Ventriculostomy
Ventriculostomy is a neurosurgical procedure that involves creating a hole within a cerebral ventricle for drainage. The procedure is performed on patients suffering from hydrocephalus.
Purpose
Preparation
If you show symptoms of hydrocephalus, your doctor will need to perform a few tests, before he/she can diagnose you.
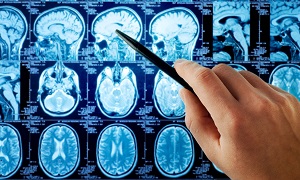
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique that can produce cross-sectional images of your brain, using radio waves and a magnetic field. This test is painless and requires you to lie still, but it is a bit noisy.
MRI scans are able to show enlarged ventricles caused by excess cerebrospinal fluid. They may identify the underlying causes of hydrocephalus or other conditions that are contributing to the symptoms.
Children might need mild sedation for MRI scans. Most hospitals, however, uses a very fast version of MRI, for which sedation is no longer required.
Computerized tomography (CT) scan
Computerized tomography (CT) scan is a specialized X-ray technology that produces cross-sectional views of your brain. Though the scanning is painless and quick, children might receive a mild sedative before trying this.
There are few drawbacks to CT scanning-
Images are less detailed as compared to an MRI, and there is also an exposure to a small amount of radiation. Generally, CT scans for hydrocephalus are used only for emergency exams.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a technique that uses high-frequency sound waves in order to produce images. It is often used for an initial assessment for infants since it’s a simple procedure with very low risks. The ultrasound device is placed over the soft spot (fontanel) on the top of the head of the infant. Ultrasound can also help to detect hydrocephalus prior to birth if the procedure is used during routine prenatal examinations.
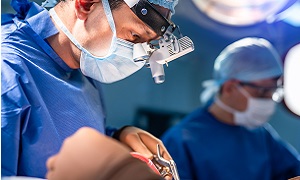
Procedure
The procedure involves your surgeon making a hole in the floor of your brain so that the trapped cerebrospinal fluid can escape to the surface of the brain, where it can be absorbed. He/she uses a small video camera to have a direct vision inside the brain. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
After the procedure
- Drinking well
- Managing their pain
- Able to get out of the bed and safely walk around
It is important to see the doctor in 7-10 days after the procedure, to have the wound checked.
Risks & complications
Some of the few complications of a ventriculostomy include infection and bleeding.
Other risks include:
- Irritability
- Fever
- Drowsiness
- Vision problems
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headache
- Recurrence of any of the initial symptoms of hydrocephalus
Some patients of hydrocephalus might also require additional treatment, depending on if they have any severe long-term complications of hydrocephalus.