Best Doctors in India for Bladder Cancer Treatment
Here are the most reputed urologists in India who are expertised in the treatment of Bladder cancer & other types of urological cancers.
Best Bladder Cancer Treatment Hospitals India
- City: Bengaluru, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Fortis Hospital Bannerghatta, Bengaluru was established in 2006.
- The hospital is a 276 bedded multi-specialty tertiary care facility.
- The hospital specializes in cutting-edge medical technology and dedicated patient care services.
- The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art technologies like trans-radial angioplasty, trans-abdominal cardiac surgery, and computerized TKR navigation surgery.
- The hospital provides specialty medical services in cardiology, cardiac surgery, orthopedics, neurology, neuro-surgery, GI, and Minimal Access Surgery (MAS).
- City: Chennai, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Fortis Malar was established in 1992 and was formerly known as Malar Hospital.
- The hospital specializes in cutting-edge medical technology and dedicated patient care services.
- The hospital is multi-specialty, tertiary care facility with 180 beds.
- The hospital offers comprehensive medical care in specialties such as cardiology, cardio-thoracic surgery, neurology, neurosurgery, orthopedics, nephrology, gynecology, gastroenterology, urology, pediatrics, and diabetes.
- City: New Delhi, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Established in 1996, Pushpawati Singhania Research Institute is one of the top hospitals in the NCR region, as well as one of the top facilities in India for gastroenterology. The hospital is one of South Asia’s first institutes in medical and surgical treatment for diseases related to digestion.
- The hospital is equipped with state-of-the art facilities coupled with the latest equipment as well as renowned consultants from various parts of India as well as other parts of the world.
- City: New Delhi, India
Hospital Highlights:
- State-of-the-art technology and devoted healthcare professionals have been brought together under one roof at Venkateshwar Hospital to provide genuine medical care. The hospital’s professionals work together as a team to deliver the best possible treatment to their patients, using the most sophisticated equipment and information technology.
- Venkateshwar Hospital’s mission is to attain global excellence in healthcare by employing evidence-based, ethical clinical practices and cutting-edge technology by a team of highly skilled experts.
- City: New Delhi, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi is known to provide the latest medical procedures with the latest technology in all of its units.
- The hospital has a team of reputed doctors, nurses, and healthcare professionals that ensure that patients receive quality care at affordable costs.
- Staffed with a team of highly qualified doctors, dedicated nurses, and paramedical and non-medical staff, the hospital aims to lead in healthcare delivery, medical education, training, and research.
- As per the vision of the founder, the hospital also provides free treatment to the economically weaker sections of society.
- Sir Ganga Ram Hospital also provides training to young doctors under the Diplomate in National Board(DNB) program. The DNB program at the hospital was started in 1984 and it is known for currently running the maximum number of DNB specialties in the country. It also has the distinction of having the first bone bank in India.
- City: Kerala, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Established in 2019, Apollo Adlux Hospital is the first Apollo Hospital in Kerala and the 73rd hospital owned by Apollo Group in India. With the state’s most advanced, comprehensive healthcare infrastructure and cutting-edge technologies, Apollo Adlux Hospital stands as an example of medical excellence in Kerala.
- With over 34 multi-specialty departments, the hospital believes in providing the best quality treatment to its patients at affordable rates, ensuring comfort at their difficult times.
- The 300-bed hospital is managed by a team of highly qualified and experienced experts who delivers exceptional hospitality to their patients and treats them with great compassion.
- With its affiliation with the Apollo Hospitals Group, the hospital aims in providing patients with top-notch healthcare services while also serving communities in Kerala.
- The hospital has good railway and road connections, and is conveniently close to Cochin International Airport.
- City: Gurugram, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Situated near DLF Cyber City, Gurugram, Narayana Superspecialty Hospital is one of the top medical facilities in the Delhi NCR region, catering to the needs of the people. Known for its commitment to quality medical care and patient service, the hospital is a state-of-the-art facility with planned and well-equipped sections, which includes a spacious OPD area as well as comfortable patient rooms.
- It is the closest super-specialty hospital from Indira Gandhi International Airport towards Gurugram, and also the nearest super specialty hospital from DLF Cyber City. It is also close to major residential areas in Gurugram.
- It is part of the renowned Narayana Health Group. Established in 2000, by Dr. Devi Shetty, a renowned cardiac surgeon, it has grown to be one fo India’s leading healthcare groups.
- City: Noida, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Fortis Hospital, Noida, stands as one of the oldest and most trusted healthcare institutions in the region, setting a benchmark for comprehensive medical care.
- As the second mega hub hospital in the Fortis Healthcare Group, Fortis Hospital, Noida, upholds a legacy of trust among more than 1.2 million patients. By integrating top-tier professionals with cutting-edge technology, the hospital delivers superior treatment across various medical disciplines.
- Specializing in advanced Neurosciences, Orthopedics, Kidney and Liver Transplant Programmes, Fortis Hospital, Noida has successfully performed over 1,500 transplants, solidifying its reputation as a leader in specialized medical interventions.
What is Bladder Cancer?
Cancer occurs when the cells grow abnormally and also invade nearby tissues and eventually spreading to other organs in the body through the bloodstream or the lymph nodes.
Bladder Cancer is the cancer of bladder wherein the cells in the bladder grow abnormally & form a tumour. Bladder is a hollow organ located in the pelvis. The main function of the bladder is it stores the urine & allows urination to be infrequent and controlled.
Causes of Bladder Cancer
- Inflammation of the bladder.
- Having family history of bladder cancer.
- Smoking
- Exposure to harmful chemicals especially working in a job that requires exposure to chemicals
- Intake of certain diabetes medications can raise the risk of bladder cancer.
- Bladder cancer risk increases with age.
Types of Bladder Cancer
- Urothelial Carcinoma: Urothelial carcinoma occurs in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma occurs when there is chronic irritation of the bladder like in the cases where there is long-term use of a urinary catheter.
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma originates in the cells that produces mucus-secreting glands in the bladder.
Signs & symptoms of Bladder Cancer
- Blood in the urine (hematuria).
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation or pain during urination
- Pain in the pelvic region & lower back.
- Loss of weight
- Swelling in the feet
- Fatigue & weakness
What are the stages of Bladder Cancer
- STAGE 0: Cancer is present in the centre of the bladder.
- STAGE I: Cancer has spread to the inner lining of the bladder.
- STAGE II: The cancer has spread to the connective tissue in the bladder and into the muscle layer of the bladder.
- STAGE III: Cancer is now is present in the fatty tissue that surrounds your bladder & it may also have spread to the prostate, uterus or vagina (for females)
- STAGE IV: The cancer has spread into your pelvic or abdominal wall, to nearby lymph nodes & has spread to distant sites like the bones, liver, or lungs.
Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
The following diagnostic tests are generally done for Bladder Cancer:
Digital rectal exam
During digital rectal exam, the doctors put on a glove and insert the finger into the rectum to feel a tumour in the bladder.
Urinalysis
Urine culture
Urine Culture allows to check for bladder infection.
Urine tumour marker
Urine tumour marker tests allows to check for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. A thin tube with a flash and video camera at the end is inserted into the bladder. Thereafter, salt water is injected in through it. The camera allows the doctor to see the inner lining of the bladder assisting in better diagnosis.
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (TURBT)
During Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (TURBT), the doctor removes the tumour & some nearby muscles as well. This sample is sent to the lab to check for cancer.
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
During Intravenous pyelogram (IVP), the doctor injects dye into the vein & this highlights tumours in the urinary tract.
Retrograde pyelogram
During retrograde pyelogram, the doctor inserts a thin tube (catheter) into the urethra and bladder. A dye is injected through the catheter so the doctor can see the lining of the bladder. & if there are any tumours in the urinary tract, they’ll show up here.
CT Scan
MRI
Ultrasound
Bone scan
Bone Scan is used to check if the cancer that has spread from the bladder to the bones.
Treatment options for Bladder Cancer
Following are the treatment options for Bladder Cancer-
Surgery
The surgical options for the treatment of Bladder Cancer are:
- Transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT)- In this procedure, a retroscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. Retroscope is a tube through which the urine flows & has a wire loop at the end. The doctor uses it to remove abnormal tissues or tumours.
- Cystectomy– It may be partial cystectomy, removal of part of the bladder or radical cystectomy, removal of entire bladder.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of anti-cancer drug that helps to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells that cause cancer. It prevents the growth of rapidly dividing cells by killing the dividing cells. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with other interventions such as surgery or radiation and other therapies.
Sometimes, chemotherapy is administered prior to a surgery, like therapy can be used to shrink a tumour before surgery. This is called as Neo-adjuvant Therapy. And when chemotherapy is used to remove any remaining cancer cells, after surgery, this is known as Adjuvant Chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy is a kind of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation beams to kill cancer cells to shrink the tumors. Radiation kills the cancer cells by destroying the DNA. Cancer cells with damaged DNA fail to multiply and die. They are then removed by the body’s mechanism.
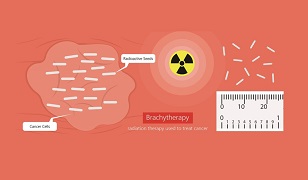
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is an internal beam radiation therapy technique where radiation seeds, the size of rice grains are placed in the location of tumor using a needle, guided by ultrasound imaging. The radioactive seeds keep emitting low dose radiation beams to the cancer over a long period of time. At one point, the seeds stop emitting radiation, but do not need to be removed.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy (also called biologic therapy) is a new type of cancer treatment where the body’s immune system is boosted to help the body fight cancer by itself. Immunotherapy uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function.