Lung Cancer
Lung cancer (lung carcinoma) is a malignant tumor of the lung. Like most cancers, Lung cancer can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas.
Causes & risk factors of Lung Cancer
- Smoking, both active & passive smoking.
- Having family history of lung cancer
- Coming in contact with radon gas, asbestos & other carcinogens.
Signs & symptoms of Lung Cancer
- Cough that doesn’t go away
- Coughing up blood
- Pain in the chest
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of weight
- Shortness of breath
Types of Lung Cancer
There are two major types of Lung Cancers:
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) occurs mostly in heavy smokers & spreads rapidly to other parts of the body.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer. It is further classified into 3 types:
- Adenocarcinomas- These occur in the gland cells that are present in the lining of the airways & produces mucus.
- Squamous cell carcinoma– Squamous Cell Carcinoma are carcinoma in the the cells that cover the surface of the airways.
- Large cell carcinoma- These cancer cells appear large and round under the microscope.
- Undifferentiated non-small cell lung cancer- These are are undeveloped cancer cells.
Stages of Lung Cancer
- STAGE I: Cancer is confined to the lung.
- STAGE II: Cancer is present in the lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- STAGE III: Cancer is present in the lymph nodes & may be present on one side of the chest where the cancer started growing or may be present on the opposite of the chest as well.
- STAGE IV: Cancer has spread to both lungs & into the area that is around the lungs.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Treatment
Surgery
Surgery is considered as preferred line of intervention specially in early stage lung cancers when the disease is still localized. Surgery may be:
Wedge resection
During Wedge resection, the cancerous tissues along with a small margin of healthy tissues are removed.
Segmental resection
During Segmental resection, a large portion of the lobe is removed.
Lobectomy
In lobectomy, an entire lobe of lung is removed.
Pneumonectomy
In Pneumonectomy, the entire lung is removed.
Besides lungs, lymph nodes of the chest may also be removed to check the metastasis of cancer.
If the size of the tumor is large, oncologists may decide to provide Chemo and Radiation treatment before surgery so as to shrink the tumor to an extent (Neo-adjuvant Chemo). Similarly, Chemo and Radiation could be done after surgery to kill residual cancer cells Adjuvant Chemo).
Chemo
Chemo is the use of anti-cancer drug that helps to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells that cause cancer. It prevents the growth of rapidly dividing cells by killing the dividing cells.
Despite its side effects, chemo is still the most widely used cancer treatment option. Unlike radiation and surgery which treats cancer cells at particular locations, chemo drugs can kill cancer cells that have metastated (spread) to different organs in the body.
Targeted Drug Treatment
Targeted treatment is a type of cancer treatment that uses cancer drugs. However, it is different from traditional chemo, which also uses drugs to kill cancer cells. In Targeted treatment, the cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival are targeted. Targeted treatment is generally used with chemo and other interventions.
Immuno Treatment
Immuno treatment (also called biological treatment) is a new type of cancer treatment where the body’s immune system is boosted to help the body fight cancer by itself. Immuno treatment uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function.
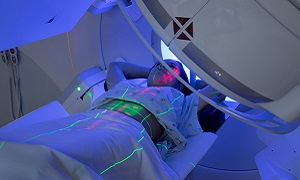
Radiation Treatment
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Steretactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is an advanced form of radiosurgery where very high doses of radiation doses are beamed on a target spot using multi dimensional imaging. Stereotactic radiosurgery manages to damage cancer cells with minimal or no damage to surrounding healthy tissues. The well-known SRS options are:
- Linear Accelerator machines. Cyberknife is the most popular machine used today.
- Gamma Knife (less common today)
- Proton Beam Radiation: Advanced Intervention and available at select hospitals globally.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery could be considered for small lung cancers, or where cancer have spread to other organs like the brain.