blood test
Barium Enema
A barium enema is an X-ray exam of the colon as well as the small intestine. Though this type of test was used in the past, now it has been mostly replaced.
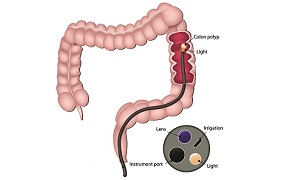
Flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
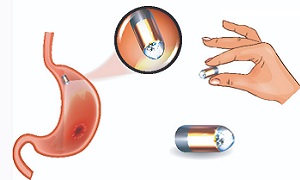
Capsule endoscopy
This test inspects the small intestine, which is quite harder to examine as compared to the large intestine. For the test, you will need to swallow a small capsule that will contain a camera.
As it moves through the small intestine, it will take pictures. Once you’ve passed the camera in your stool, the healthcare team can see the pictures on a computer. This test is used only when other tests have failed to find the cause of the symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
Plain film or X-ray
Treatment
Generally, the first step in treating inflammatory bowel disease is anti-inflammatory drugs. Although these drugs can help you decrease inflammation of your digestive tract, they come with many side effects. Immune suppressant drugs might also prevent the immune system from attacking the bowel and causing inflammation.
You also need certain changes when you are having inflammatory bowel disease. Drinking plenty of fluids is important, though you need to avoid dairy products. Avoid too much stress as well. It is also important to exercise and quit smoking.
Your doctor can also recommend vitamin and mineral supplements to help with nutritional deficiencies.
Talk to your doctor before you add any new supplements to your diet.
Surgery
Surgery can also sometimes be necessary with inflammatory bowel disease. Some of the surgeries include:
- strictureplasty to widen a narrowed bowel
- closure or removal of fistulas
- removal of affected portions of the intestines, for people having Crohn’s disease
- removal of the entire colon and rectum, for those suffering from severe cases of ulcerative colitis
Routine colonoscopy is also used for monitoring colon cancer since those having inflammatory bowel disease are at a higher risk for having it.
Complications
Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease have complications that are common, including colon cancer, inflammation of the skin, eye, and joint.
It might also lead to a condition called primary sclerosing cholangitis, where there is scarring within the bile ducts, eventually making them narrow and causing liver damage.
Inflammatory bowel disease also increases the risk of blood clots in veins and arteries.
Prevention
You can reduce your risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease by eating healthy and exercising regularly. It’s also best if you can quit smoking.