Prostatectomy
Prostatectomy is a procedure for removing part or all of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is responsible for carrying urine from the bladder to the penis. This gland is located in the male pelvis below the urinary bladder.
Depending on your situation, prostatectomy can be performed in many ways. Options generally include traditionally open surgery and minimally invasive surgery which is performed with robotic assistance.
This procedure is used for treating a number of conditions which affect the prostate. Generally, it is used as a treatment for prostate cancer.
Purpose
Prostatectomy is generally done for treating localized prostate cancer. It might be used alone or in combination with radiation, hormone therapy and chemotherapy.
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery for removing the entire prostate gland and surrounding lymph nodes. This is for treating men with localized prostate cancer. Different techniques can be used for performing a radical prostatectomy, some of which includes:
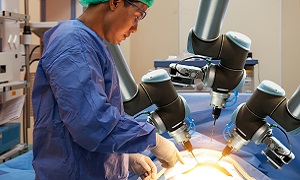
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy- In this method, the surgeon makes five to six small incisions in your lower abdomen for removing the prostate. He or she sits at a console and uses instructions attached to a computer-assisted mechanical device. The robotic device can allow a more precise response to the movement of the surgeon’s hands.
Open radical prostatectomy- In this method, your surgeon generally makes an incision in your lower abdomen for removing the prostate.
Less often, simple prostatectomy might be recommended for men who suffer from severe urinary symptoms and enlarged prostate glands. Generally, simple prostatectomy is performed as a minimally invasive procedure using robotic assistance.
Before the procedure
Before your procedure, your doctor might want to do a test, which uses a visual scope for looking inside your urethra and bladder. It is important for your doctor to check the size of your prostate and examine your urinary system. Your doctor might also sometimes want to perform a few other tests.
It is important to let your doctor known about any medications or supplements that you might take. You might need to stop taking any blood-thinning medications and pain relievers such as aspirin.
It is also important to fast before the surgery, for at least 12 hours. You might also be given a kit and instruction so that you can give yourself an enema for clearing your bowels before the surgery.
It is important to avoid wearing items such as jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures or contact lenses. It is also important to ask your doctor how long you will be in the hospital. It is best if you are able to arrange a ride home in advance, as you won’t be able to drive for some time after the procedure.
It is also important to talk with your doctor regarding how much time will be required for recovery.
Procedure
This procedure is performed using general anesthesia. It means that you are asleep during the procedure. You might also be receiving an antibiotic right before the surgery to prevent an infection.
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: In this method, your surgeon sits at a remote-control console near you and the operating table. He/she precisely controls the motion of the surgical instruments with the aid of two hand-and-finger control devices. The console is able to display a magnified, 3D view of the surgical area which enables your surgeon to visualize the procedure in detail.
The robotic system allows smaller and precise incisions. This usually helps in faster recovery as compared to traditional surgery.
Open radical prostatectomy
Open radical prostatectomy: In this method, the surgeon will make an incision in the lower abdomen from below your navel to just above your pubic bone. Then he/she will be carefully dissecting the prostate gland from the surrounding nerves and blood vessels. Then the surgeon will remove the prostate along with its nearby tissues. After this, the incision will be closed with sutures.
Simple prostatectomy
In simple prostatectomy, first, your doctor might be inserting a long, flexible viewing scope, i.e. a cystoscope through the tip of your penis to see inside your bladder, bladder and prostate area. Your doctor will next insert a tube known as a Foley catheter into the tip of your penis that extends into your bladder. This is done to drain urine during the procedure. The location of incisions will depend on what technique is used by your doctor. If you also have a hernia or bladder problem, your doctor might repair it using the same surgery.
After your doctor has removed part of your prostate that causes your symptoms, one to two drain tubes might need insertion through punctures in your skin near your surgery site. These tubes are temporary. One tube will go directly into your bladder and the other tube will be going into the area where the prostate was removed i.e. pelvic drain.
After the procedure
After your procedure, you might receive pain medications from your doctor. You might be able to walk on the day of the surgery or after one day. It is important to do exercises to move your feet, while you are still in bed.
You can expect to go home one day after the surgery. Most men generally need a urinary catheter for around seven to ten days after surgery. Full recovery of urinary control might take up to a year after surgery.
In around four to six weeks, you should be able to resume your normal routine. It is also important for you to see your doctor a few times in order to make sure everything is okay. If you are going through any problems, you might need to see your doctor sooner.
If you undergo a simple prostatectomy, you may still be able to orgasm during sexual activities, but there might be little or no semen. After radical prostatectomy, it might take around 18 months for a full recovery of erectile function.
Risks
Both radical and simple prostatectomy carries few risks. The risks associated with radical prostatectomy include:
- Bleeding
- Urinary tract infection
- Narrowing of the urethra or bladder neck
- Urinary incontinence
- Formation of cysts containing lymph
- Erectile dysfunction
Risks associated with a simple prostatectomy include:
- Bleeding
- Dry orgasm
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary incontinence
- Erectile dysfunction
- Narrowing of the urethra or bladder neck