Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a type of stroke, which in most cases, is caused by head trauma. In patients without head trauma, it is generally caused by a brain aneurysm. A brain aneurysm is a ballooning of the artery in the brain, which may rupture and bleed into the space between the brain and the skull.
This condition can occur suddenly, and immediate medical intervention is extremely crucial. If someone you know shows symptoms of subarachnoid hemorrhage, it is best to call an ambulance.
Symptoms
When this condition develops, there are usually several symptoms. A sudden, severe headache is generally the most common symptom. Generally, it is described as the worst headache people ever experience. Sometimes people may even feel a popping sensation in the head before the hemorrhage.
You may also have a few more symptoms, which can include any of the following:
- Pain in the neck
- Numbness throughout your body
- Shoulder pain
- Sensitivity to light
- Decreased vision
- Double vision
- Nausea
- Seizures
- Confusion
- Irritability
- Vomiting
- Rapid loss of alertness
The symptoms of subarachnoid hemorrhage come on suddenly, and you may lose consciousness quickly. Seek emergency medical attention right away if you experience any of these symptoms combined with a severe headache.
Causes & risk factors
Subarachnoid hemorrhage can occur spontaneously or due to head trauma. If it is spontaneous, it might be related to brain aneurysms, which are abnormalities within the arteries of the brain.
When an aneurysm erupts, it bleeds quickly, forming a clot. This condition is responsible for most cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain aneurysms are more common among women, among people having high blood pressure, and among people who smoke often. Sometimes, trauma to the brain during an injury may also cause aneurysms, which can result in subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage may also be caused by bleeding disorders, use of blood thinners, or bleeding from an arteriovenous malformation.
A serious head injury, which can occur during a fall or during a car crash, can also lead to Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage can occur at any age. Some people are born with cerebral aneurysms that might lead to this condition. Smoking and high blood pressure increase your risk of an aneurysm as well. Using illegal recreational drugs can also contribute not only to an aneurysm but also to a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Diagnosis
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is generally detected during a physical exam. Your doctor might notice you having a stiff neck and vision problems. If you experience the worst headache of your life, this makes the condition more likely as well. Therefore if this happens, you will also require more testing to find out how severe the hemorrhage is, so that you can get proper treatment.
Some other tests which your doctor might need include the following:
MRI
An MRI scan, which makes the use of radio waves for getting clear and detailed images of the brain.
Ultrasound
A transcranial ultrasound, which can help your doctor to detect blood flow in the arteries within the brain.
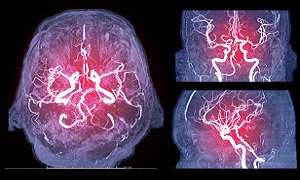
Angiography
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture to see if there are blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment
Early treatment is important to save a patient’s life as well as reduce the possibility and extent of the brain damage. Bleeding and pressure might build up in the brain, which can cause coma as well as further brain damage. This pressure needs to be alleviated with the use of medications or a procedure that will drain some of the cerebrospinal fluid.
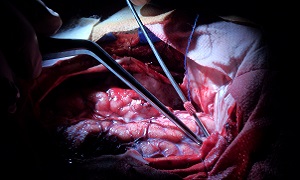
Next, the cause of the bleeding needs to be identified as well as treated, since new bleeding from the same aneurysm may frequently occur without treatment. Surgery is performed in order to clip, or close the aneurysm and stop any future bleeding.
If your aneurysm is being clipped, a craniotomy is performed after which the aneurysm is closed. A craniotomy involves opening the skull in order to expose the area of involvement. A technique which is termed as endovascular coiling might also be used for reducing the risk of further bleeding.
If the subarachnoid hemorrhage leads to a coma, appropriate life support with artificial ventilation will be required along with protection of the airways, and placement of a draining tube in the brain in order to relieve pressure.
If that patient does not lose consciousness from the subarachnoid hemorrhage, strict instructions will be given for preventing post-treatment coma. Bed rest is standard for all patients recovering from this condition.
In some cases, even after the treatment, you may be at risk for related complications. The most common complication is known as repeated bleeding. This occurs when a rupture that has healed ruptures once again. Repeated bleeding can increase a patient’s risk of death. Comas which are caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage can also eventually lead to death.
In some cases, people might experience seizures or strokes after the treatment.