Thyroid Cancer
Cancer occurs when the cells grow abnormally and also invade nearby tissues and eventually spreading to other organs in the body through the bloodstream or the lymph nodes.
Thyroid cancer is the cancer of thyroid. Thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the lower front of the neck. The function of thyroid is to control the body’s metabolism and it also controls the heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight.
Causes & risk factors of Thyroid Cancer
- Women are more likely to develop thyroid cancer than men.
- Exposure to high levels of radiation.
- Certain inherited genetic disorders like multiple endocrine neoplasia.
- Deficiency of iodine.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
- Papillary thyroid cancer tends to grow slowly, but may spread to the nymph nodes in the neck.
- Follicular thyroid cancer can spread into the lymph nodes and the blood vessels as well.
- Medullary cancer most likely it is found at an early stage.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer spreads rapidly to other parts of the body and is hardest to treat.
Signs & symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
- Pain in the neck & throat.
- Lump in the neck.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Hoarseness in voice.
- Cough
Stages of Thyroid Cancer
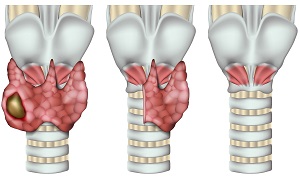
- Stage 1: The tumour is small, less than 2 cm & is confined to the thyroid.
- Stage 2: The tumour increases in size but is smaller than 4 cm, still confined to thyroid.
- Stage 3: The tumour is larger than 4cm, but is still confined to the thyroid.
- Stage 4: The tumour is fully grown & has spread to the nearby soft tissue, the larynx, trachea, oesophagus, or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
Physical Examination
Blood tests
Biopsy
CT scan
CT scan is used to measure the tumor’s size.
PET CT scan
PET CT scan is used to produce images of the inside of the body.
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is done in those patients diagnosed with medullary thyroid cancer as those patients diagnosed with medullary thyroid may have genetic changes.
Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
The treatment of Thyroid Cancer depends on the stage and grade of cancer. Depending on the stage & grade of disease, your oncologist is going to use a combination of the following interventions for Thyroid Cancer treatment. A small percentage of patients with a very small and low grade cancer may not need treatment, but only active monitoring.
Surgery
Most people with Thyroid Cancer undergo surgery. However, the extent of surgical excision depends on the exact location of cancer, the size and spread. Following are the different variants of surgeries done for Thyroid Cancer.
Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy is the removal of all or most parts of the thyroid.
Thyroid lobectomy
Thyroid lobectomy is done when cancer is confined to half of the thyroid and the grade of the cancer is low. In Thyroid Lobectomy, only half of the thyroid is removed.
Lymph node dissection
Thyroid hormone therapy

After thyroidectomy, thyroid hormone medication is recommended for lifetime as it supplies the missing hormone the thyroid would normally produce and it suppresses the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland which otherwise could stimulate growth of remaining cancer cells.
Radioactive iodine
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy is a kind of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation beams to kill cancer cells to shrink the tumors. Radiation kills the cancer cells by destroying the DNA. Cancer cells with damaged DNA fail to multiply and die. They are then removed by the body’s mechanism.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of anti-cancer drug that helps to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells that cause cancer. It prevents the growth of rapidly dividing cells by killing the dividing cells.
Despite its side effects, chemo is still the most widely used cancer treatment option. Unlike radiation and surgery which treats cancer cells at particular locations, chemotherapy drugs can kill cancer cells that have metastated (spread) to different organs in the body.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses cancer drugs. However, it is different from traditional chemotherapy, which also uses drugs to kill cancer cells. In Targeted therapy, the cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival are targeted. Targeted therapy is generally used with chemotherapy and other interventions.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy (also called biologic therapy) is a new type of cancer treatment where the body’s immune system is boosted to help the body fight cancer by itself. Immunotherapy uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function.