Egg Freezing
Egg freezing also termed as mature oocyte cryopreservation, is a method meant for saving a woman’s ability to get pregnant in the future. Basically, it helps a woman to delay her pregnancy to a later stage.
Over time, social patterns have been changing; due to which many women choose to have children at a later stage in life. However, the biological realities of fertility remain the same. This procedure can help a woman delay her pregnancy to a later stage by freezing her eggs.
If you are considering this procedure, it is best that you understand how egg freezing works, for which you need to consult an experienced doctor. Also, make sure you discuss the potential risks and whether this method of fertility preservation is right for you based on your needs as well as reproductive history.
Purpose
Egg freezing is generally an option preferred by women who are not ready to become pregnant at the present, but want to make sure that they can get pregnant later. Unlike with fertilized egg freezing, egg freezing doesn’t require sperm since the eggs aren’t fertilized before they are frozen.
If you are considering egg freezing, you will need to use fertility drugs to make you ovulate so that you produce multiple eggs for retrieval.
Egg freezing is generally considered if:
- You have a condition or circumstance which might affect your fertility- This might include autoimmune diseases like lupus or sickle cell anemia.
- You are undergoing in vitro fertilization- When undergoing in vitro fertilization, people prefer egg freezing to embryo freezing for various reasons which might be ethical or religious.
- You need treatment for cancer or any other ailment which can affect your ability to get pregnant- There are several medical treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which can harm your fertility. Therefore, if you undergo egg freezing before treatment, you might be able to have biological children later.
- You wish to preserve your younger eggs for future use- Sometimes, you might feel that you are not ready for pregnancy, but might be ready at an older age. This can be due to career plans or personal circumstances.
Preparation
If you have decided to go for egg freezing, first you will need to look for a fertility clinic with expertise in this field. Doctors who specialize in this field are known as reproductive endocrinologists.
You will also need to go through some tests which include:
Ovarian reserve testing
To determine the quality and quantity of your eggs, your doctor might need to test the concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone and estradiol in your blood on the third day of your menstrual cycle. Results can help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility medication. Also, another blood test and an ultrasound of the ovaries might be used for getting a more complete picture of ovarian function.
Infectious disease screening
You’ll also need to be screened for certain infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Procedure
Egg freezing consists of multiple steps which include ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval and freezing.
Ovarian stimulation
You’ll need to take synthetic hormones to stimulate your ovaries to produce multiple eggs rather than the single egg that typically develops monthly. For this medications might be required:
During the treatment you will be monitored by the doctor- You will need blood tests for measuring your response to ovarian stimulation medications. Estrogen levels also typically increase as the follicles develop. The progesterone levels will be remaining low until after the ovulation.
During your follow-up visits you will also need to have a vaginal ultrasound, a procedure that uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of the ovaries for monitoring the development of fluid-filled sacs where the eggs mature.
For the follicles to be ready for egg retrieval, it can generally take 10 to 14 days. Once they are ready injection or medication can help the eggs mature.
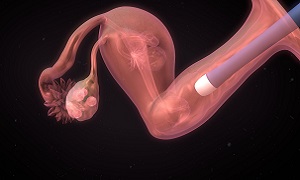
Egg retrieval
During the process of egg retrieval, you will be under general anesthesia. This is typically done in a doctor’s office or clinic. A transvaginal ultrasound aspiration is a common approach. In this method an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina for identifying the follicles.
Then a needle is guided through the vagina and into a follicle. To remove the egg from the follicle a suction device connected to the needle is used. Multiple eggs can be removed and according to studies, the more the eggs are retrieved the better the chances of birth.
After this process of egg retrieval, you might experience feelings of cramping, fullness or pressure. This might continue for weeks since the ovaries remain enlarged.
Freezing
Shortly after your unfertilized eggs are harvested, they will be cooled to subzero temperatures so that they can be preserved for future use. The makeup of an unfertilized egg makes it a bit more difficult to freeze and lead to a successful pregnancy as compared to the makeup of a fertilized egg.
The process which is most commonly used for egg freezing is called vitrification. High concentrations of substances that help prevent ice crystals from forming during the freezing process are used with rapid cooling.
After the procedure
After the process of egg retrieval, you should be able to resume your activities within a week. You can consider avoiding unprotected sex to prevent unintended pregnancy.
If you experience severe abdominal pain, a fever higher than 101.5 F, a weight gain of over 2 pounds in 24 hours, difficulty while urinating, heavy vaginal bleeding then you need to contact your doctor.
Results
Whenever you feel you are ready to use your frozen eggs, they will be thawed, fertilized with sperm in a lab and implanted in your uterus or the uterus of a gestational carrier.
After the implantation the chances of pregnancy are around 30 to 60 percent, depending on your age at the time of egg freezing. If you are older at the time of egg freezing, the likelihood of having a pregnancy through egg freezing is lower.
Risks
There are various risks associated with egg freezing. It includes:
- Conditions related to the use of fertility drugs- In rare cases, the use of injectable fertility drugs can cause the ovaries to become swollen and painful soon after ovulation or egg retrieval. This is known as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Signs and symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting. Although rare, there is also the possibility of developing a more severe form of the syndrome which might be life-threatening.
- Egg retrieval procedure complications- In rare cases the use of an aspirating needle to retrieve eggs can cause bleeding, infections or damage to the bowel, bladder or a blood vessel.
- Emotional risks- Although egg freezing can provide hope for a future pregnancy, it can’t be guaranteed that the procedure will be a success.