Pleural Effusion
Symptoms
Sometimes patients suffering from pleural effusion show no symptoms, and the condition is discovered during a chest X-ray performed for another reason. The patient may also have unrelated symptoms due to the disease or condition causing the effusion.
The symptoms of pleural effusion include the following:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath, or difficult, labored breathing
- Dry, nonproductive cough
- Orthopnea (the inability to breathe properly unless a person is sitting up or standing erect)
Causes
Pleural effusion can be caused by various reasons. Some of the common ones include the following:
Leaking from other organs- This usually occurs if you have congestive heart failure when your heart is not properly pumping blood to your body. But it can also occur due to liver or kidney disease when fluid builds up in your body and can leak into the pleural space.
Pulmonary embolism- This is a blockage in an artery in one of your lungs, which sometimes leads to pleural effusion.
Infections- Pneumonia and Tuberculosis and similar ailments can also lead to pleural effusion.
Cancer– Lung cancer can lead to pleural effusion, but other cancers that have spread to the lung or pleura also cause it.
Autoimmune conditions- Diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid can cause it as well.
Types
Pleural Effusion is of two main types-
Transudative- This pleural effusion fluid is similar to the fluid which you have normally in your pleural space. It forms if a liquid is leaking across normal pleura. Unless it is large, this type rarely needs to be drained. This type of pleural effusion is generally caused by congestive heart failure.
Exudative- This type of pleural effusion forms from extra liquid, blood, inflammatory cells, or sometimes even bacteria that can leak across damaged blood vessels into the pleura. Depending on its size and how much inflammation there is, drainage may be required. Generally, lung cancer and pneumonia cause this type of pleural effusion.
Diagnosis
First, your doctor will conduct a physical exam, and to confirm the pleural effusion, he/she may recommend multiple imaging tests such as:
Chest X-ray
Computed tomography (CT scan)
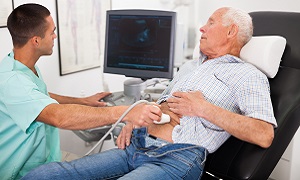
Ultrasound
This method involves a probe being placed on your chest which helps to create images of the inside of your body, which then shows up on a video screen. Your doctor can use the ultrasound to locate the fluid so they can get a sample to be sent for analysis.
Sometimes, your doctor may do a procedure called thoracentesis. This involves taking a little bit of the fluid to test. For this, they will need to insert a needle and a tube known as a catheter between your ribs, into the pleural space.
Treatment
In most cases, your doctor may need to treat only the medical condition which is causing your pleural effusion. You will get antibiotics if you are having pneumonia, for example.
If your pleural effusion is getting large, infected, or inflamed, then drainage is going to be required to help you feel better and avoid any complications.
Some of the procedures for treating pleural effusion include: