Prostate Cancer
Signs & symptoms of Prostate Cancer
- Incontinence or frequent urination
- Pain during urination.
- Blood may be present in urine or semen.
- Pain in pelvis and lower abdomen.
- Pain or burning sensation during urination.
Prostate Cancer causes
- Prostate cancer rarely effects young men.
- Family history
- Overweight or Obesity
- In some cases, it has been noted that taller men are at higher risk than shorter men.
- Swelling or inflammation if the prostate gland.
- Risk of getting prostate cancer is slightly higher in men who have had a vasectomy.
- Diet
- Smoking
Stages of Prostate Cancer
Stage 1: Cancer is at early stage and is growing. You still cant feel the tumor and it involves one-side of prostate or even less. PSA levels are low, and cancer cells still look like healthy cells (well-differentiated)
Stage 2: The tumor is still localized to prostate. PSA level is low to medium. Tumor may grow larger, cancer cells are mostly well-differentiated in earlier phases of stage 2.
Stage 3: In stage 3, PSA levels will be high, the cancer would be growing and may be of high grade too. Cancer may start spreading.
Stage 4: Cancer has spread beyond the prostate. First it reaches the Lymph node and through Lymph node, to other parts of the body.
Grading of Prostate Cancer
As discussed before, not all cases of prostate cancer require immediate treatment. Urgent treatment is recommended only in the case of high grade prostate cancers.
When the tissue sample is taken for biopsy and cancer is confirmed, the pathologists will evaluate the grade of cancer, that is, how fast the cancer is likely to spread. The most common score to measure the grade of prostate cance is called a Gleason score. Gleason score ranges from 2 to 10 where 10 would be extremely high grade prostate cancer. A scale of upto 6 is considered low grade cancer, 7 is considered medium and above 7-10 are high grade prostate cancers.
These days, genomic testings are also done to assess risk factors of Prostate Cancers.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
PSA or Prostate Specific Antigen test
The patient will have high levels of a protein (PSA) that is released by prostate tissue in blood.
Digital rectal exam or DRE
The doctor feels the part by using his/her finger to find abnormal parts of the prostate.
Biomarker test
Biomarker is a substance that is found in the blood, urine, or body tissues of a person with cancer. This test is called as the Biomarker test.
Trans-rectal Ultrasound
The patient undergoes trans-rectal ultrasound in which the picture of prostate gland is taken using sound waves that bounce off the prostate.
Biopsy
A small amount of tissue from the affected area is removed and send for examination. This is known as Biopsy.
Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Depending on the grades of the prostate cancer, further treatment plan in decided.
For low grade prostate cancers, your oncologist may decide to do Active Surveillance involving regular blood tests, rectal exams and biopsies. However, active surveillance may also be risky at times if the cancer suddenly grows between surveillance periods.
For Medium to High Grade Prostate Cancers, following interventions are commonly considered.
Radical Prostatectomy
For Prostate Cancer, the whole prostate gland is removed. The procedure is called Radical Prostatectomy. Radical Prostatectomy is done in two ways:
Laparoscopic or open radical prostatectomy
The surgeon makes one or more incisions in your lower abdomen and takes out the prostate glad.
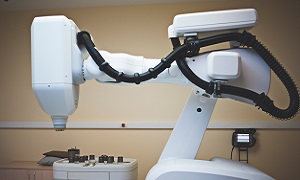
Robotic radical prostatectomy
These days, high number of patients opt for Robotic Radical Prostatectomy where robotic arms conduct the surgeon with high degree of preciseness and the arm is controlled by the surgeon sitting at the console.
Patient undergoing Radical Prostatectomy could have erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence. Your urologist will discuss the possible implications of the procedure with you. You can also discuss all your concerns.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy is a kind of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation beams to kill cancer cells to shrink the tumors. Radiation kills the cancer cells by destroying the DNA. Cancer cells with damaged DNA fail to multiply and die. They are then removed by the body’s mechanism.
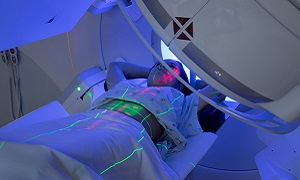
External Beam Radiation
Cyberknife Radiosurgery
These days, Stereotactic Radiosurgery is commonly used for highly precise and effective radiation doses to prostate cancers. The most popular SRS is Cyberknife Radisourgery. The Cyberknife is a highly advanced SRS machine which delivers robot-controlled radiation beams from 1400 different angles to the tumor. The machine adjusts against movement of the body and does little or no harm to surrounding healthy tissues. Cyberknife doesn’t have any cut and doesnt need any hospitalization. (Know more about Cyberknife Radiosurgery)
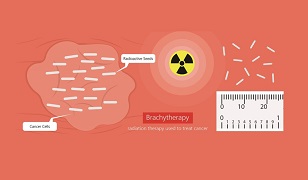
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is an internal beam radiation therapy technique where radiation seeds, the size of rice grains are placed in the prostate using a needle, guided by ultrasound imaging. The radioactive seeds keep emitting low dose radiation beams to the cancer over a long period of time. At one point, the seeds stop emitting radiation, but do not need to be removed.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of anti-cancer drug that helps to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells that cause cancer. It prevents the growth of rapidly dividing cells by killing the dividing cells.
Despite its side effects, chemo is still the most widely used cancer treatment option. Unlike radiation and surgery which treats cancer cells at particular locations, chemotherapy drugs can kill cancer cells that have metastated (spread) to different organs in the body (Read more on: Chemotherapy)
Hormone Therapy
Prostate cancers rely on the hormone, Testosterone to grow. Hormone Therapy can stop producing Testosterone, thereby slowing or killing cancer cells of prostate.
*Testosterone is produced in Testicles. Sometimes, doctors can decide to surgically remove the testicles to inhibit testosterone production. The procedure is called Orchiectomy (Read more on: Hormone Therapy)
Cryosurgery or Cryoablation
Cryosurgery uses the principle of freezing and thawing to kill cancer cells. In cryosurgery, ultrasound guided needles are inserted in the prostate on the tumor and extremely cold gas is passed through the needles. Thereafter hot gas is passed again. The process of cooling and heating kills the cancer cells. Cryosurgery is generally used as an option when Radiation Therapy fails to be effective.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy (also called biologic therapy) is a new type of cancer treatment where the body’s immune system is boosted to help the body fight cancer by itself. Immunotherapy uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function ( Read more on: Immunotherapy)