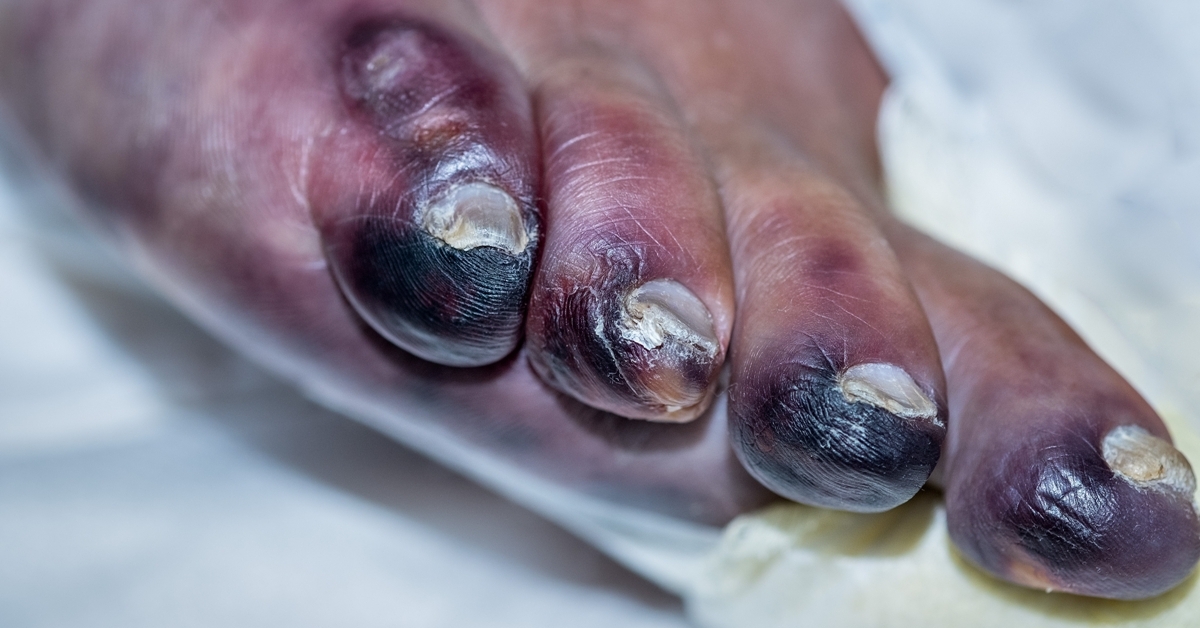
Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to lack of blood flow, infection, or injury.

Gangrene is a serious condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to lack of blood flow, infection, or injury.
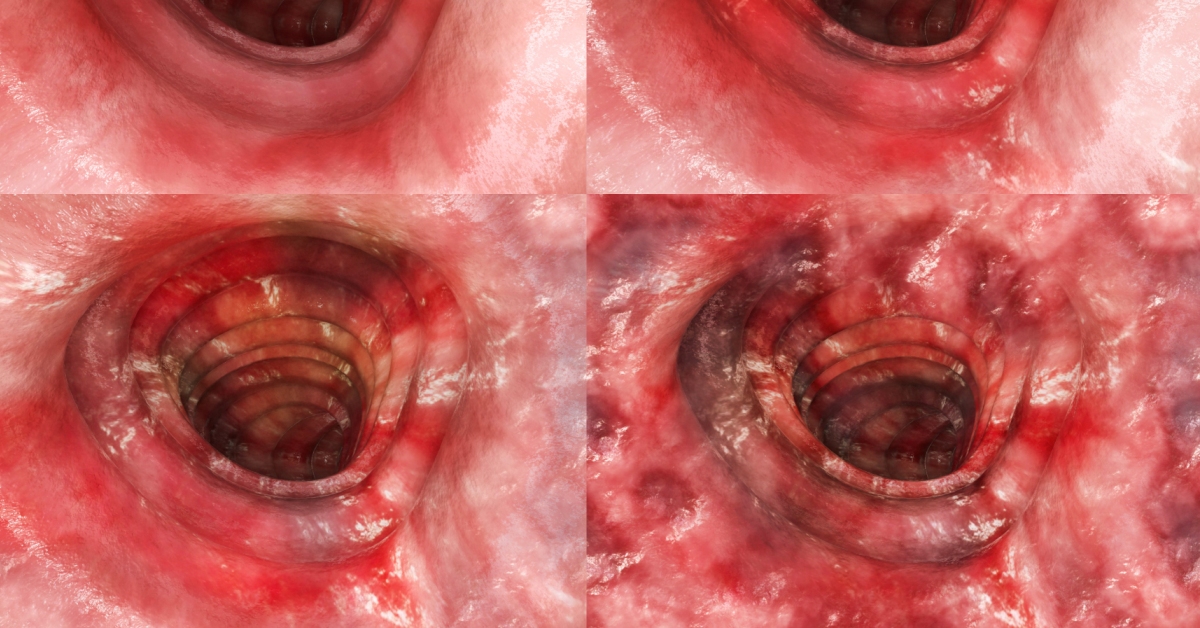
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea.
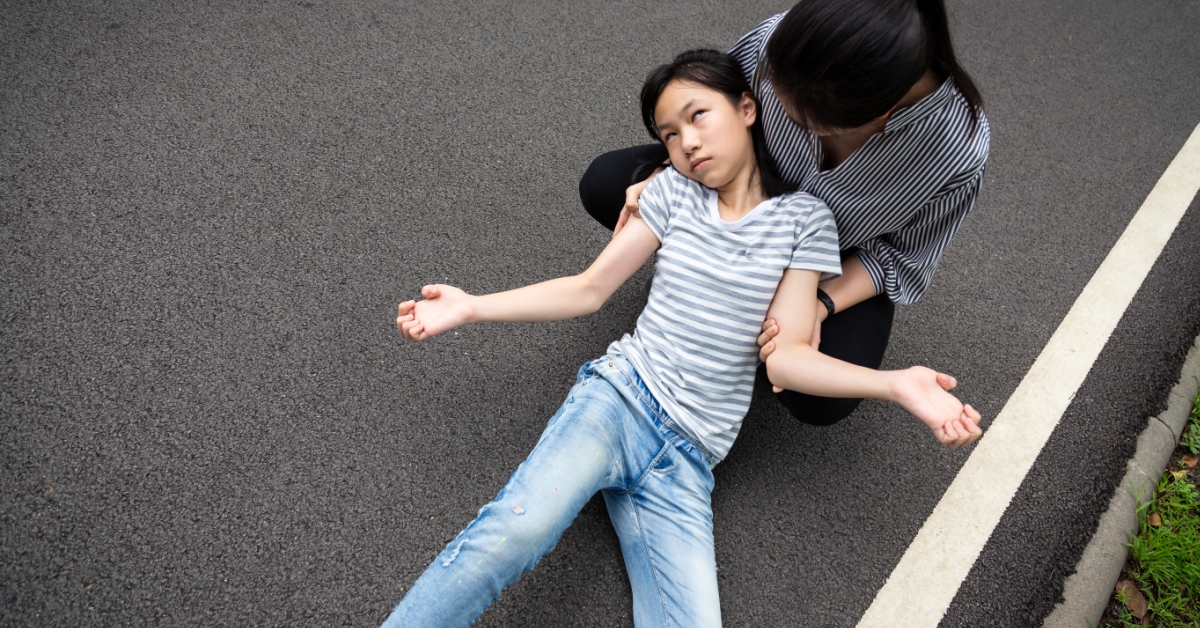

Seizures are sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, including convulsions, loss of consciousness, and changes in behavior.
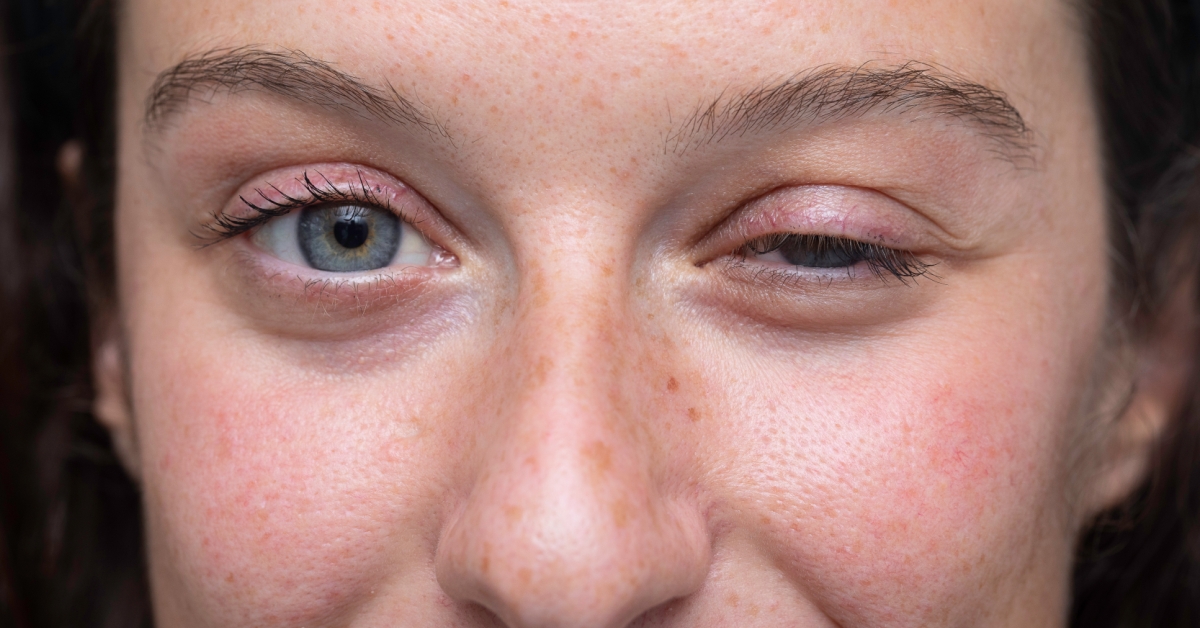
Myasthenia Gravis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by weakness in the voluntary muscles, often worsening with activity and improving with rest.
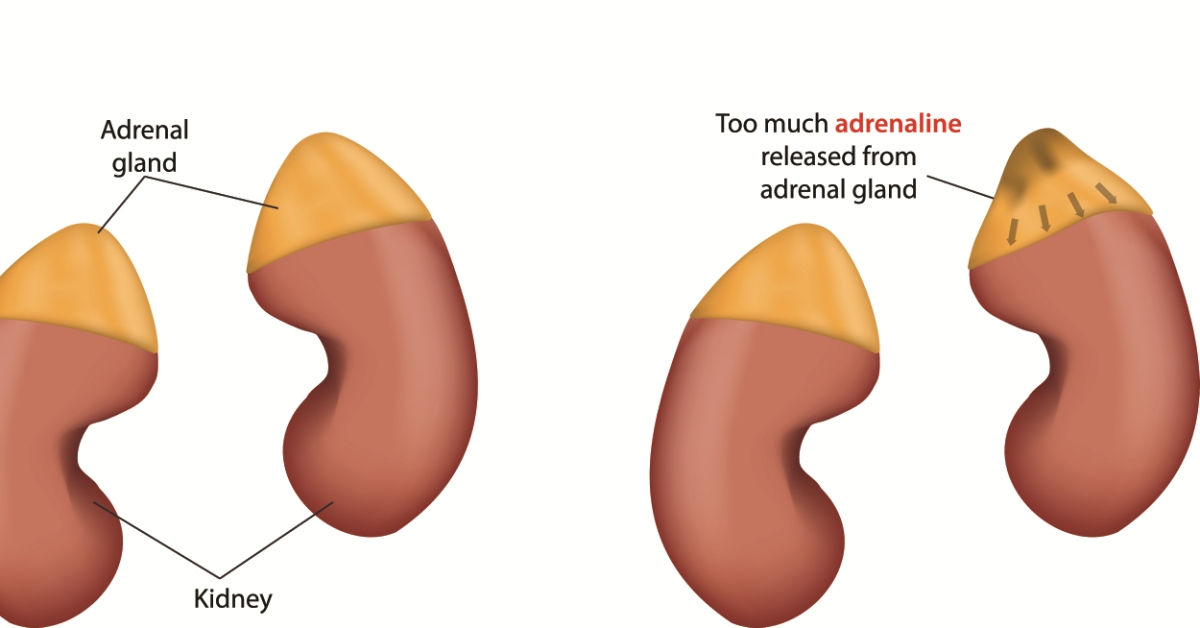
Cushing syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol, leading to symptoms such as weight gain, high blood pressure, and changes in mood.

Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS) is a rare neurological disorder characterized by muscle stiffness and spasms, leading to significant mobility challenges.
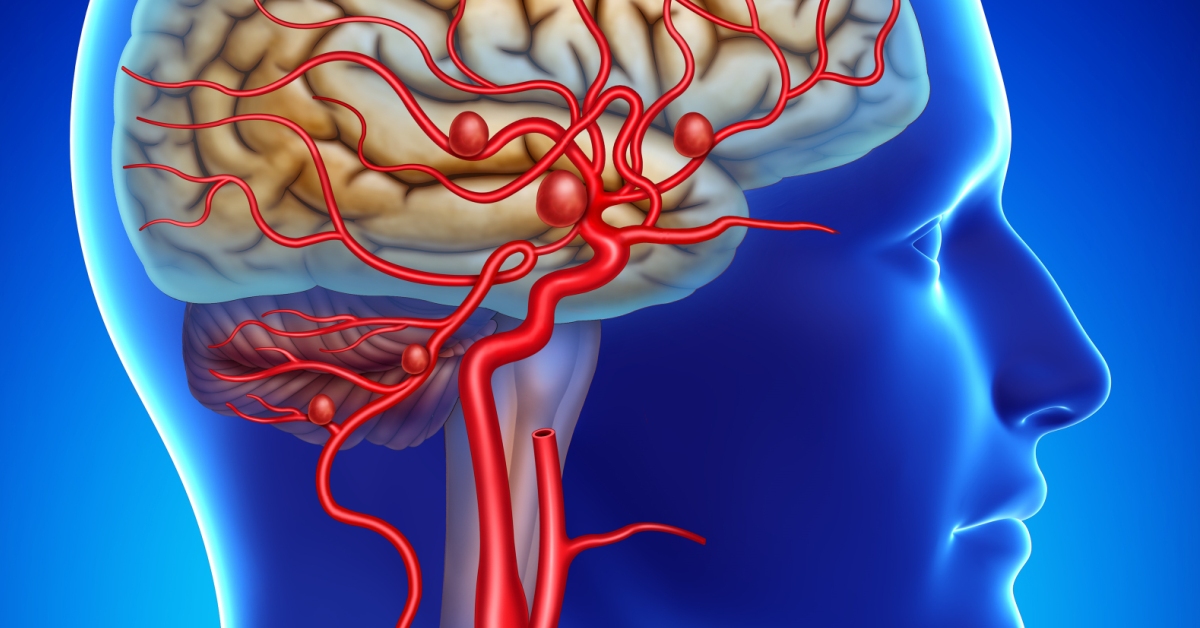
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to a range of neurological symptoms due to the immune system attacking the protective myelin sheath of nerve fibers.
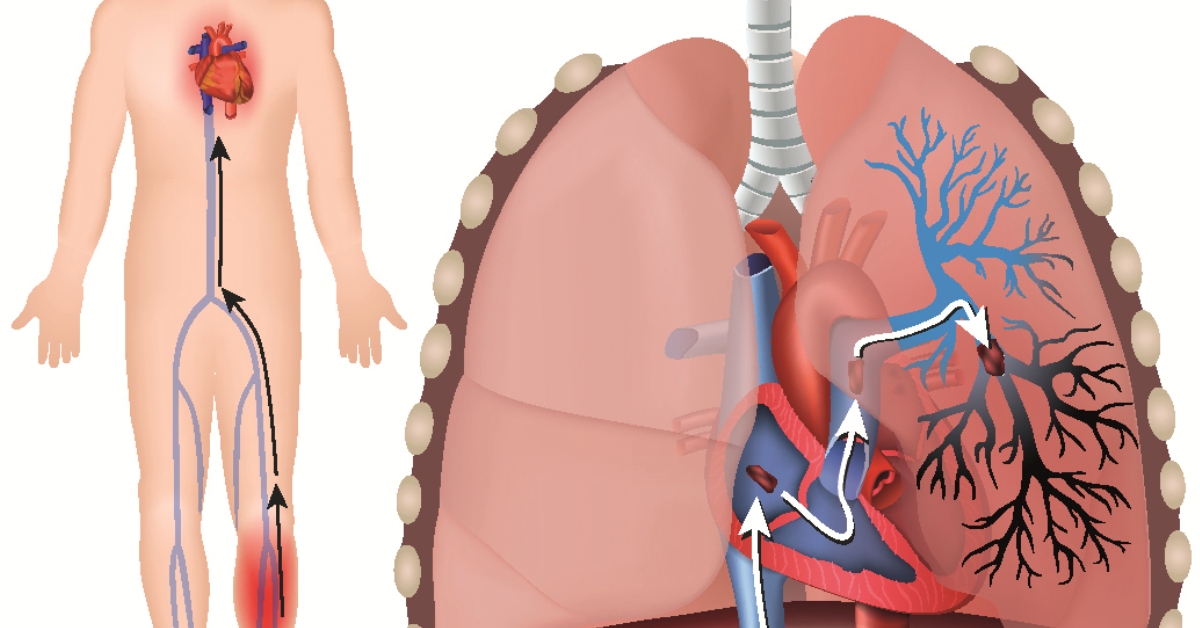
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs, blocking a blood vessel and potentially leading to severe complications.
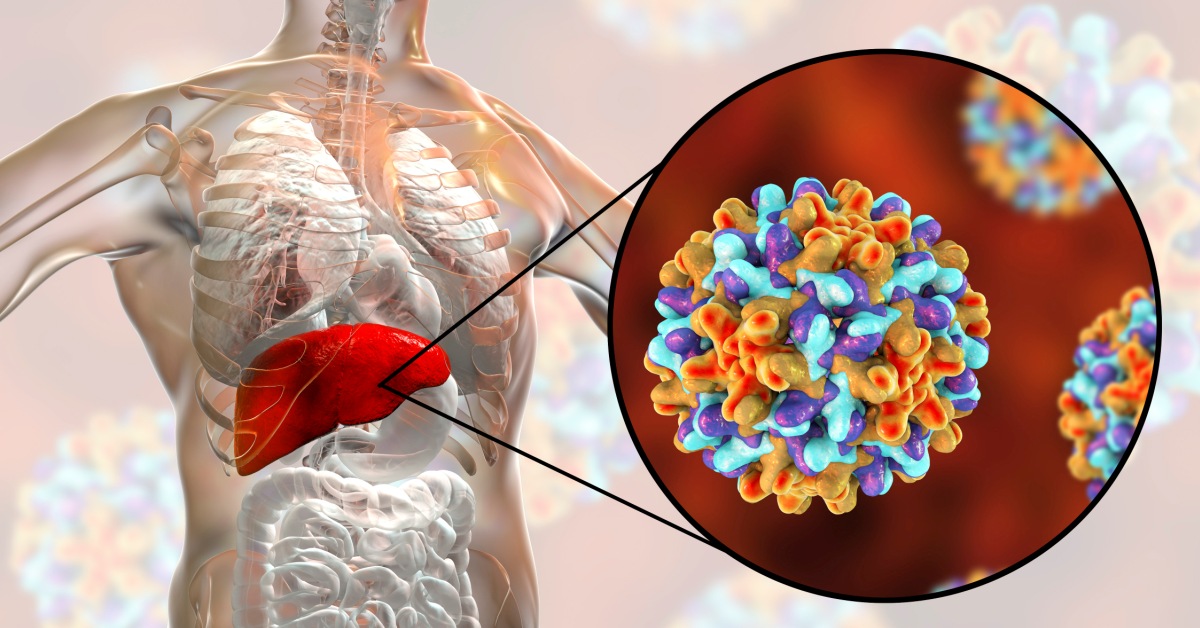
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver, leading to inflammation, liver damage, and potentially severe complications.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI), commonly known as “brittle bone disease,” is a genetic disorder characterized by fragile bones that break easily, often with little or no apparent cause.
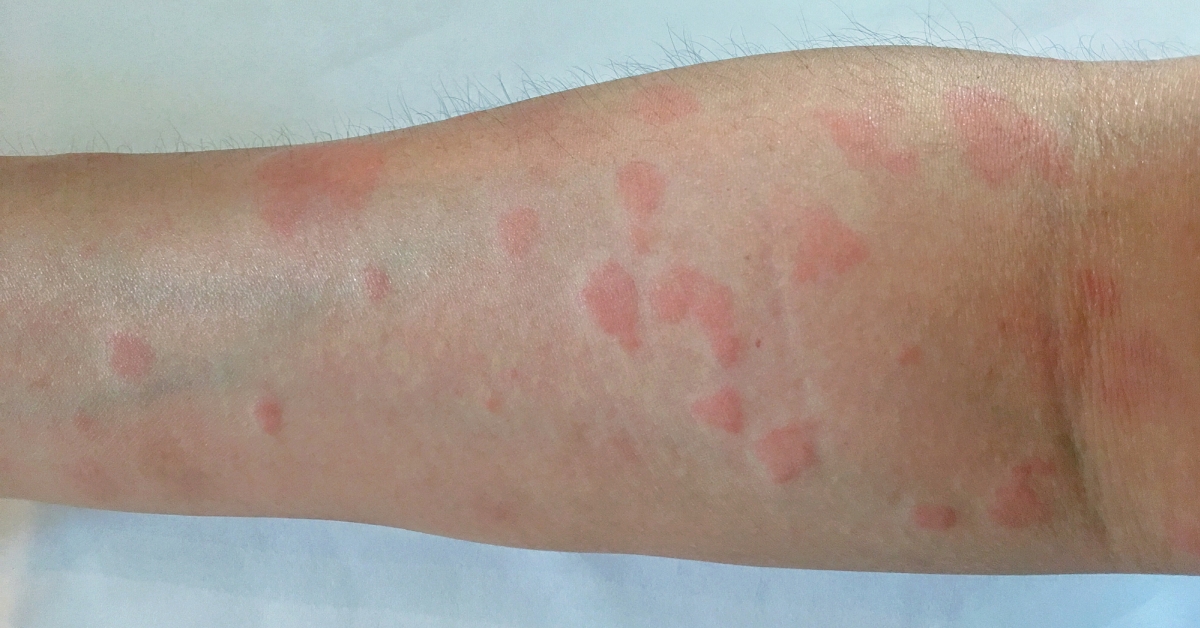
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, causing inflammation and damage to various organs.
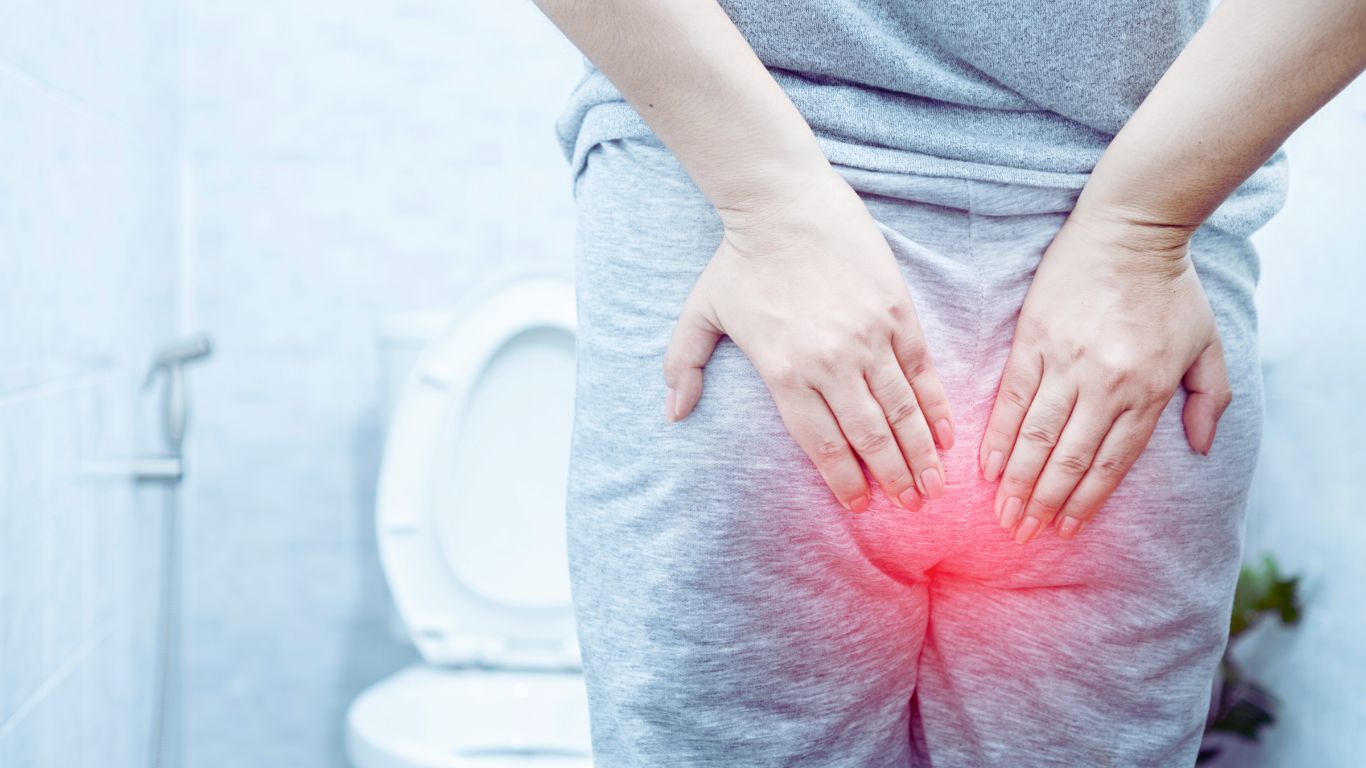
Hemorrhoids, often referred to as piles, are swollen veins located in the anus and lower rectum, similar in nature to varicose veins.

Tonsil cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tonsils, which are located at the back of the throat.
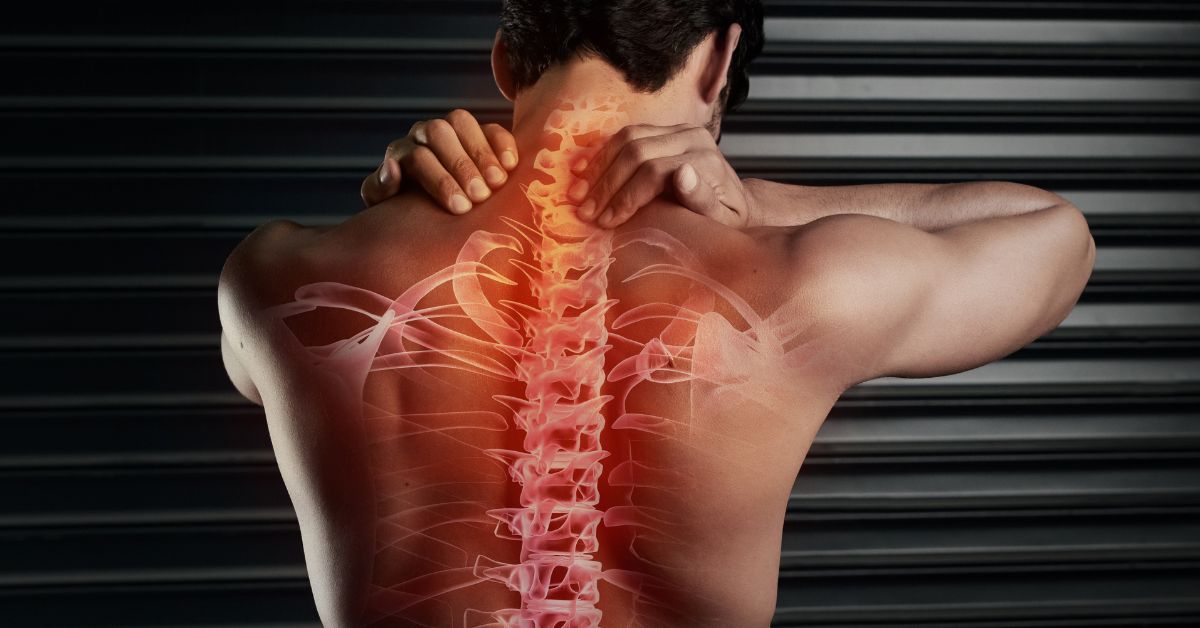
A spinal tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue within or surrounding the spinal cord, which can lead to pain, neurological deficits, or other serious complications.
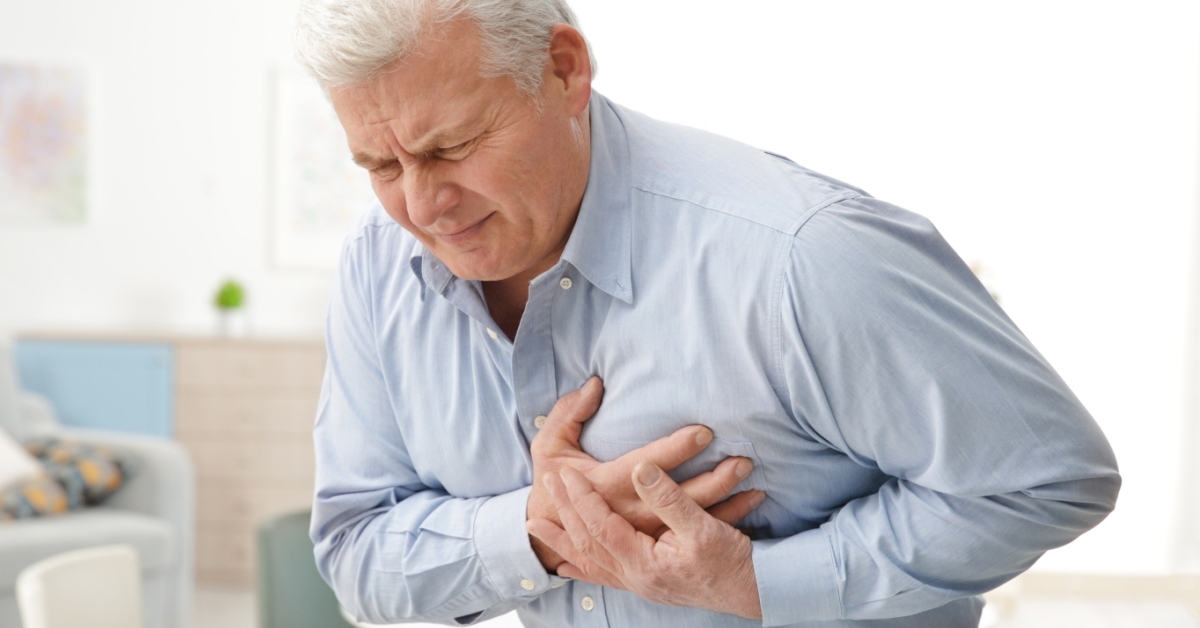
A heart attack, medically known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot.
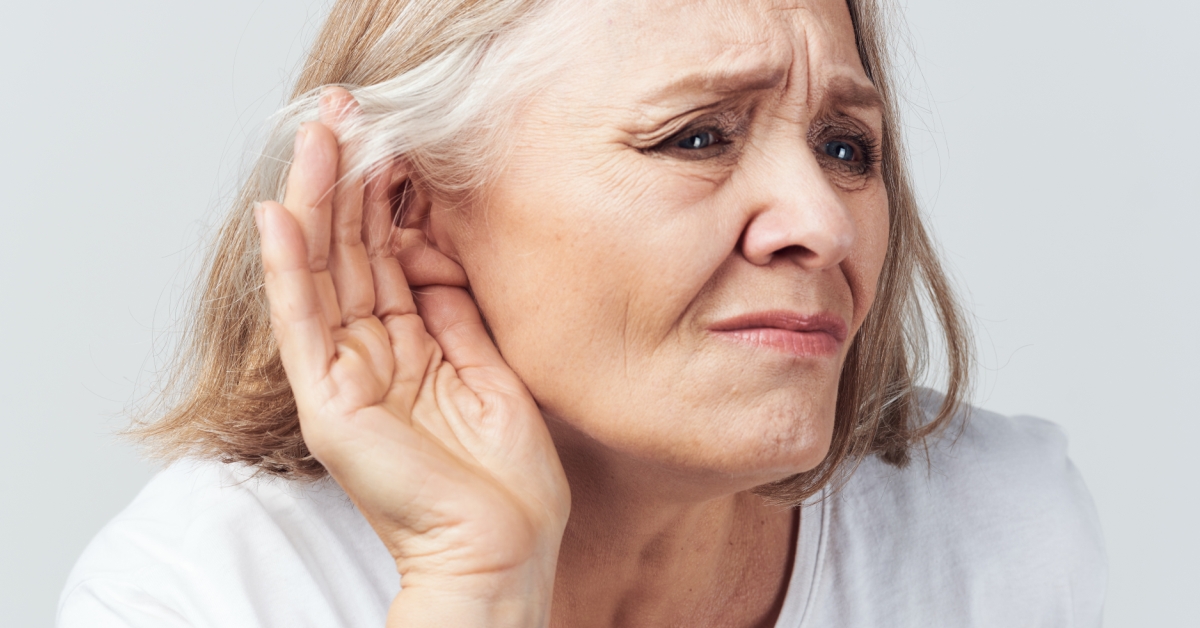
Hearing loss is a prevalent condition that can range from mild to profound, affecting individuals of all ages.
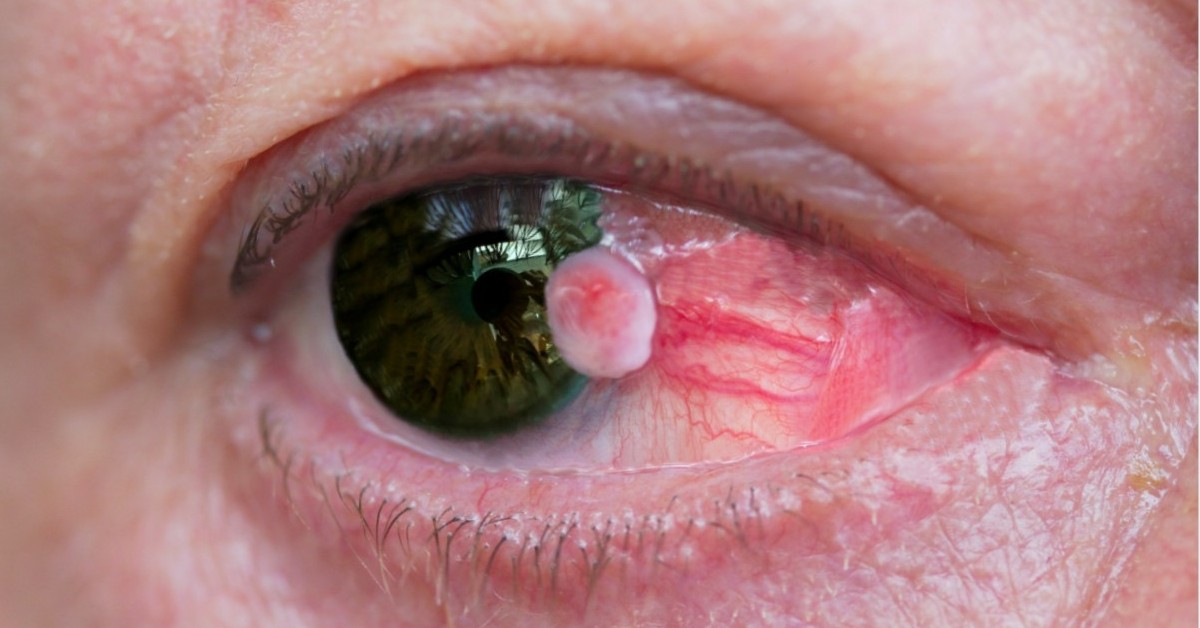
Eye cancer, while relatively rare, can significantly impact vision and overall health. It refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the eye, which can occur in various parts, including the retina, conjunctiva, and the surrounding tissues.
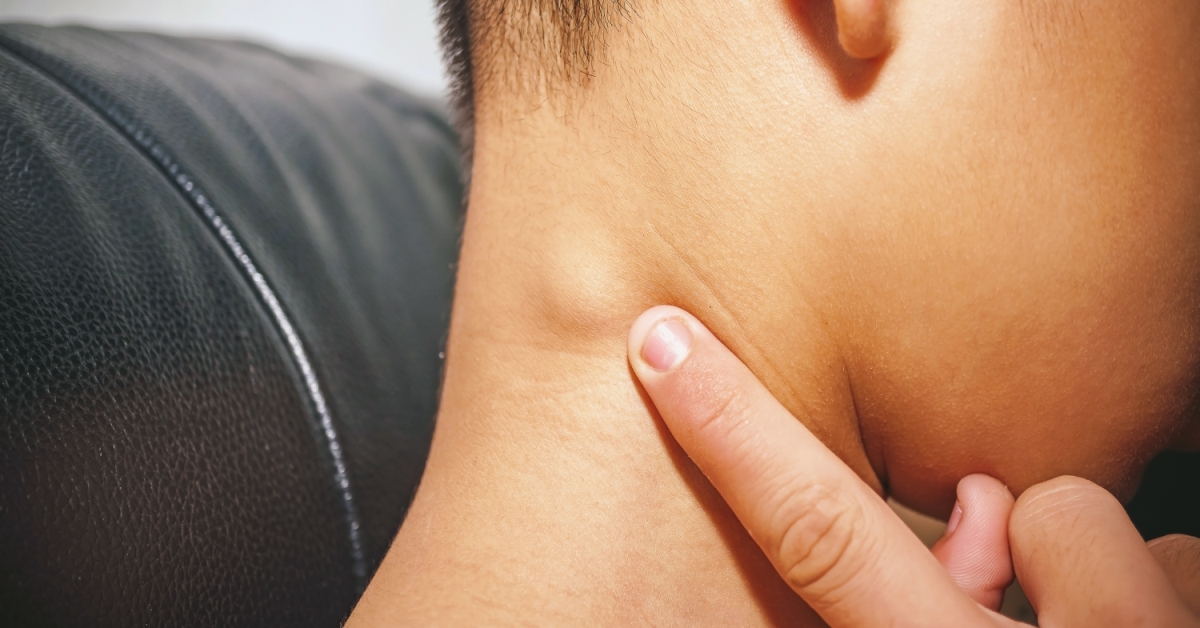
Swollen lymph nodes, often a sign of infection, occur when the lymph glands—small, bean-shaped structures in the immune system—become enlarged.
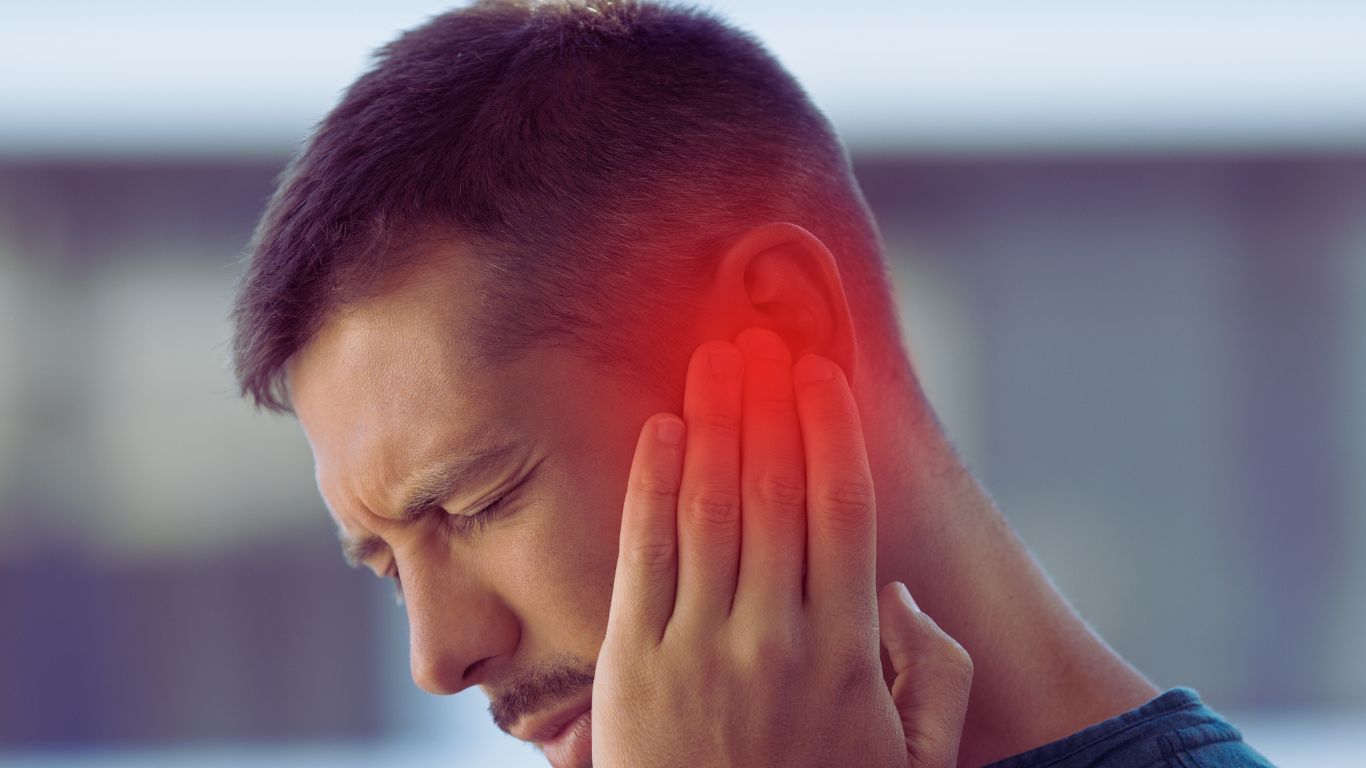
Meniere’s disease is a chronic inner ear disorder characterized by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), fluctuating hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness in the ear.
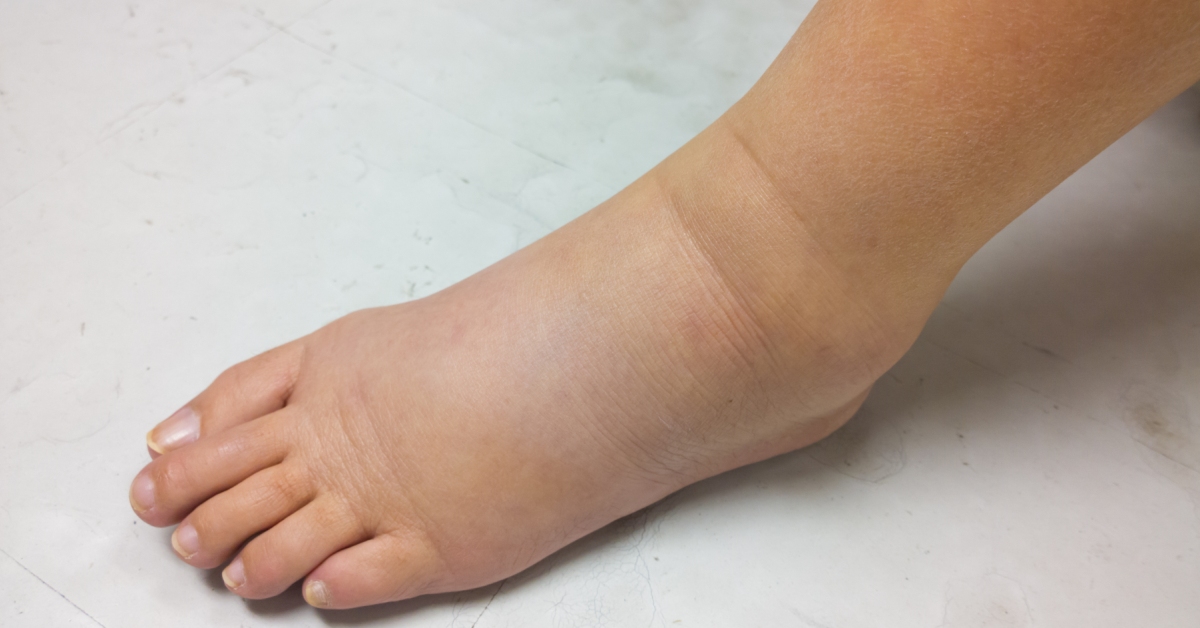
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, usually resulting in swelling, most commonly in the arms or legs.
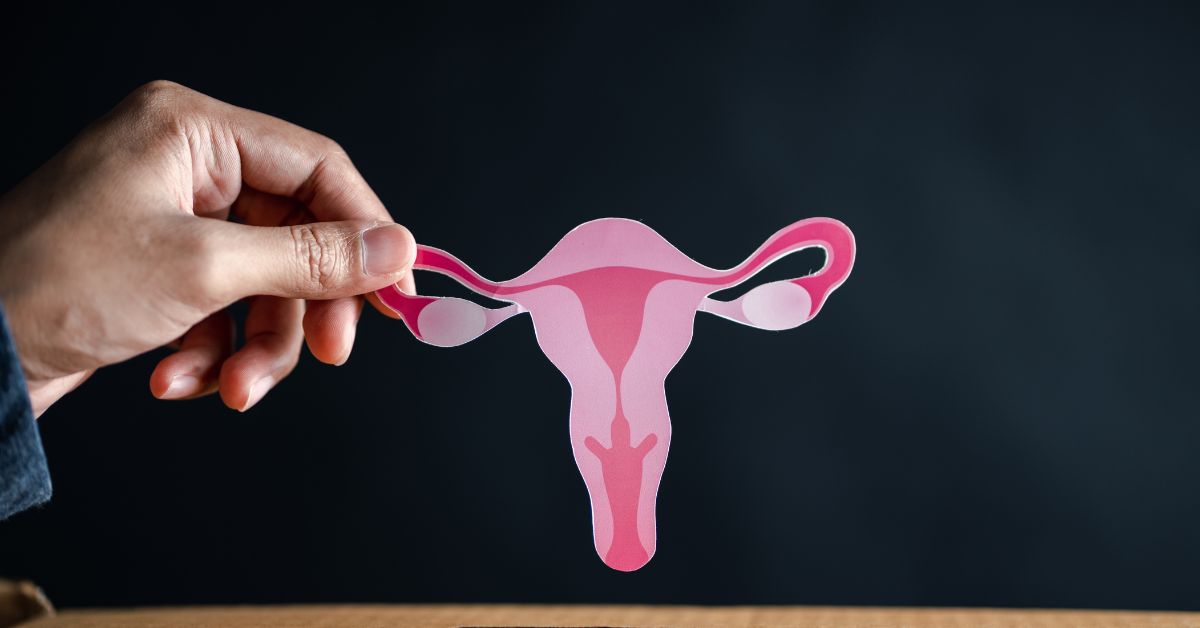

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries, leading to symptoms such as weight gain, acne, and fertility issues.
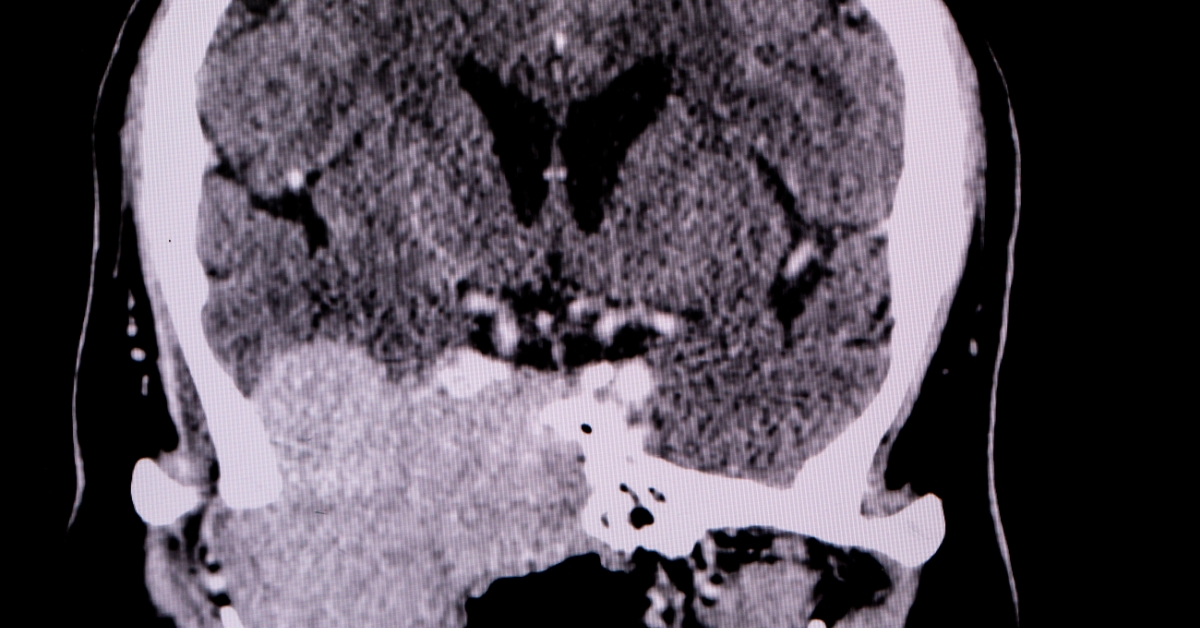
Pineal region tumors are growths that develop in or around the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain responsible for regulating sleep patterns through melatonin production.
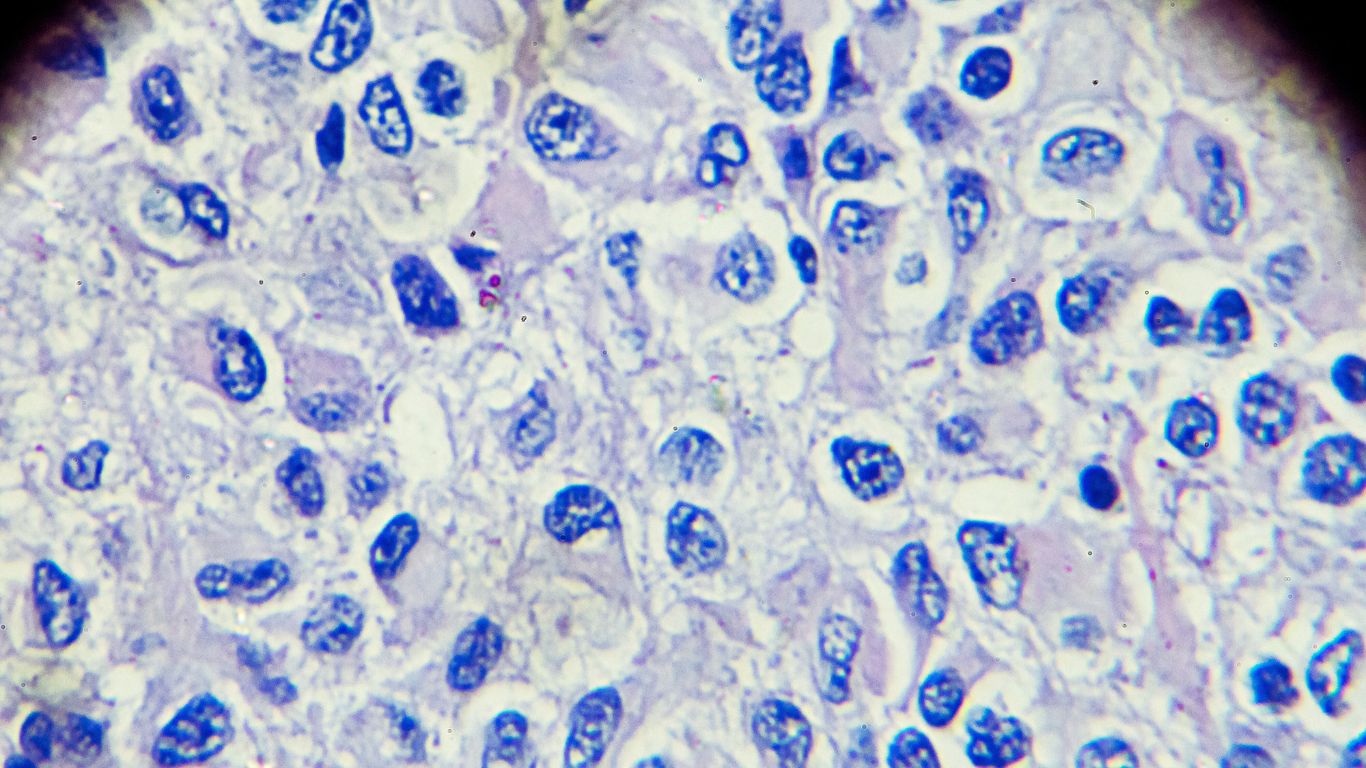
Ovarian germ cell tumors arise from reproductive cells in the ovaries, often manifesting in younger individuals with a range of benign and malignant forms.
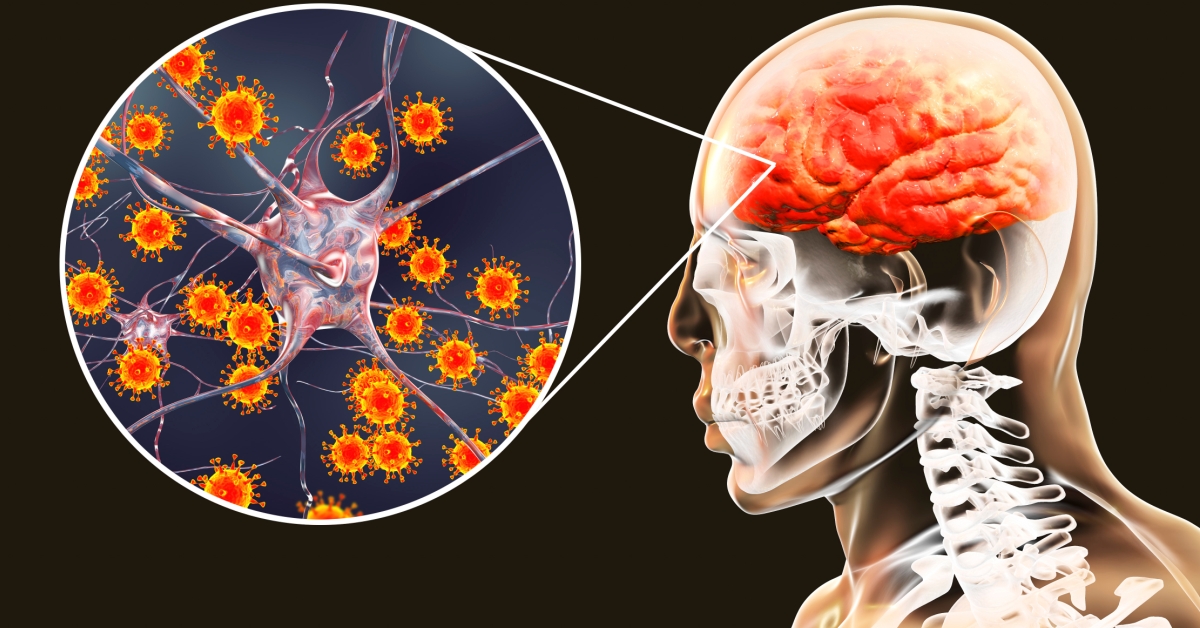
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known as the meninges.
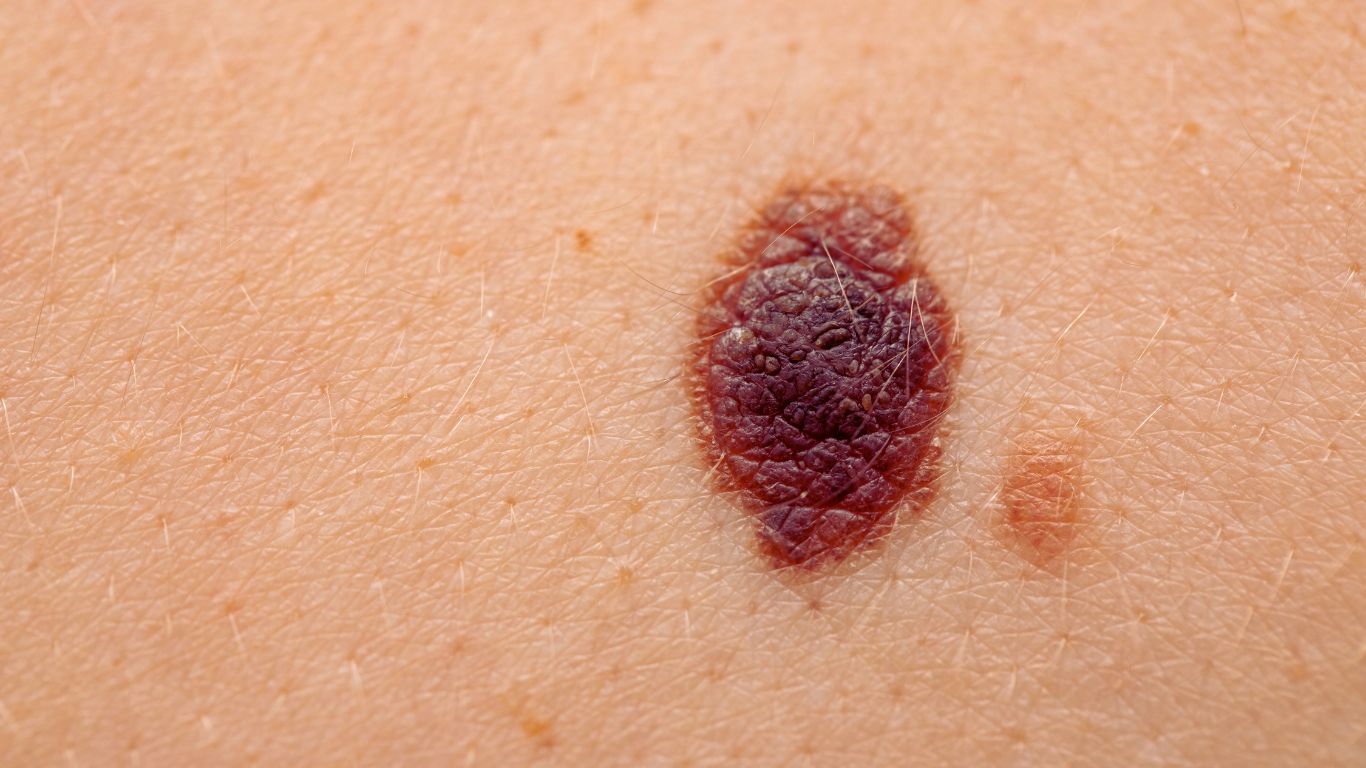
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin.
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye to treat various conditions affecting the retina and vitreous humor.
Osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and reshaping bones to correct deformities or misalignments, often performed to alleviate pain and improve function in joints, particularly in conditions like osteoarthritis.
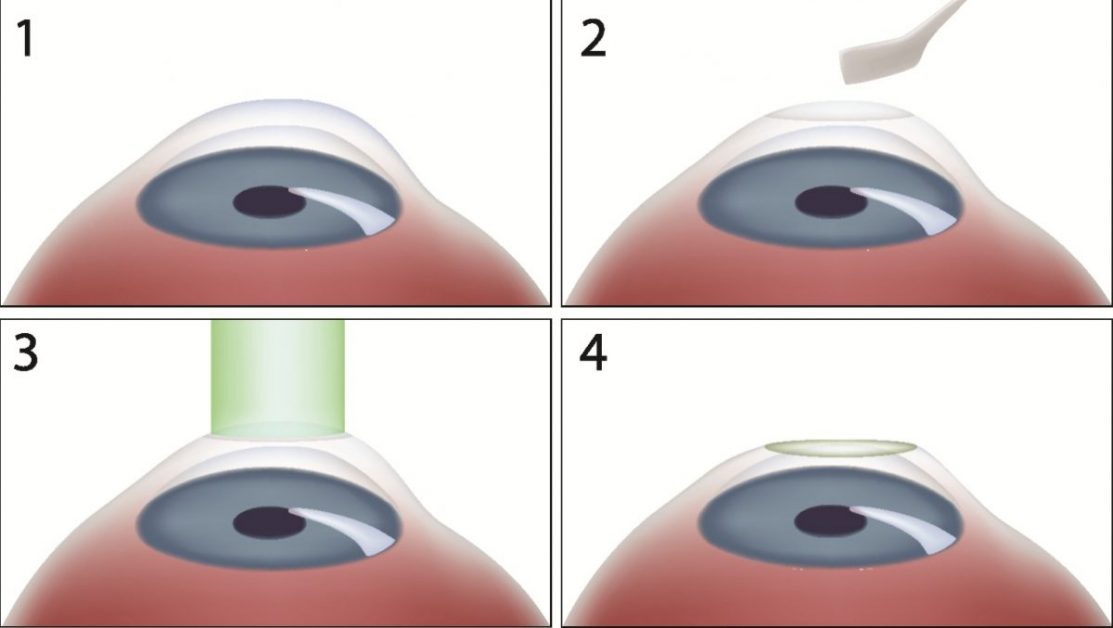
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) is a type of laser eye surgery designed to correct vision problems such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Temporal lobectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of a portion of the temporal lobe of the brain, primarily to treat refractory epilepsy or certain brain tumors.
CT Angiography (64 Slice) is a sophisticated imaging technique that provides detailed views of blood vessels using a 64-slice computed tomography scanner.
Cortisone shots are injections that deliver corticosteroids directly into an inflamed area of the body to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
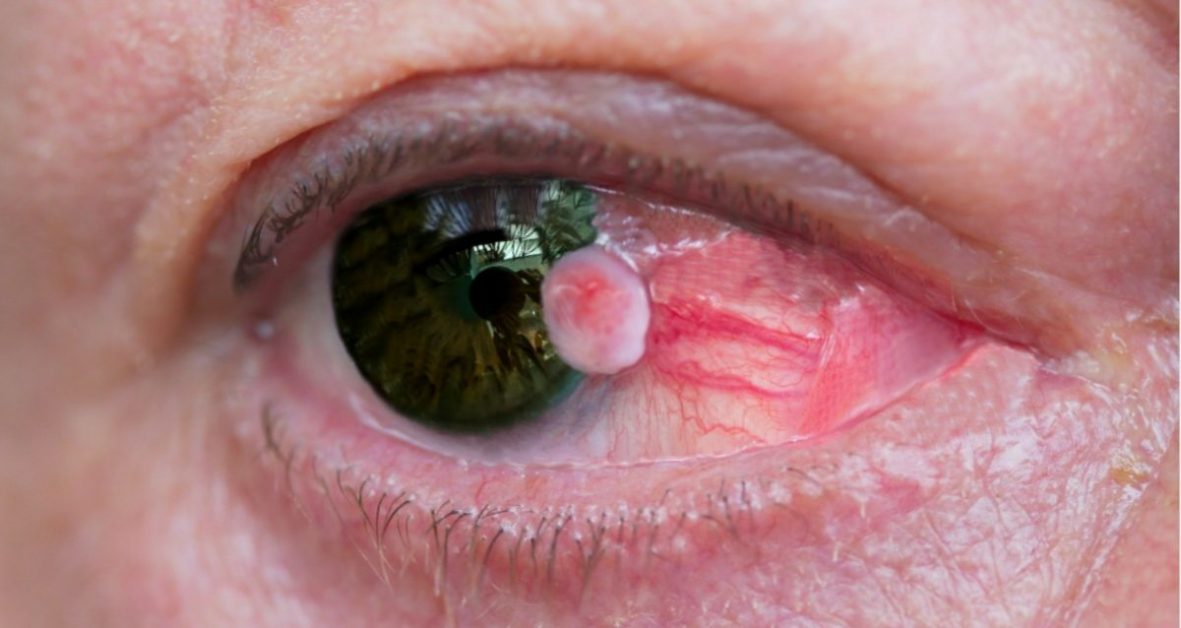
Corneal implants are innovative devices surgically placed in the cornea to improve vision or address conditions like keratoconus.
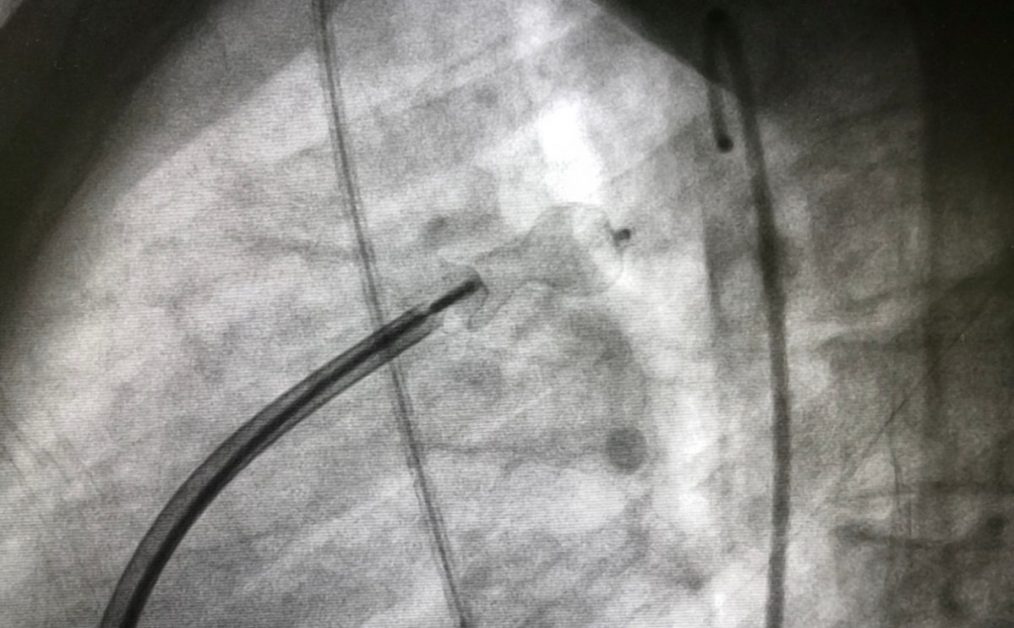
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) device closure is a minimally invasive procedure used to close an abnormal connection between the aorta and the pulmonary artery known as the ductus arteriosus.
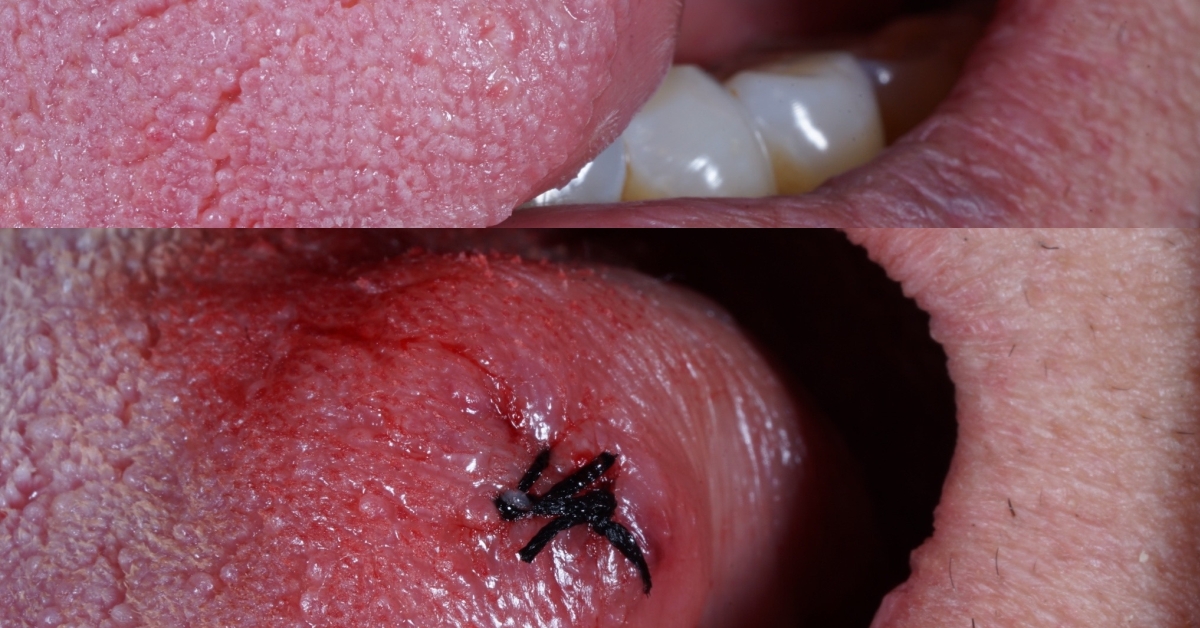
Hemiglossectomy is a surgical procedure involving the partial removal of the tongue, often performed to treat tongue cancer or other severe conditions affecting oral health.

Laser iridotomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat certain types of glaucoma, particularly angle-closure glaucoma.
Corpus callosotomy is a neurosurgical procedure that involves severing the corpus callosum, the band of nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
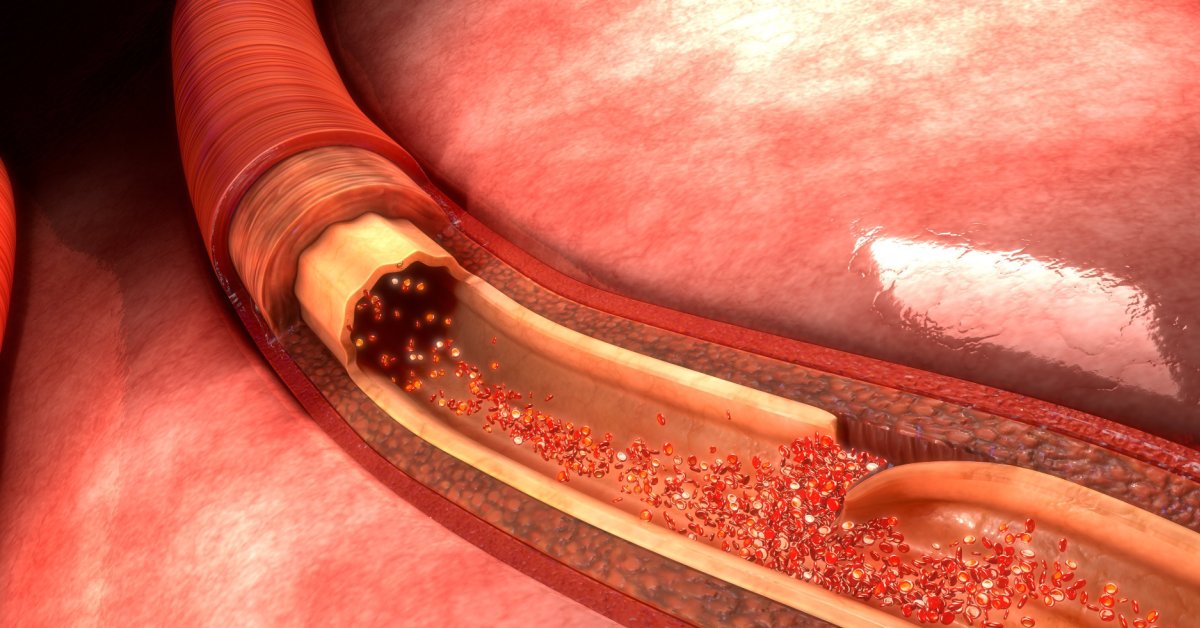
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) is a rare and often life-threatening condition where a tear forms in the coronary artery wall, leading to a disruption of blood flow and potential heart attack.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) is a surgical procedure that involves fusing two or more vertebrae in the lower back to alleviate pain and stabilize the spine.
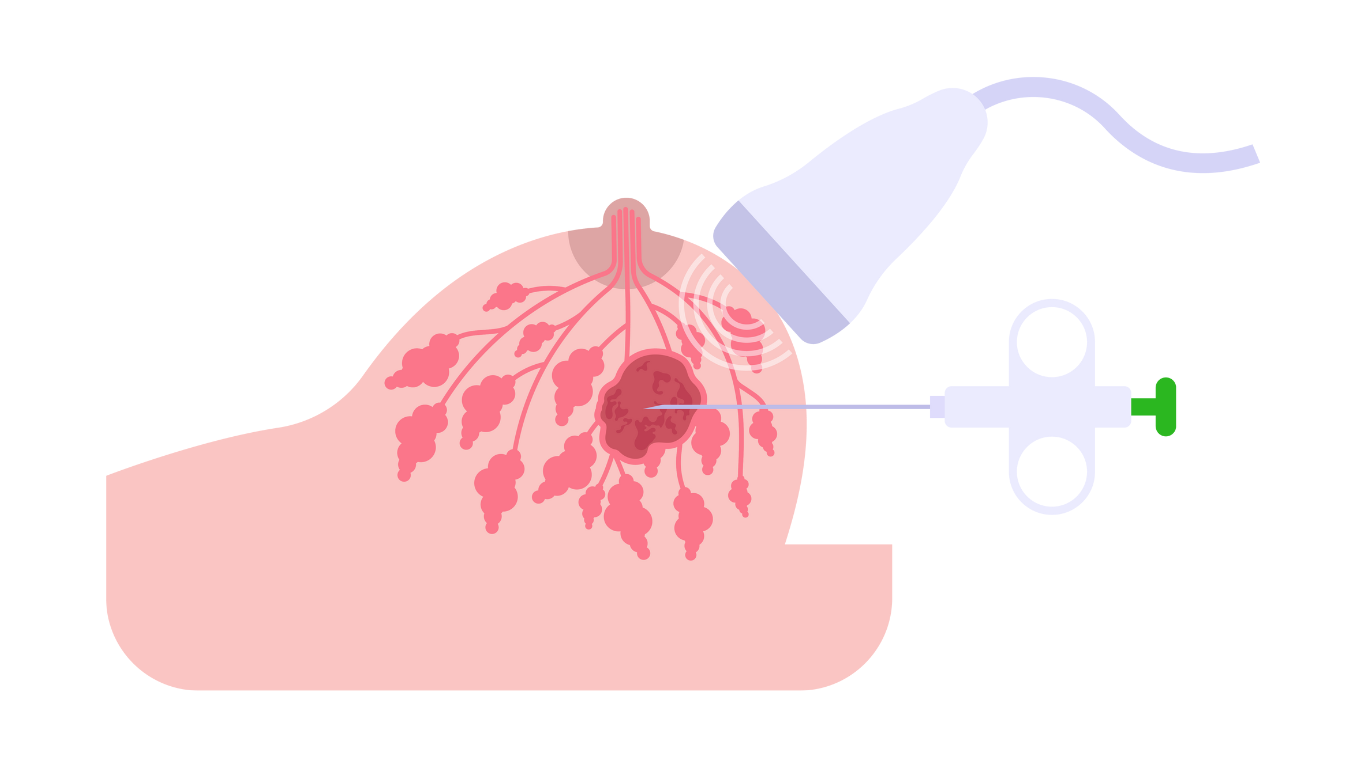
Sentinel node biopsy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to determine if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes by examining the first node(s) that drain lymphatic fluid from a tumor site.
Cryoablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue, often employed in the treatment of various tumors and cardiac arrhythmias.
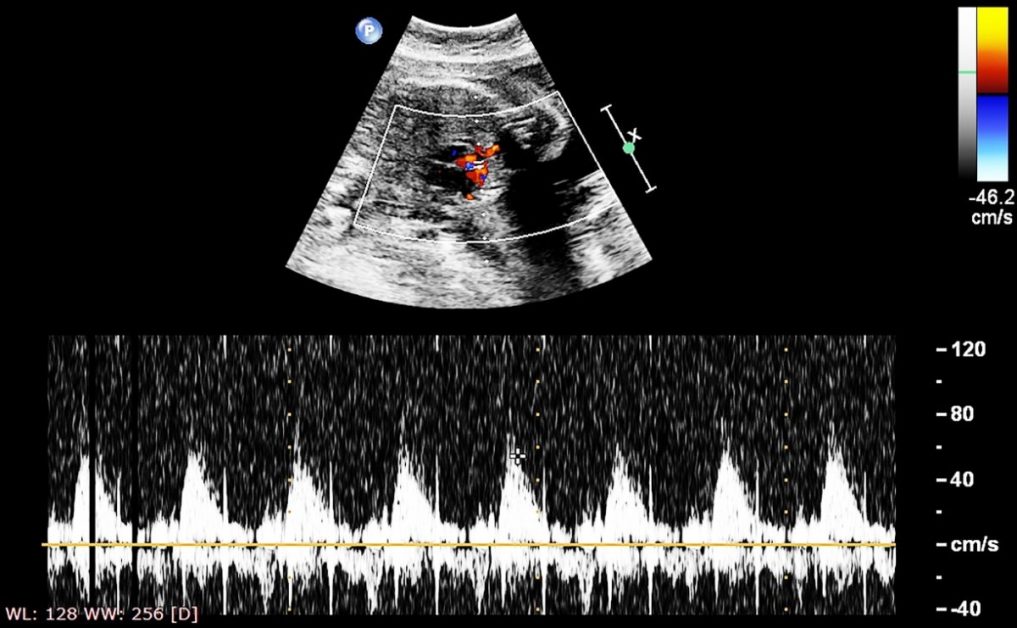
Fetal echocardiography, or fetal echo, is a specialized ultrasound technique used to assess the heart’s structure and function in a developing fetus.

Facial feminization is a surgical procedure aimed at modifying masculine facial features to achieve a more traditionally feminine appearance.
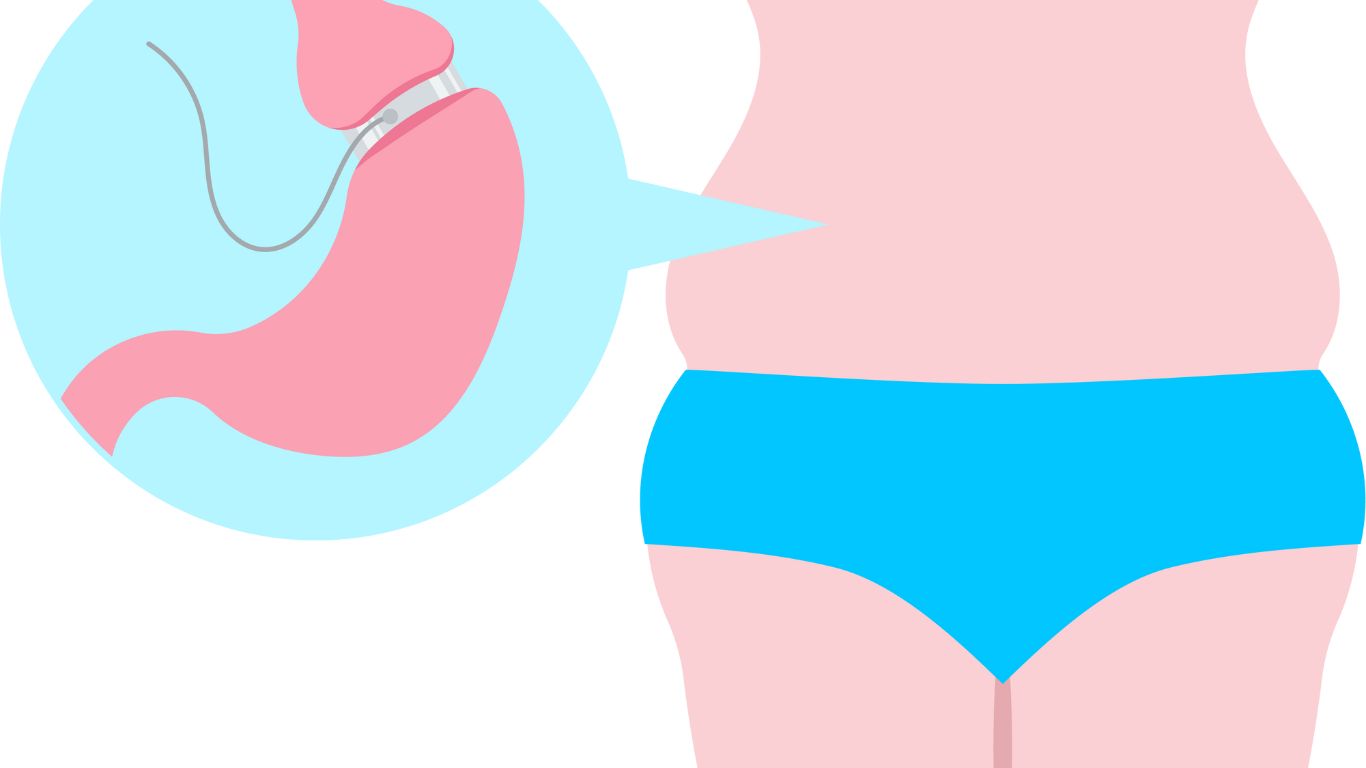
Duodenal switch is a weight-loss surgery that combines gastric restriction with malabsorption, significantly reducing stomach size and altering the small intestine’s absorption capacity.

Extracapsular cataract extraction is a surgical procedure in which the cloudy lens of the eye is removed while leaving the surrounding capsule intact.
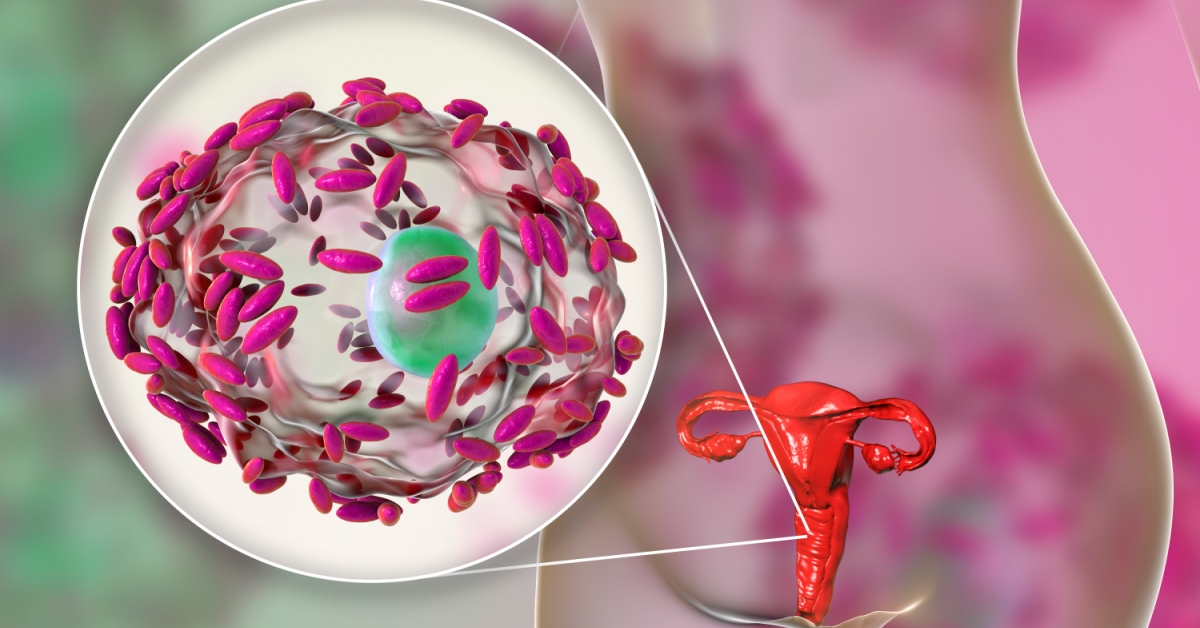
An imperforate hymen is a congenital condition where the hymen lacks an opening, preventing menstrual fluid from exiting the body.
Microvascular Decompression (MVD) is a surgical procedure primarily used to relieve symptoms associated with conditions like trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm.
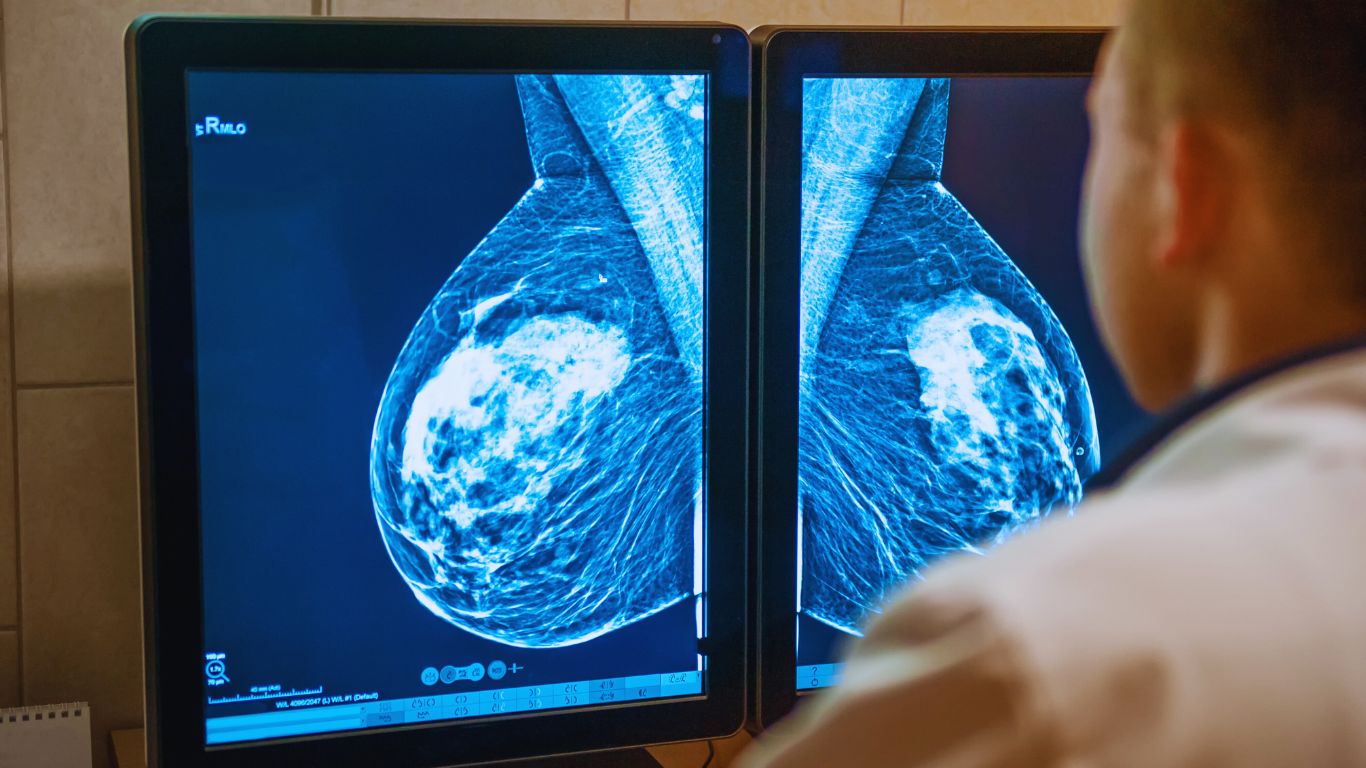
A mammogram is a specialized X-ray examination of the breast used to detect early signs of breast cancer and other abnormalities.
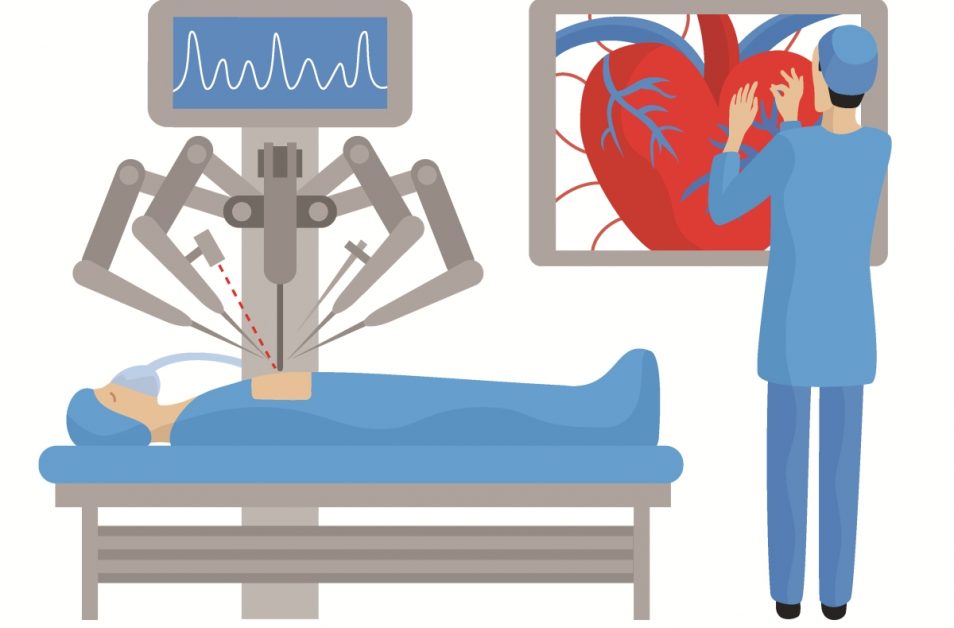
Robotic cardiac surgeries utilize advanced robotic systems to perform minimally invasive procedures on the heart, enhancing precision and reducing recovery time.
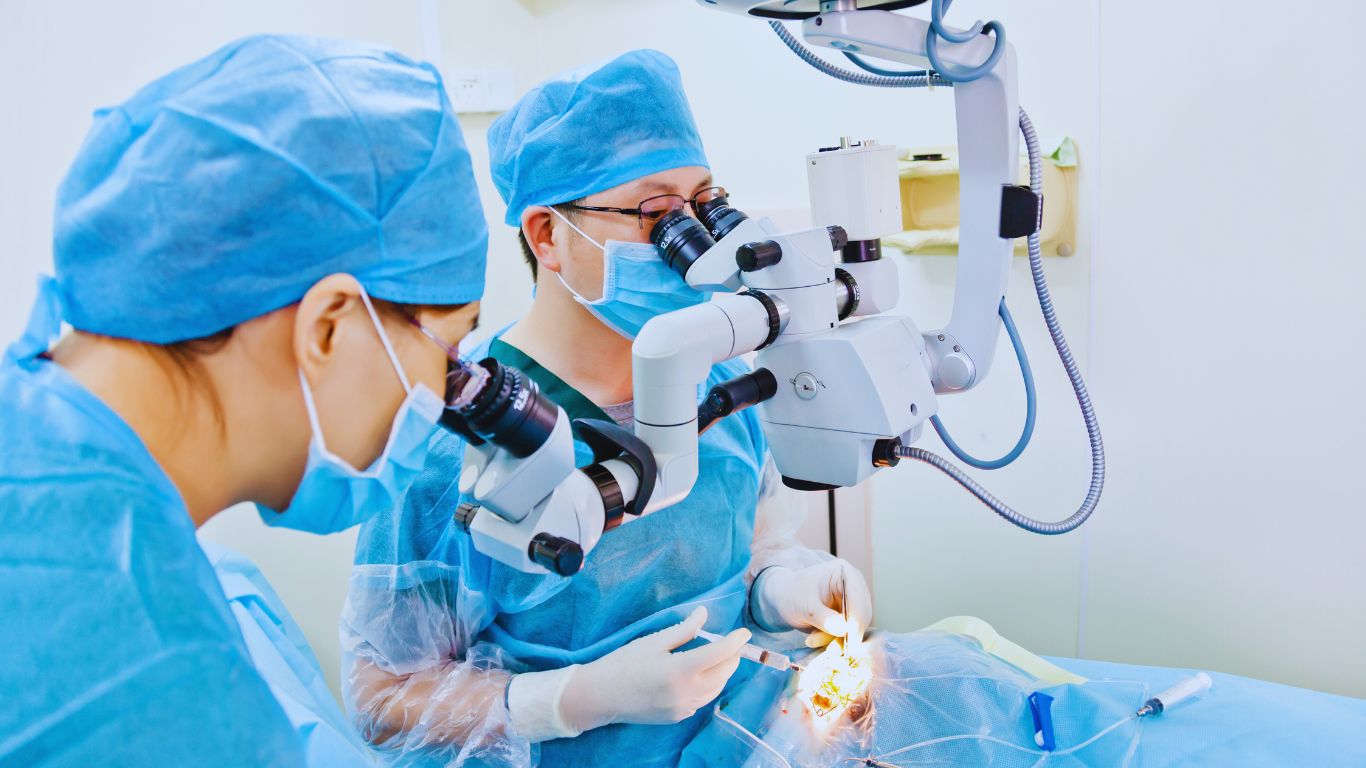
Robotic brain surgery uses advanced robotic systems to enhance precision and reduce invasiveness in neurosurgical procedures.
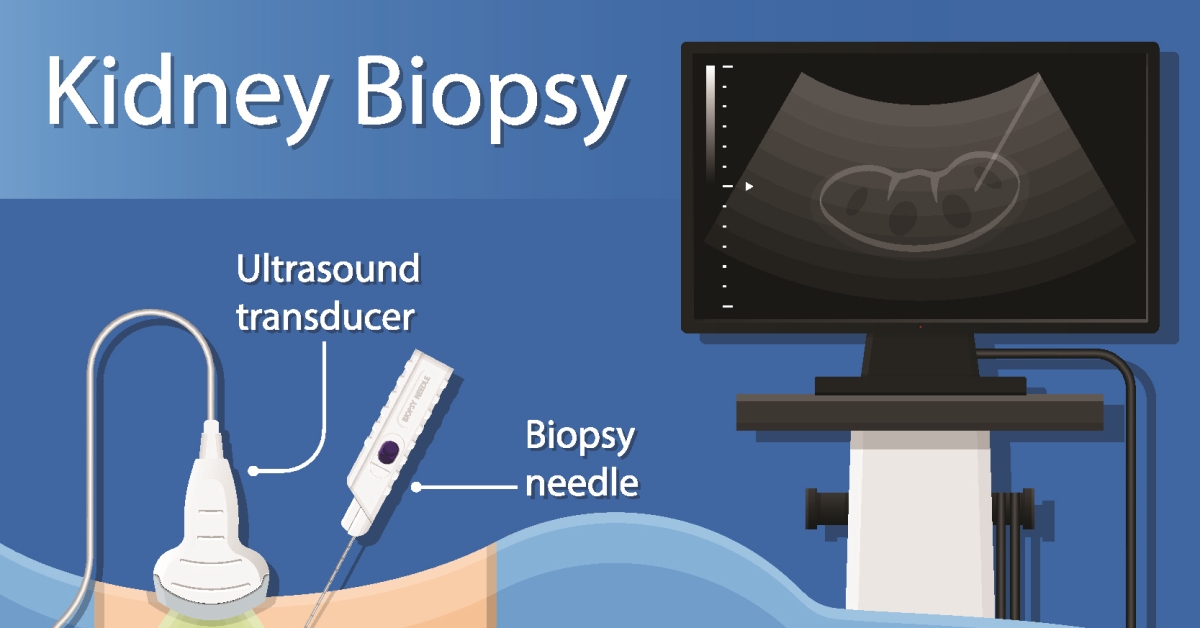
A kidney biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of kidney tissue is removed for examination, helping diagnose various kidney diseases and conditions.
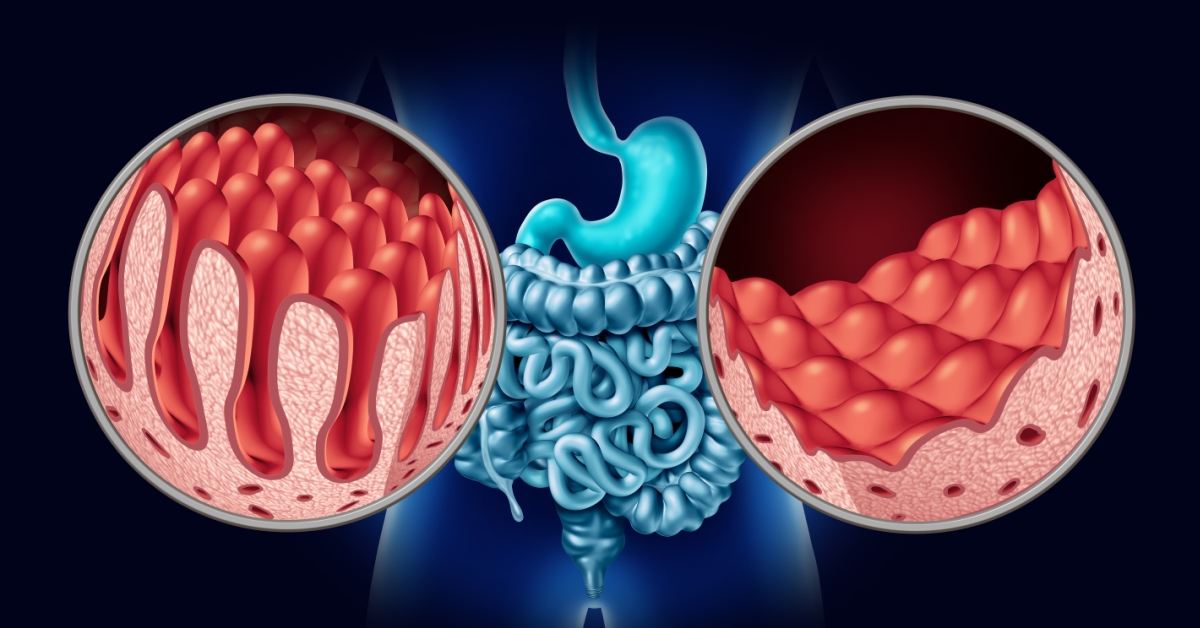
Small intestine cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops in the tissues of the small intestine, often leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, weight loss, and changes in bowel habits.
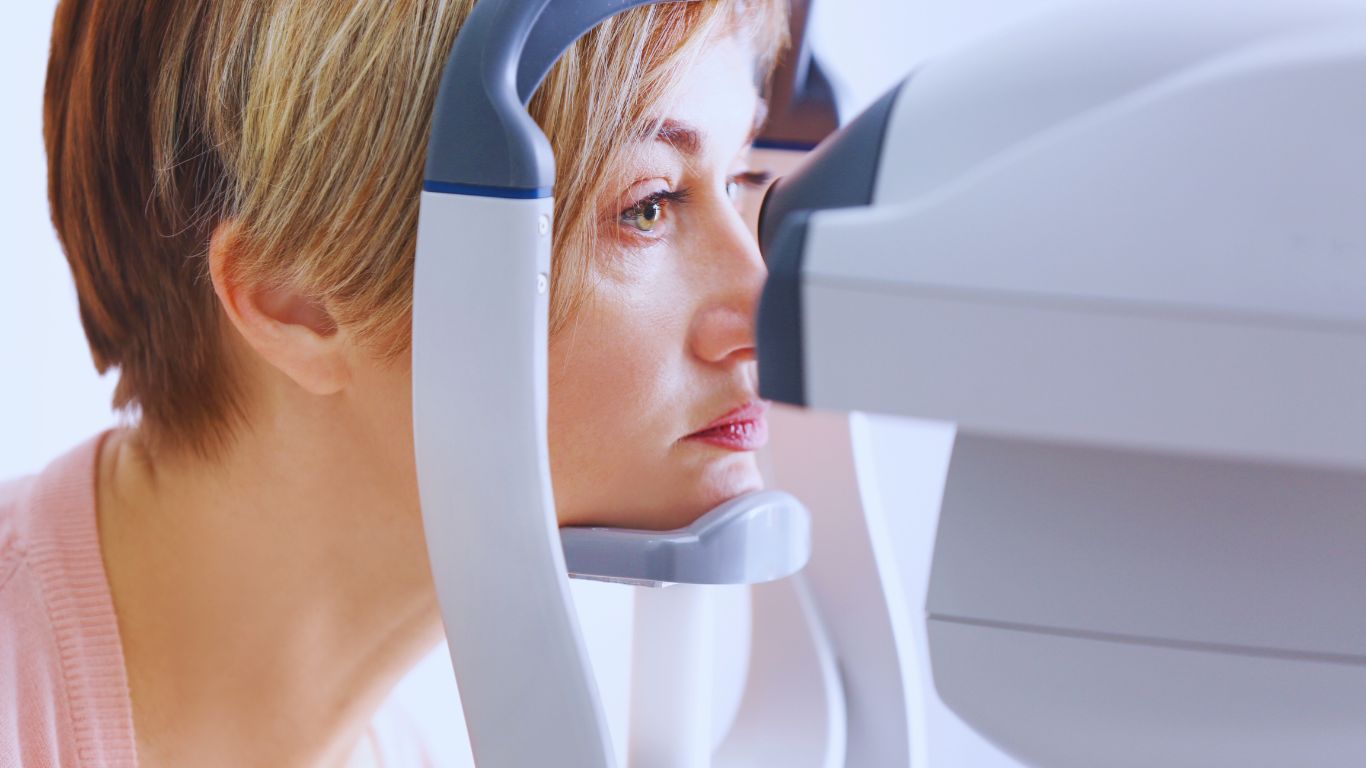
Intraocular implants are medical devices surgically placed inside the eye to correct vision or replace damaged structures, commonly used in cataract surgery.
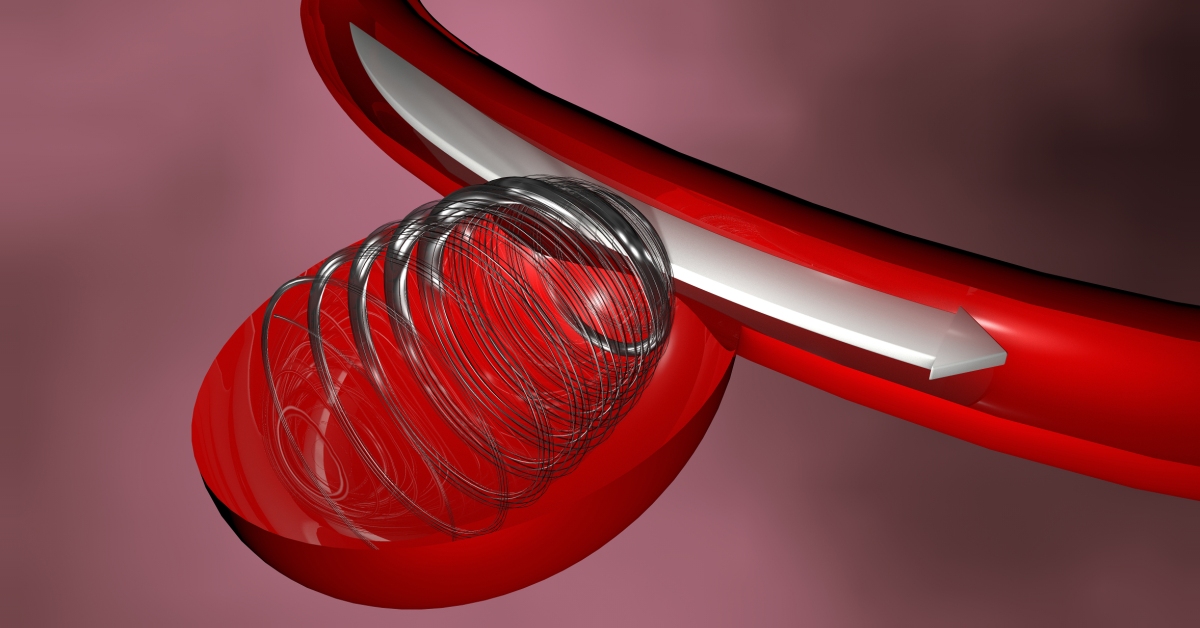
Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat cerebral aneurysms by placing soft coils into the aneurysm to promote clotting and seal it off from blood flow.
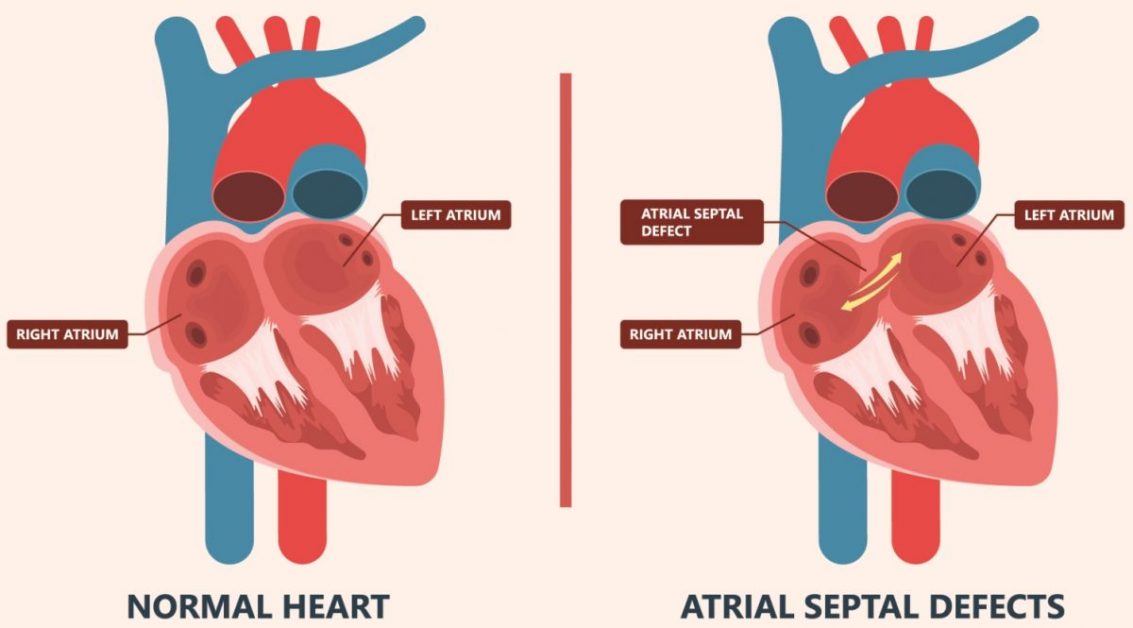
The Arterial Switch Operation is a complex surgical procedure performed to correct certain congenital heart defects, particularly transposition of the great arteries.

Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (DALK) is a specialized corneal transplant procedure that selectively removes and replaces the front layers of the cornea, preserving the patient’s healthy endothelium.
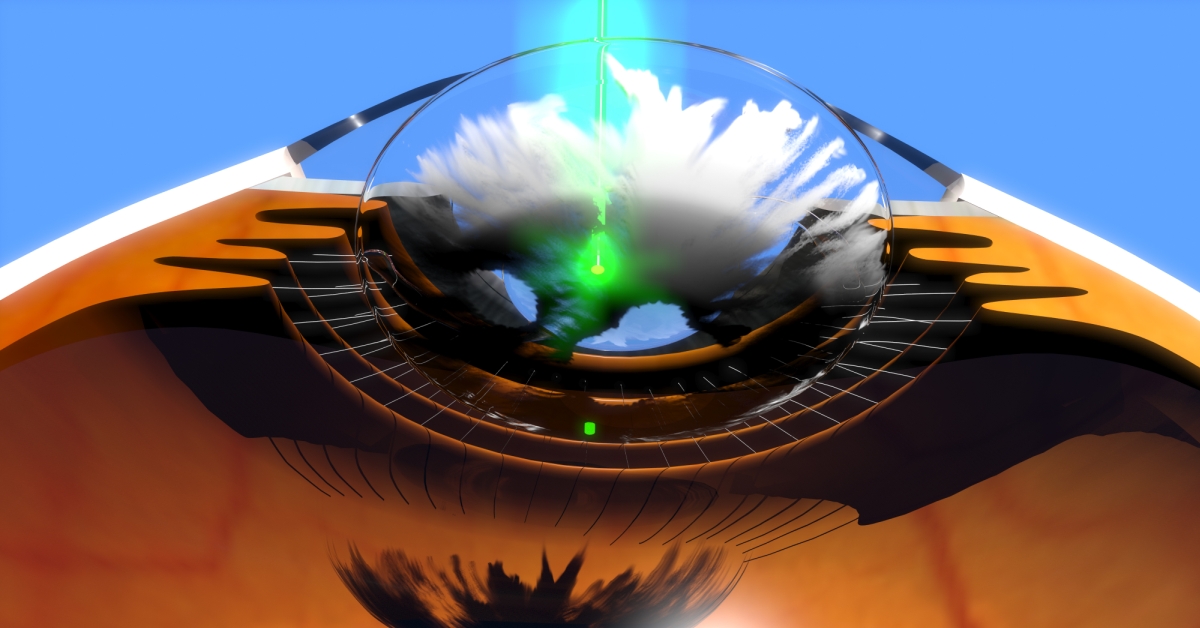

YAG laser capsulotomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat posterior capsule opacification, a common complication after cataract surgery.
A thigh lift is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to remove excess skin and fat from the thigh area, enhancing contour and firmness.
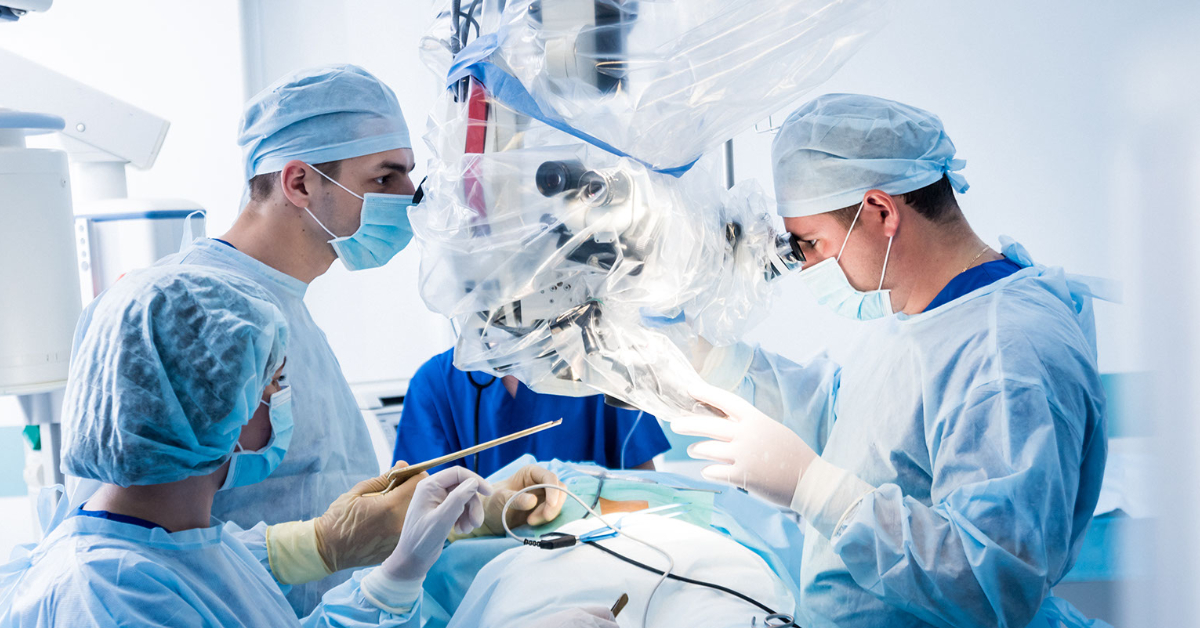
Laminoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to create more space in the spinal canal by reshaping the lamina, often used to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) is a surgical procedure designed to stabilize the spine by fusing vertebrae in the lower back, often performed to alleviate pain from conditions like herniated discs or spinal instability.
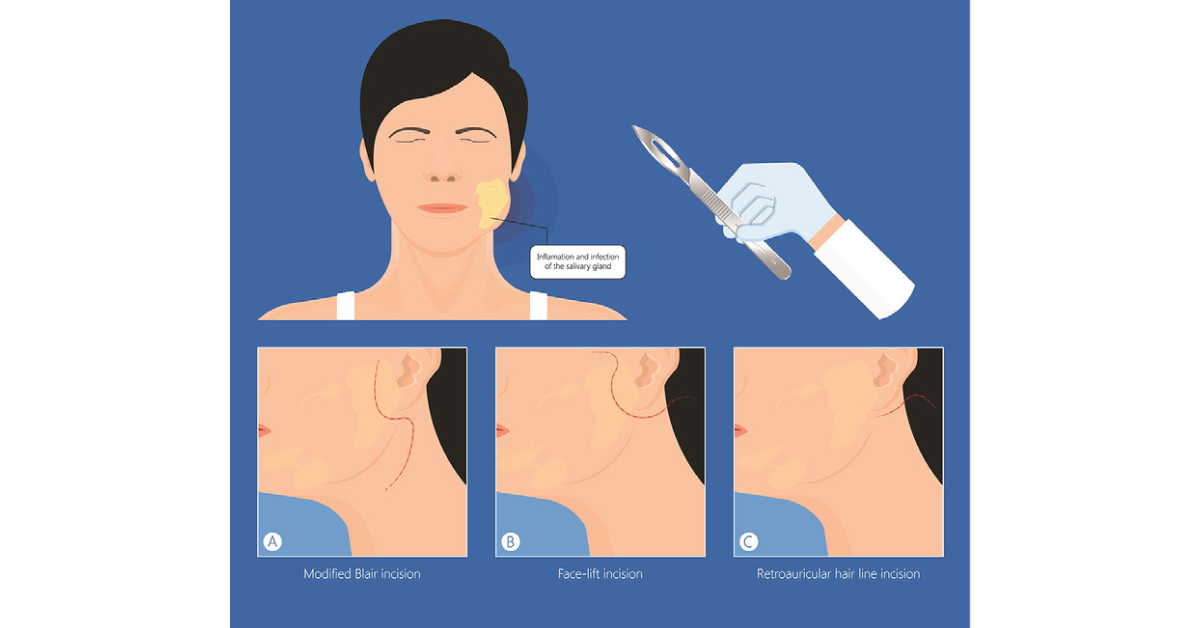
Parotidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove part or all of the parotid gland, often performed to treat tumors or infections.
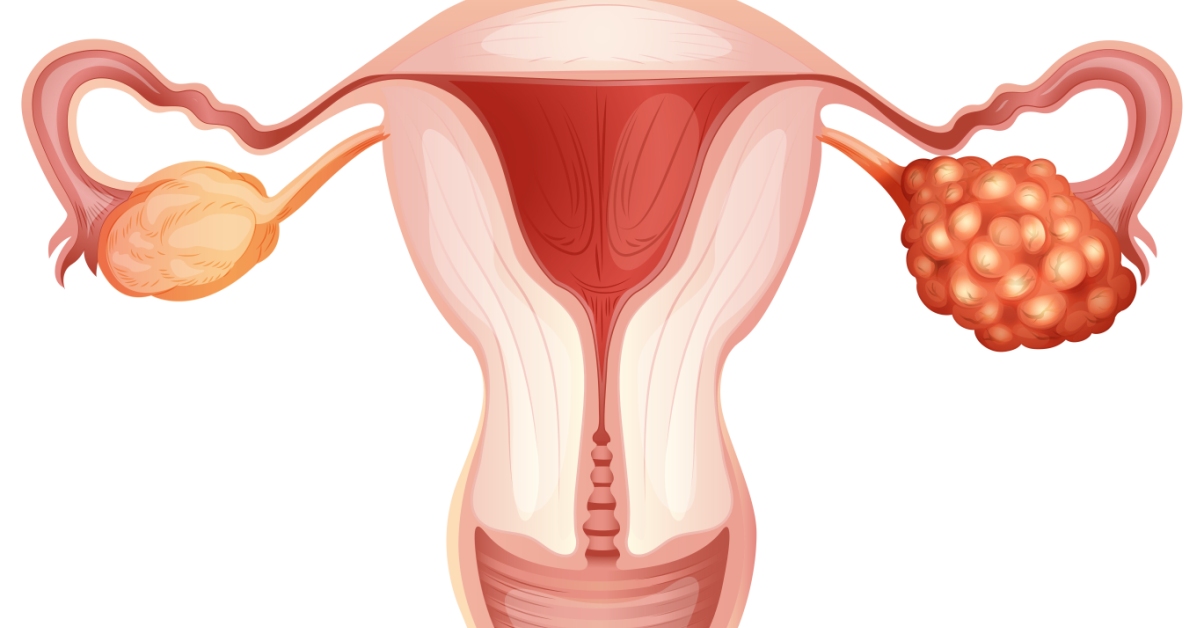
Colporrhaphy is a surgical procedure aimed at repairing and reconstructing the vaginal wall, often performed to treat pelvic organ prolapse or vaginal defects.
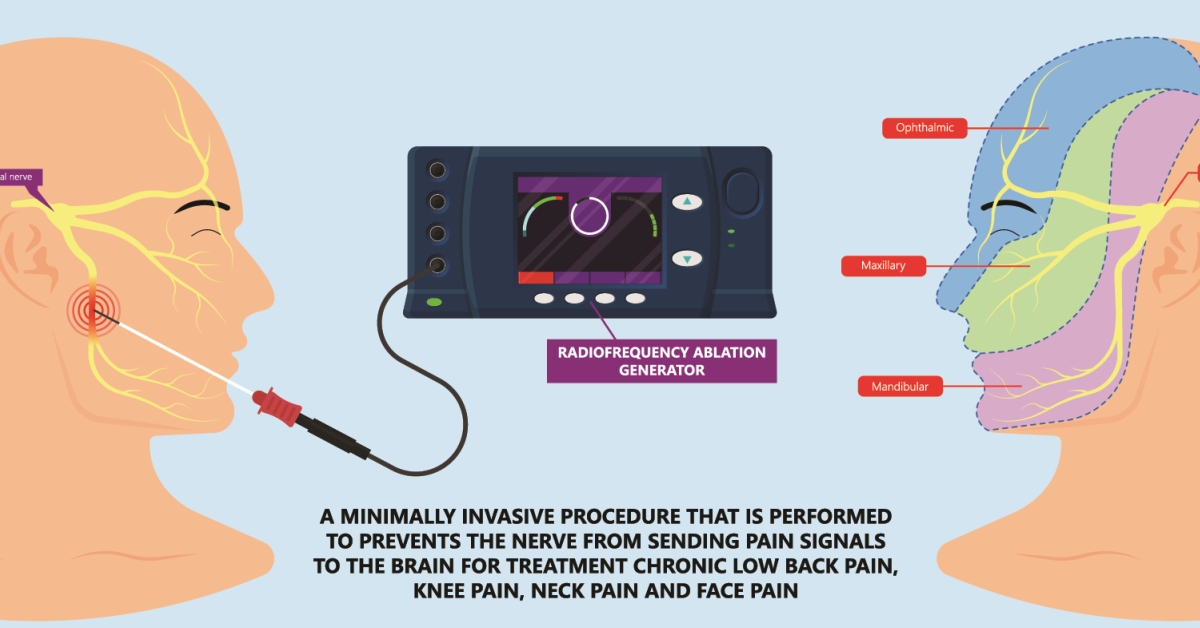
Rhizotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting specific nerve roots in the spinal cord to alleviate pain or muscle spasms.
An eye transplant involves the surgical replacement of damaged or diseased eye tissue, primarily focusing on restoring vision or cosmetic appearance.
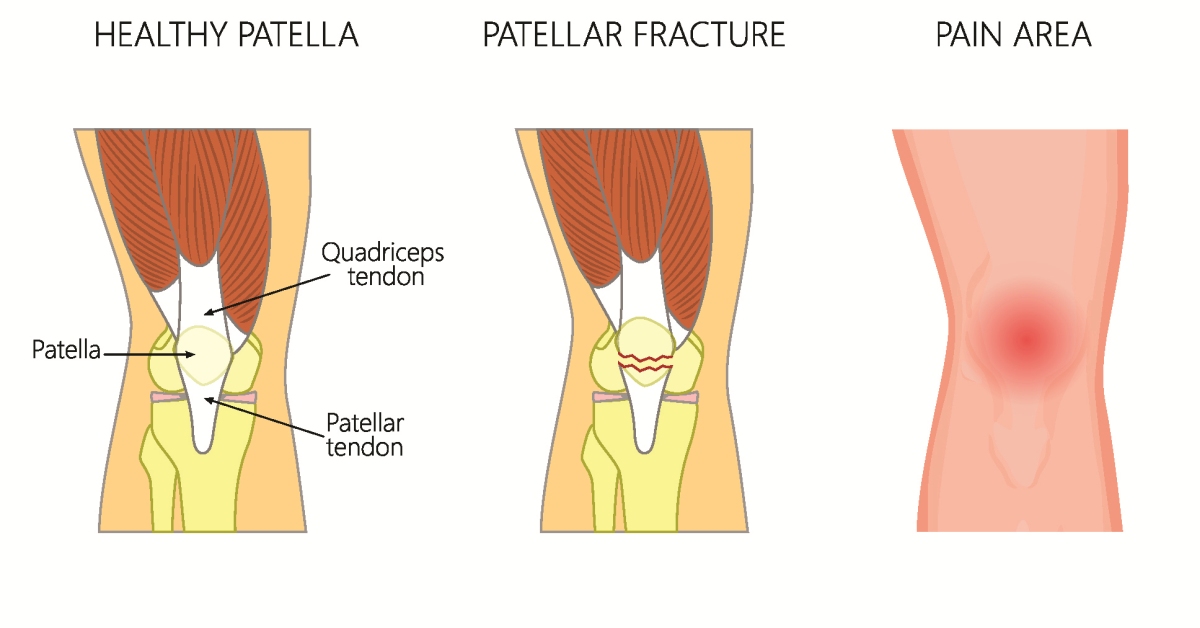
A patellar fracture involves a break in the kneecap, typically resulting from trauma or falls, and can significantly impair knee function.
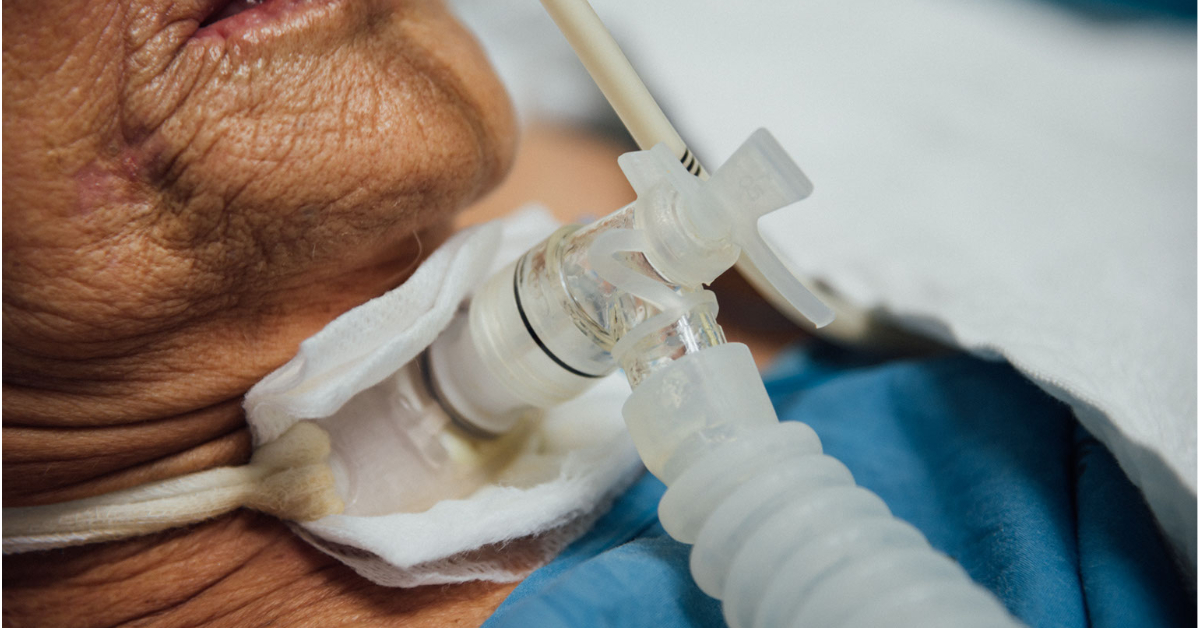
Laryngectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the larynx (voice box), often due to cancer or severe injury, leading to the creation of a stoma for breathing.
A heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart, often necessary for patients with severe heart disease or heart failure.
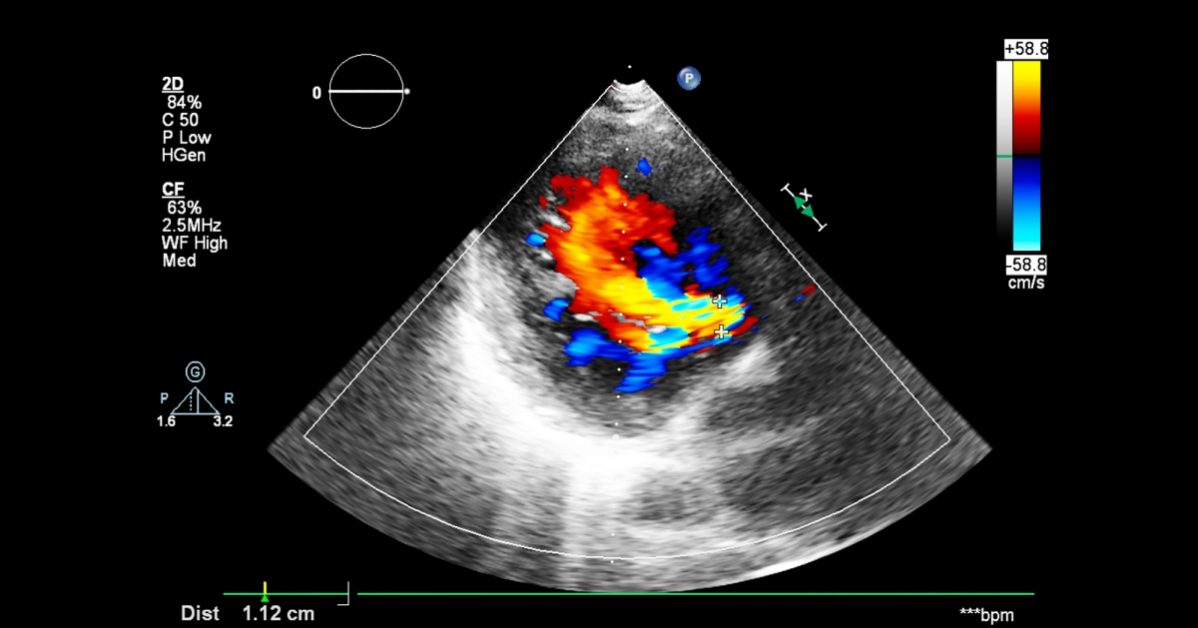
Doppler echocardiography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses ultrasound waves to assess blood flow and heart function.
Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical weight-loss procedure that involves removing a large portion of the stomach, resulting in a tubular “sleeve” shape.
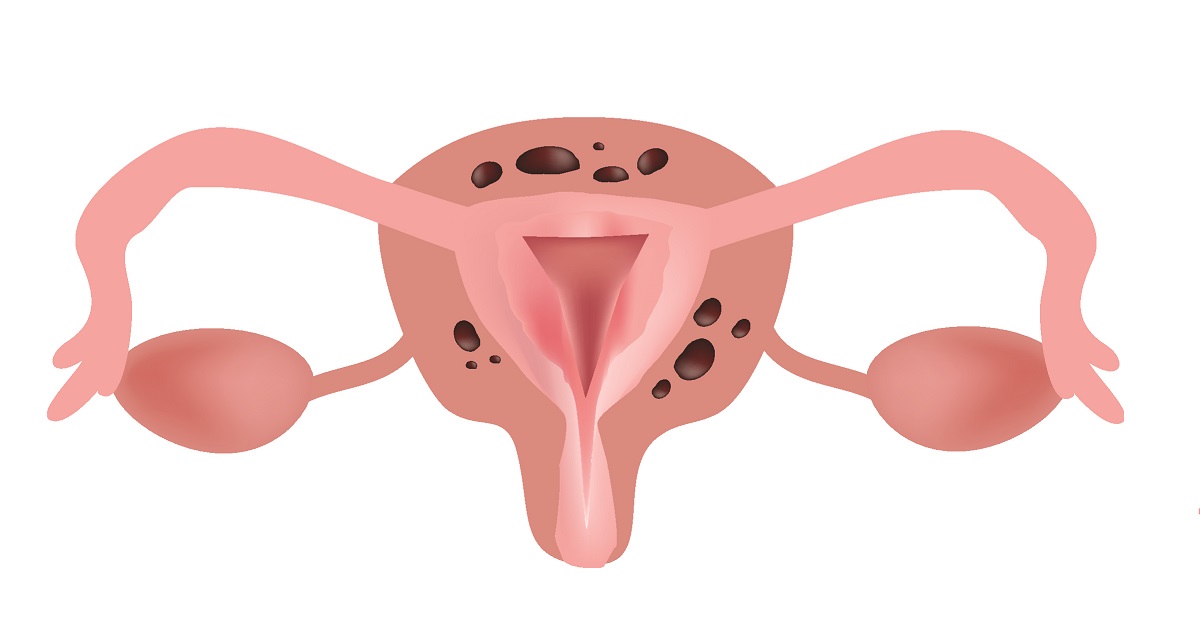
Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure designed to destroy the uterine lining, often used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding.
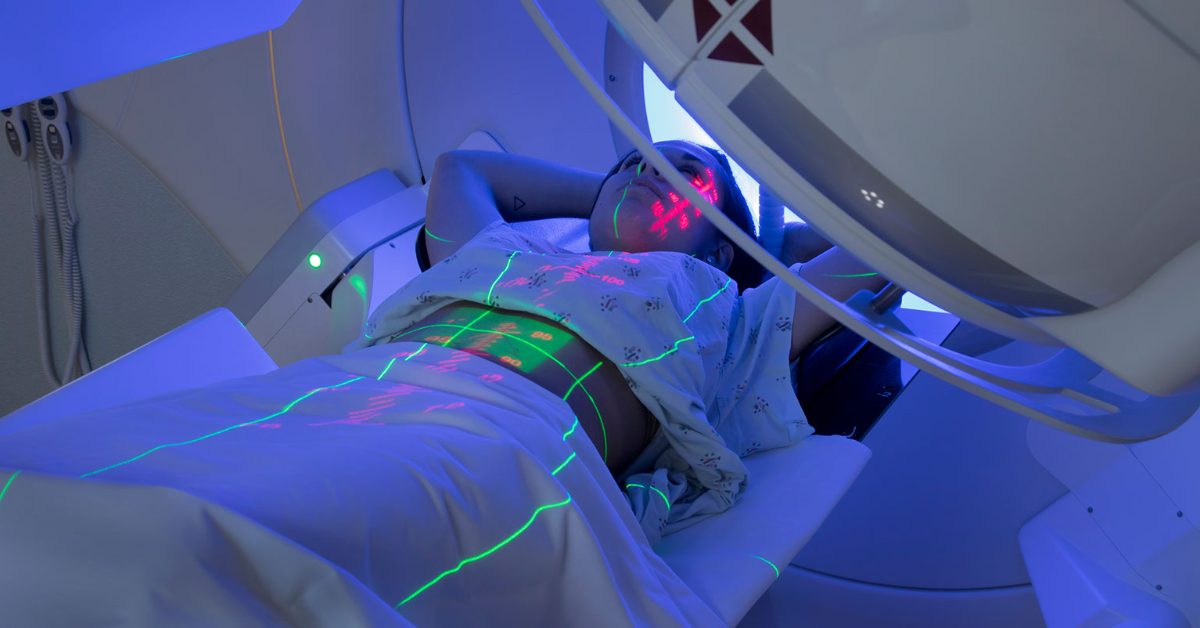
Radiation therapy harnesses high-energy particles to target and destroy cancer cells, aiming to shrink tumors and alleviate symptoms.
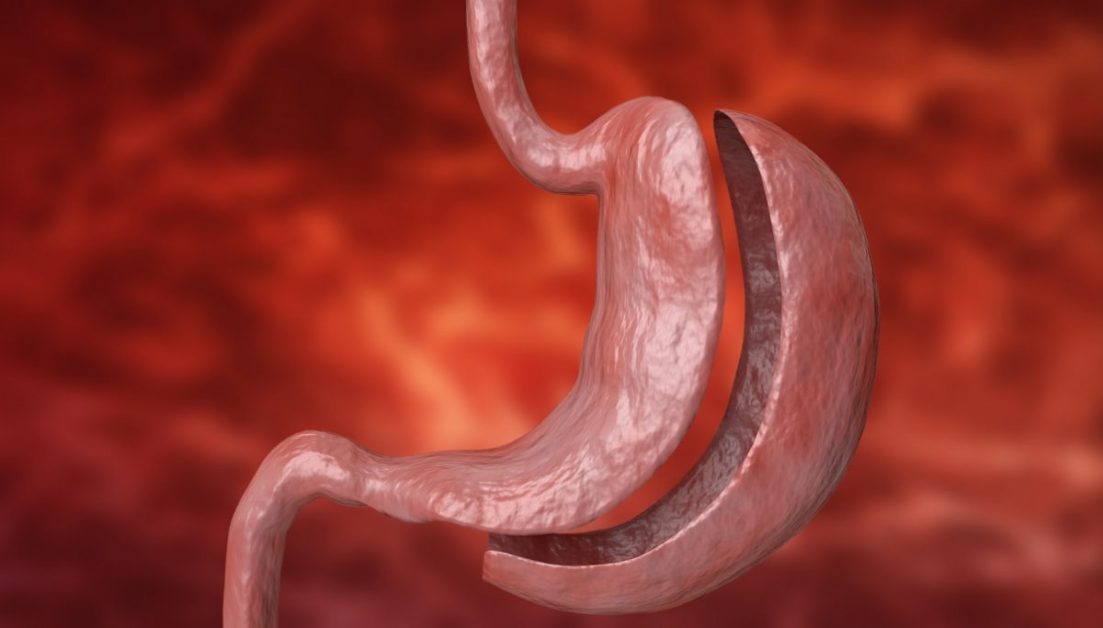
Gastric bypass is a surgical weight-loss procedure that alters the digestive system by creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine.
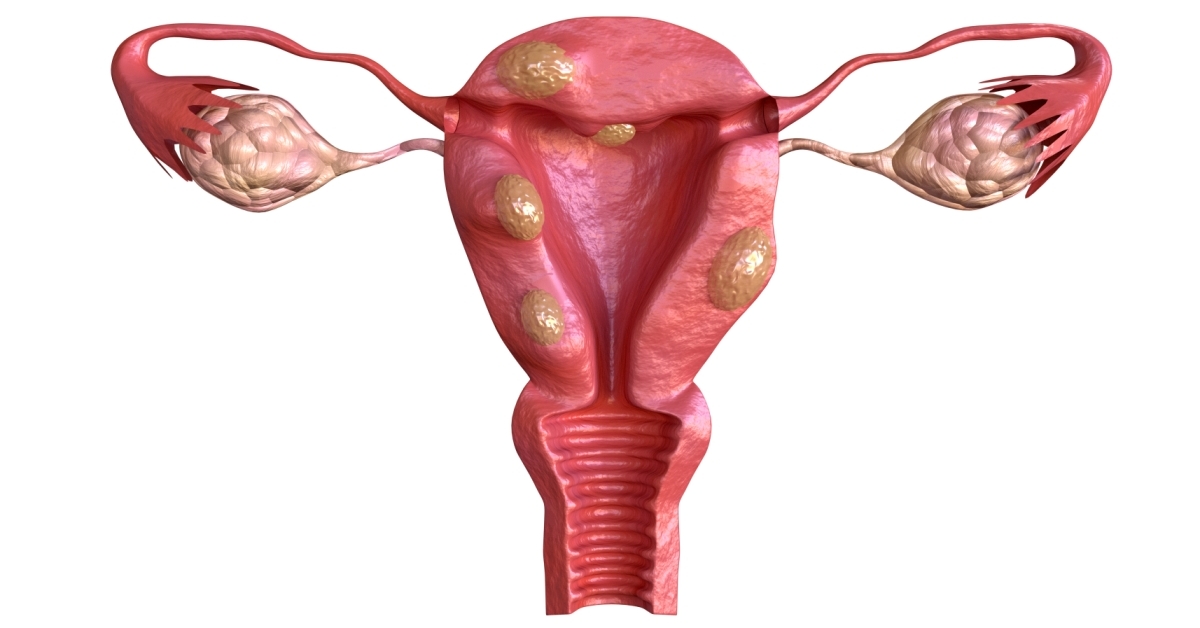
Colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure that uses a specialized microscope to examine the cervix and vagina for abnormal cells or tissue.
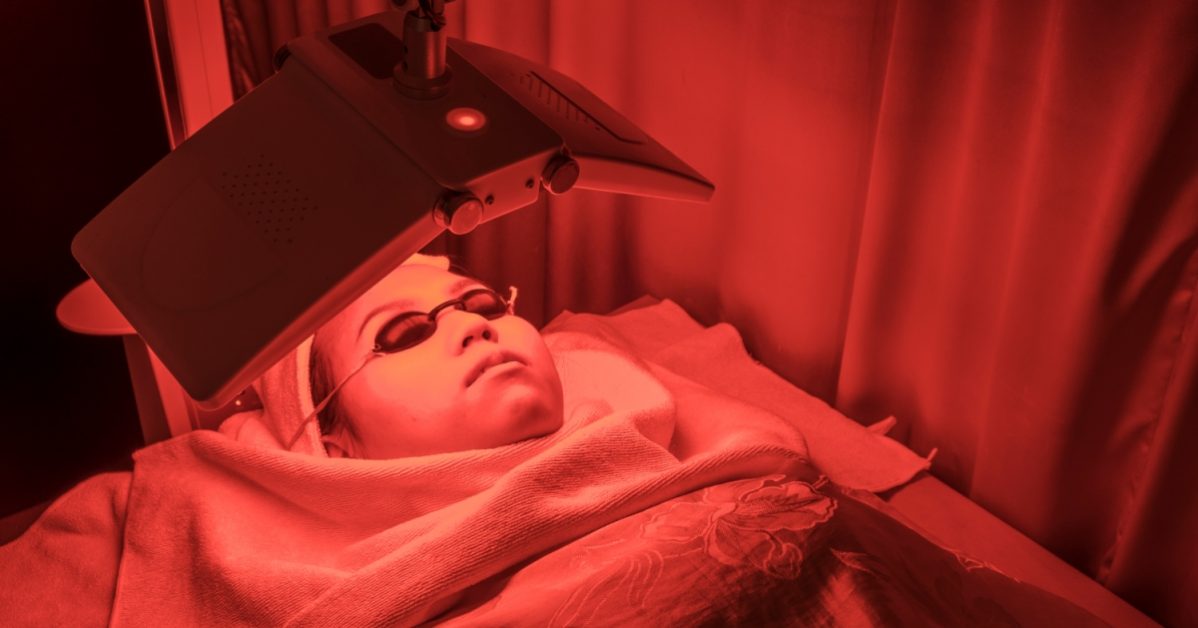
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an innovative two-stage treatment that uses light energy to activate a nontoxic photosensitizer, which then selectively destroys cancerous and precancerous cells.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
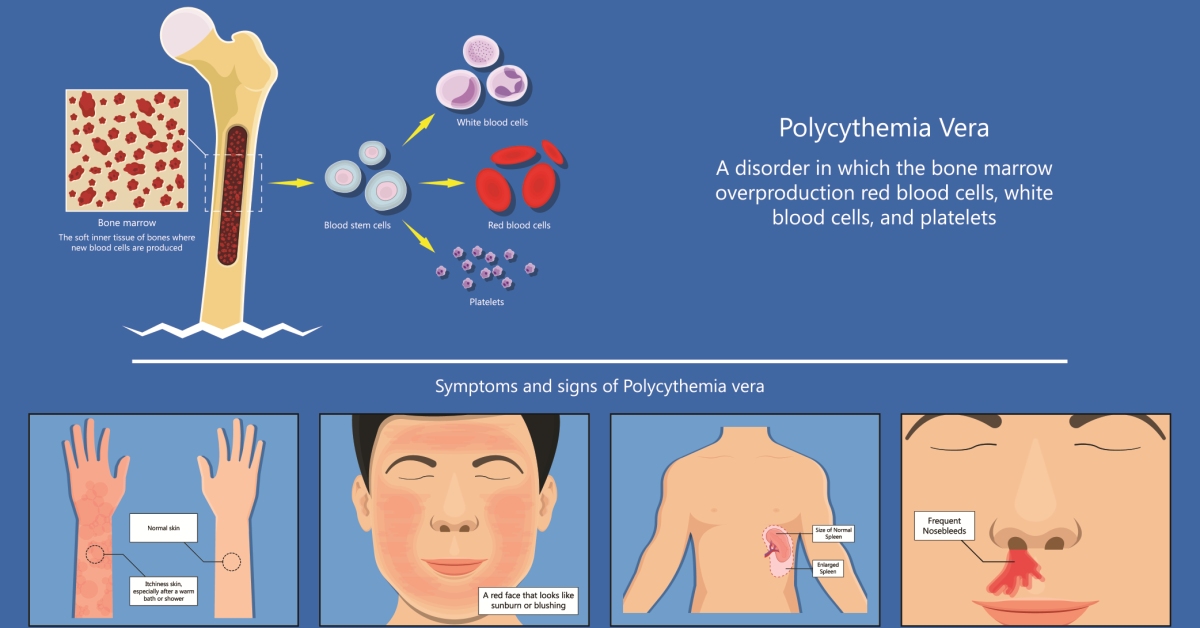
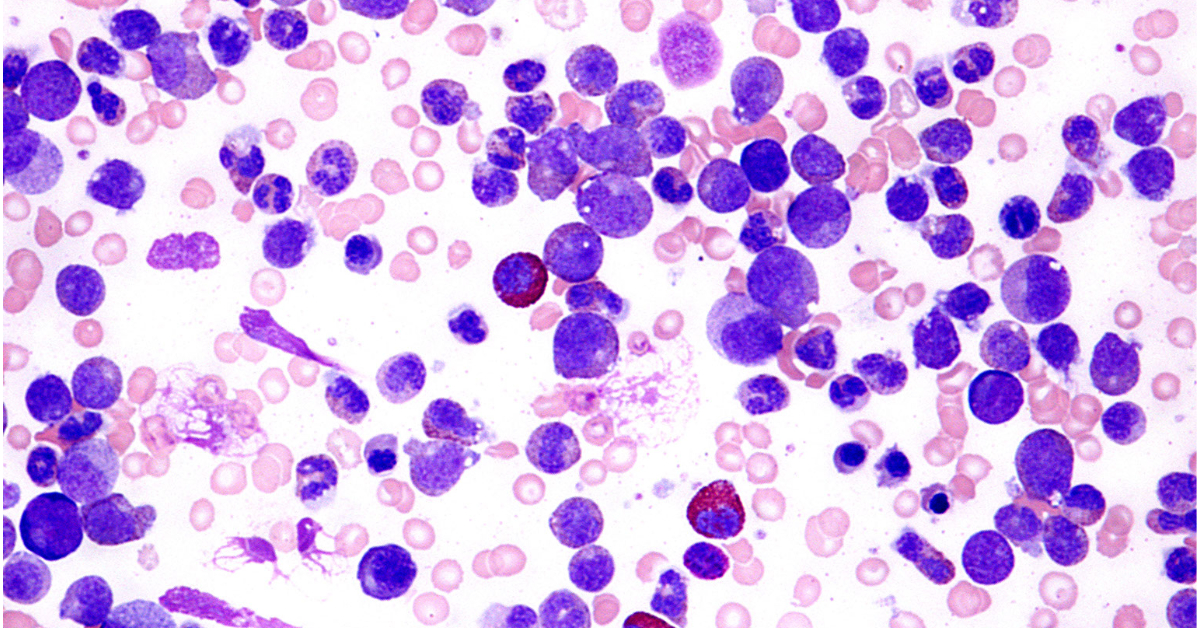
Bone marrow cancer refers to various malignancies affecting the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced.
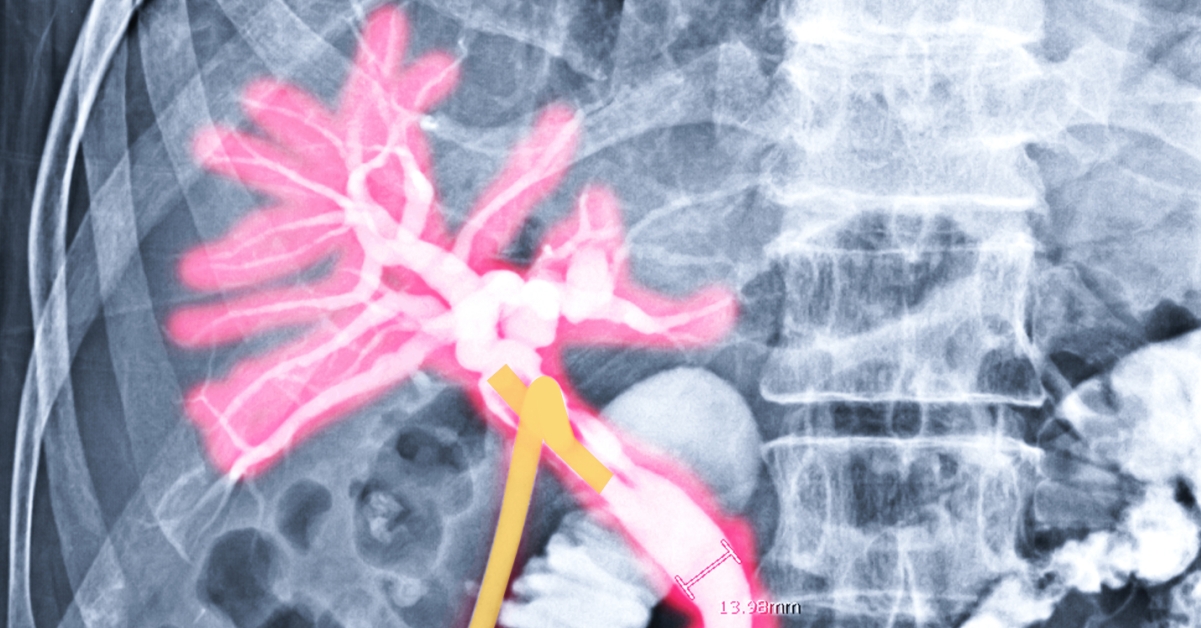
A cholangiogram is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to visualize the bile ducts, helping to identify blockages, strictures, or other abnormalities.
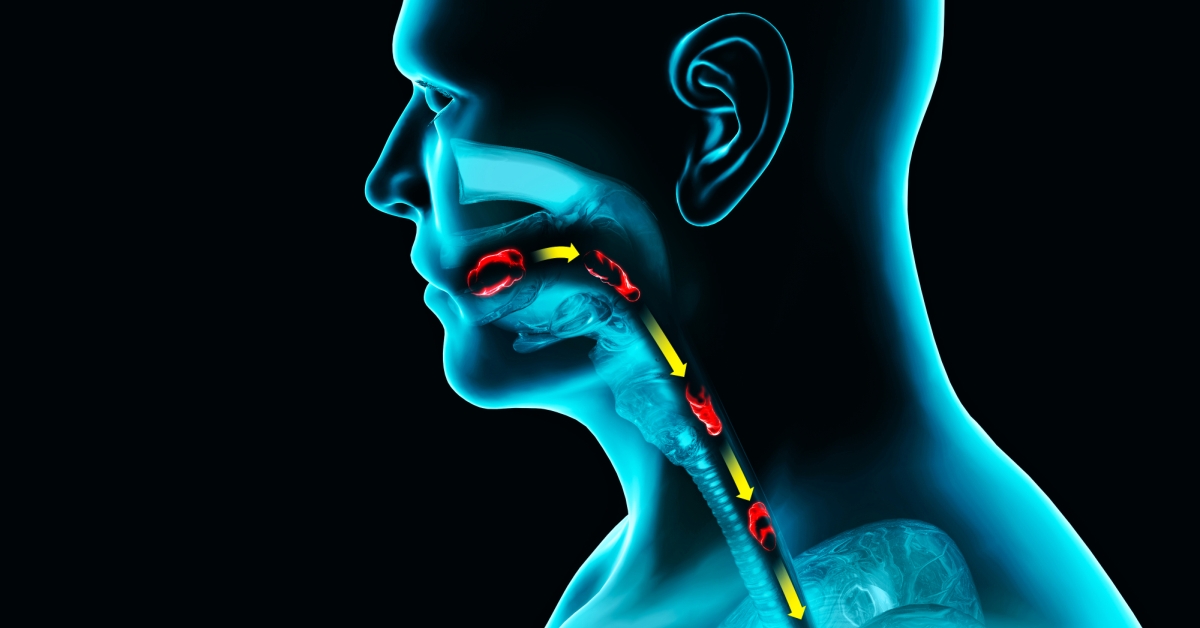
Choanal atresia is a congenital condition characterized by the incomplete formation of the nasal passages, leading to a blockage that can affect breathing.
Chiari malformation is a structural abnormality in the brain where the lower part of the brain, called the cerebellum, extends into the spinal canal.
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition of the cervical spine characterized by the wear and tear of cartilage and discs, leading to neck pain and stiffness.
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition caused by the compression or irritation of nerves in the cervical spine, often resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness that radiates down the arm.

Cervical dystonia is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions in the neck, causing twisting and abnormal postures.
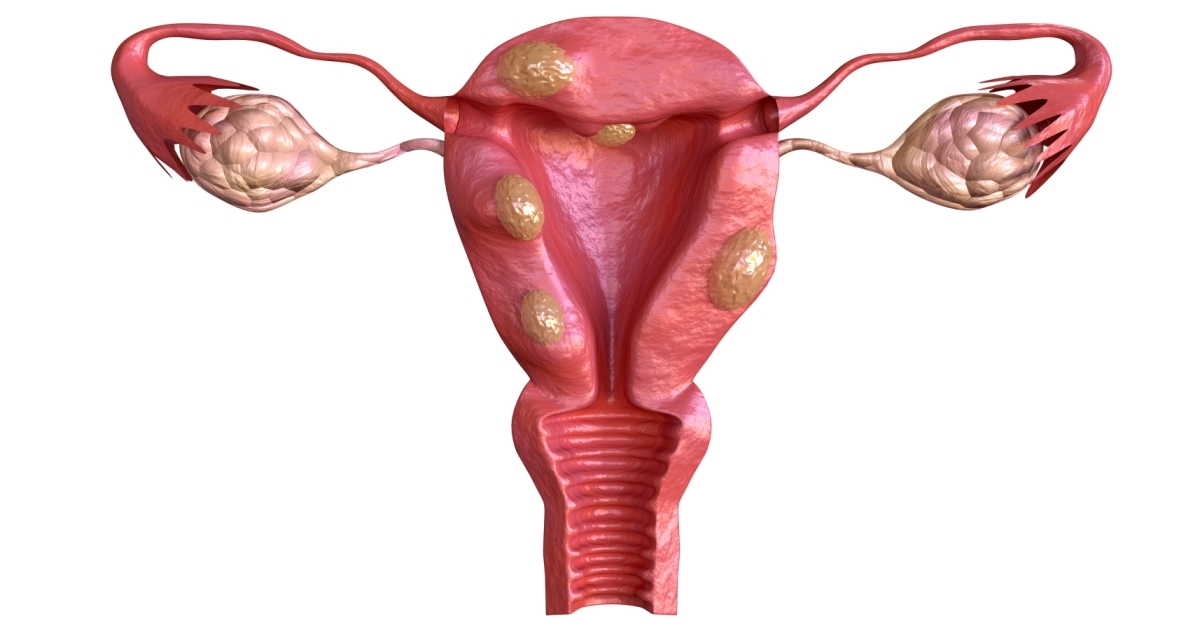
Cervical dysplasia is a condition characterized by abnormal cell changes on the surface of the cervix, often detected through routine screenings.
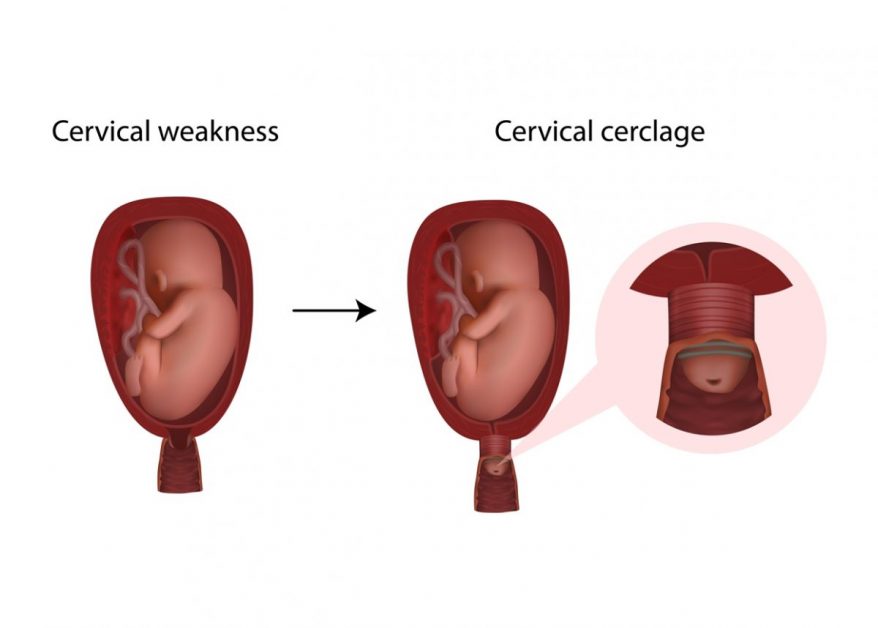
Cervical cerclage is a surgical procedure used to support the cervix during pregnancy, typically performed in women with a history of cervical insufficiency.

Cerebrovascular disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting blood flow to the brain, including stroke, transient ischemic attacks, and vascular malformations.
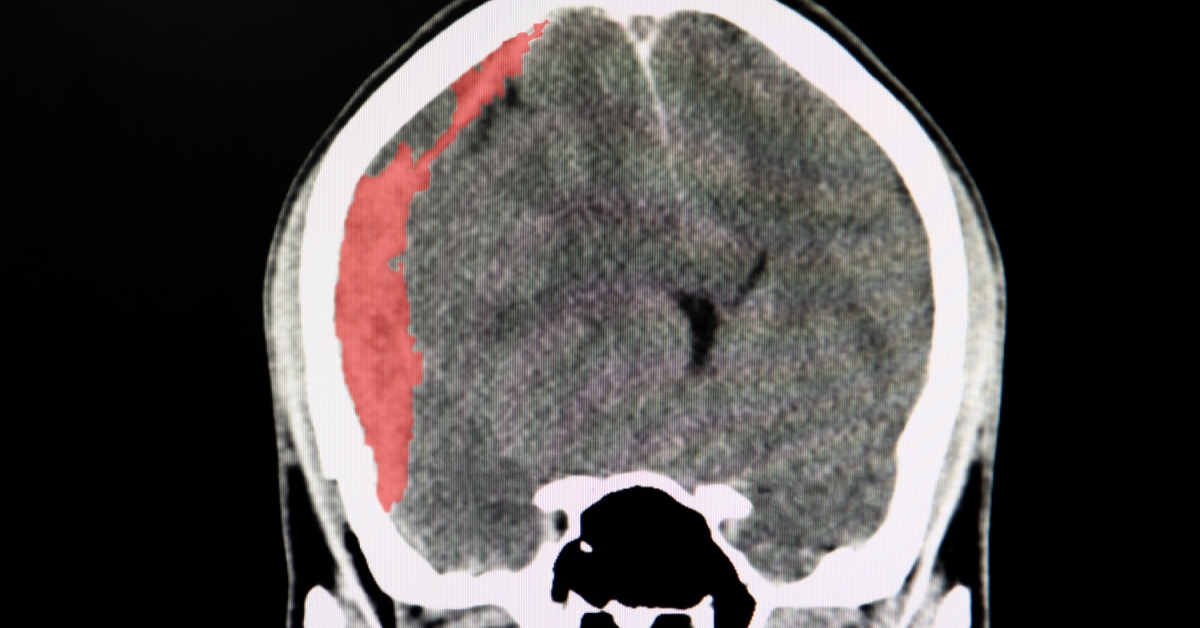
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs when the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord escapes due to a tear or hole in the protective membranes.
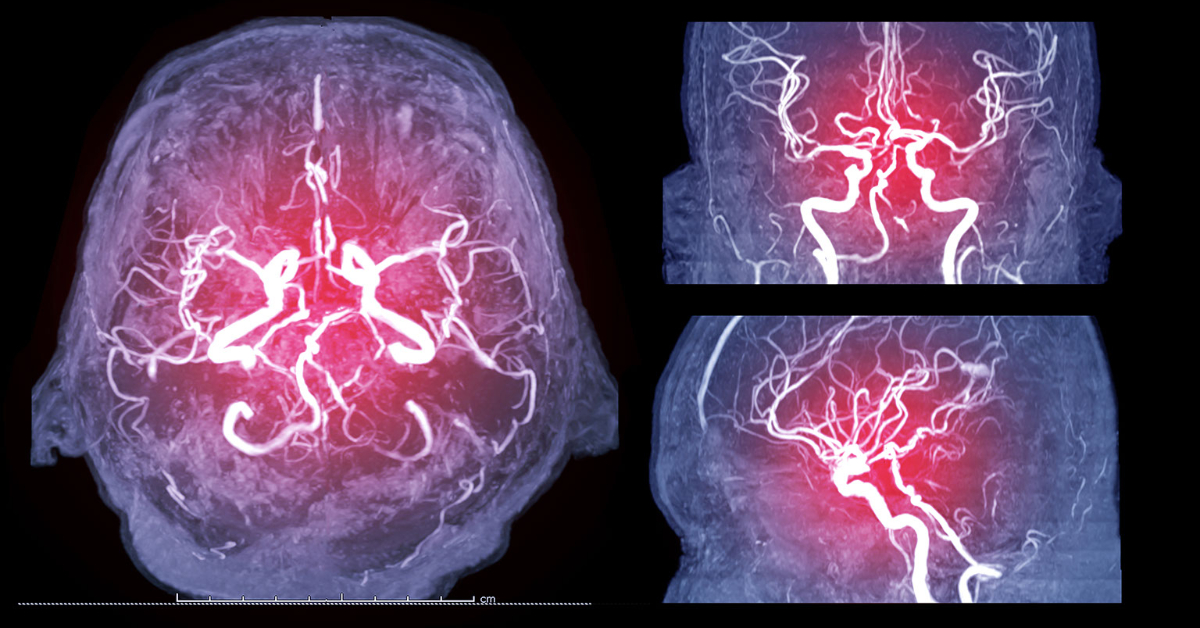
A cerebral angiogram is a specialized imaging procedure used to visualize blood vessels in the brain.

Central Cord Syndrome is a neurological condition resulting from damage to the central part of the spinal cord, often characterized by weakness and loss of sensation in the arms more than the legs.

Castleman disease is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by the abnormal growth of lymphoid tissue, which can lead to enlarged lymph nodes and various systemic symptoms.
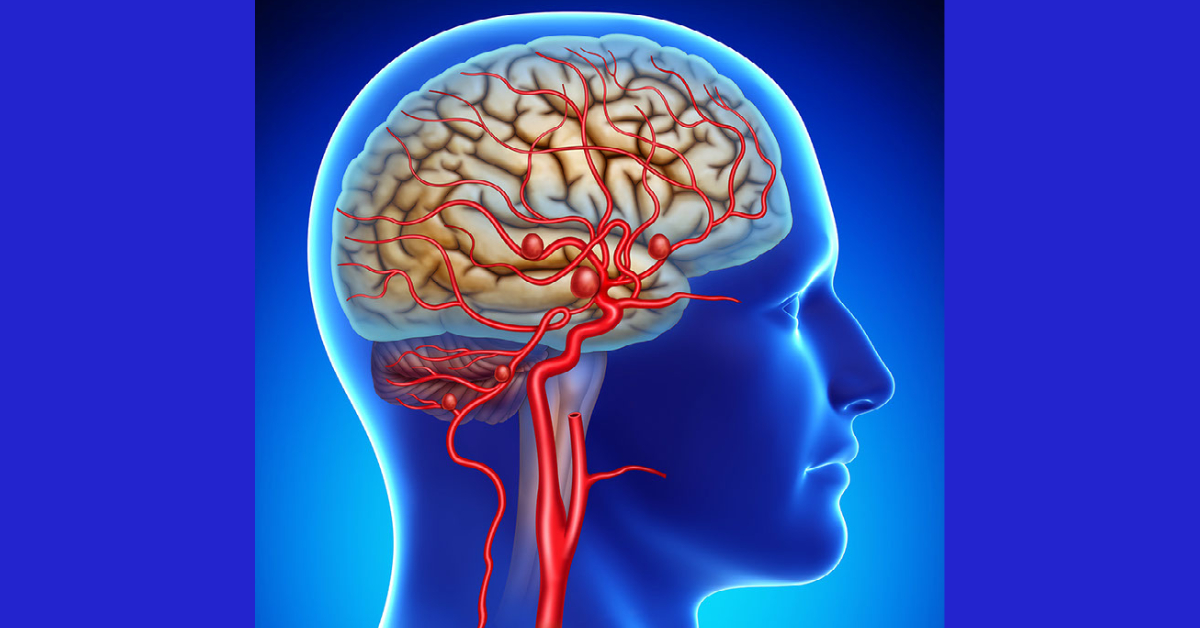
Carotid artery surgery, often referred to as carotid endarterectomy, involves removing plaque buildup from the carotid arteries to restore blood flow to the brain.
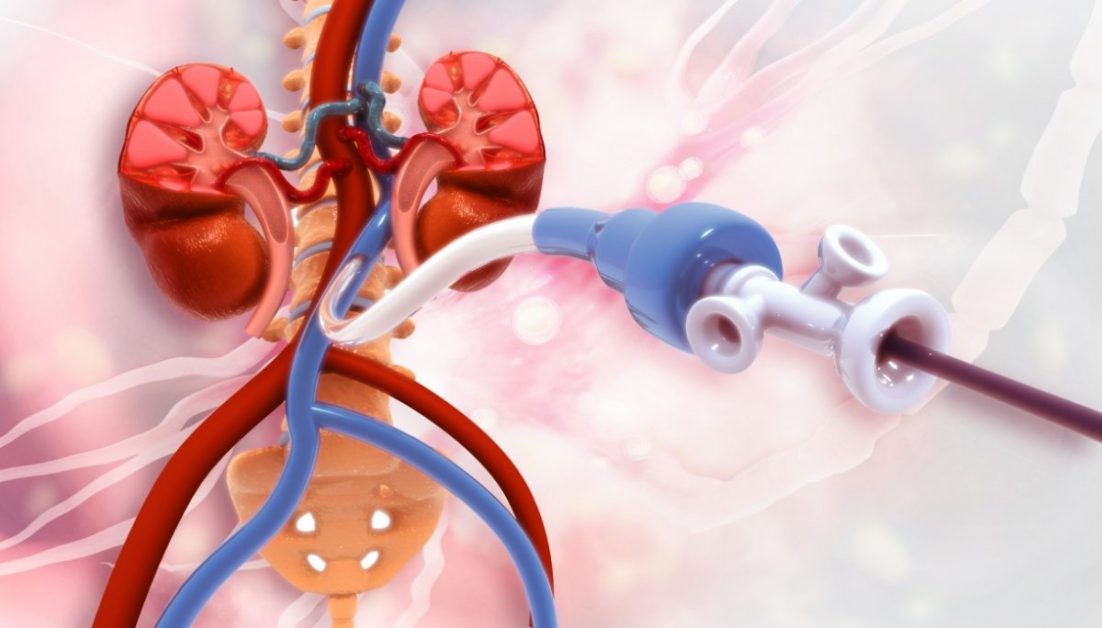
Carotid angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at widening narrowed carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain.
Cardiomyoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to enhance heart function by using skeletal muscle to support the weakened heart muscle.
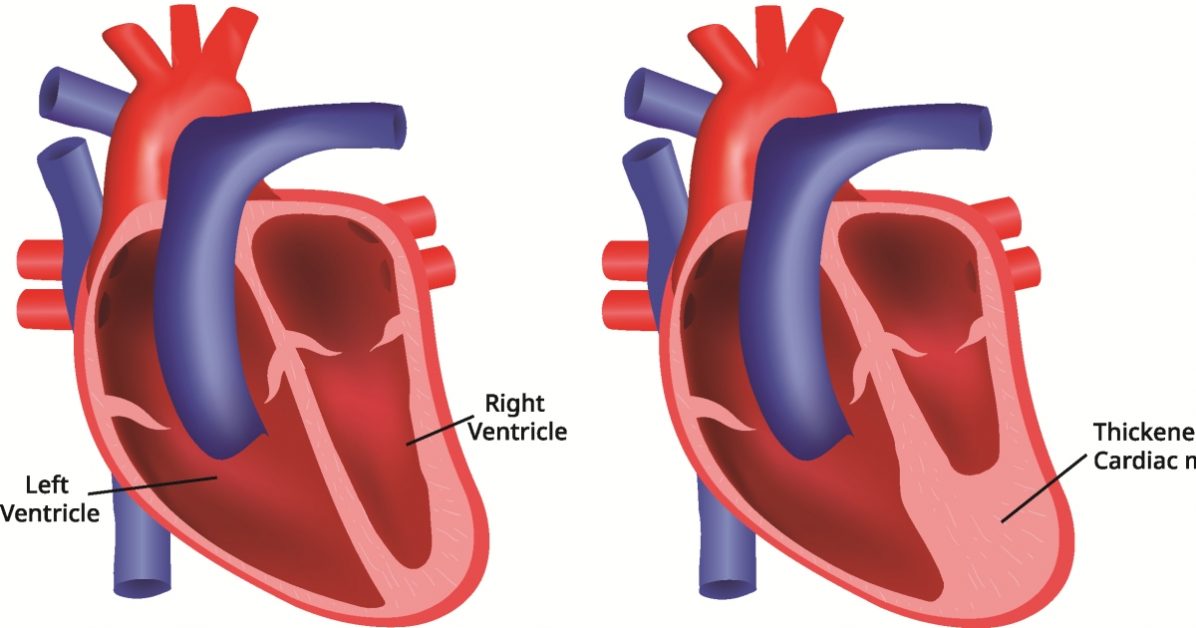
Cardiomyopathy is a condition that affects the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively. This can lead to various complications, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and increased risk of stroke.
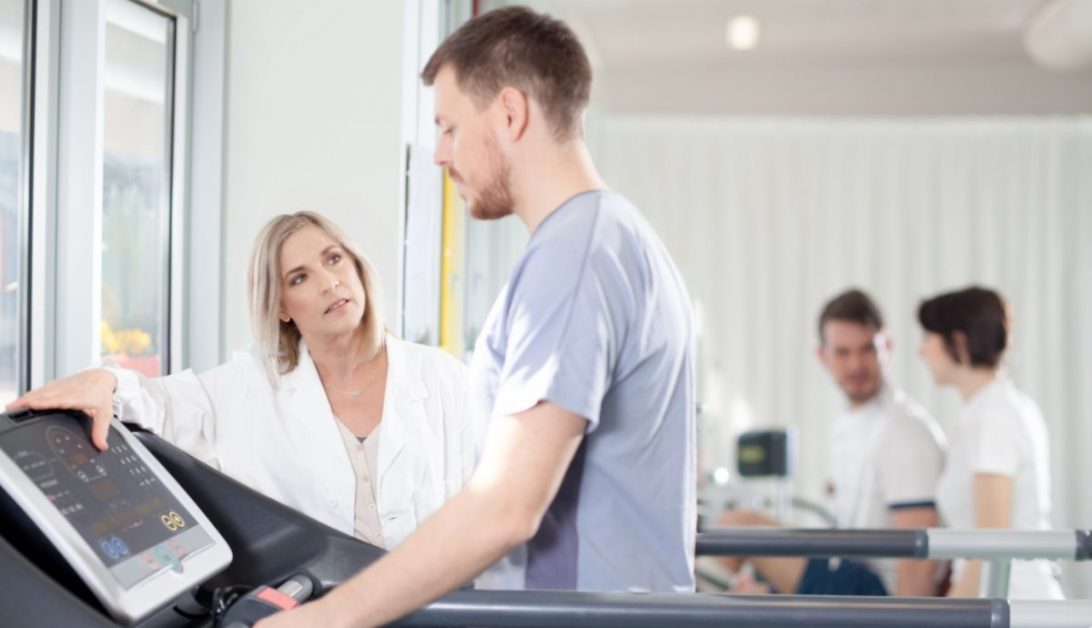

Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program designed to improve heart health after a cardiac event or surgery.
Central Auditory Processing Disorder (CAPD) is a condition that affects the brain’s ability to process and interpret auditory information.
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary (CUP) is a type of cancer where metastatic tumors are detected, but the primary tumor site remains unidentified.
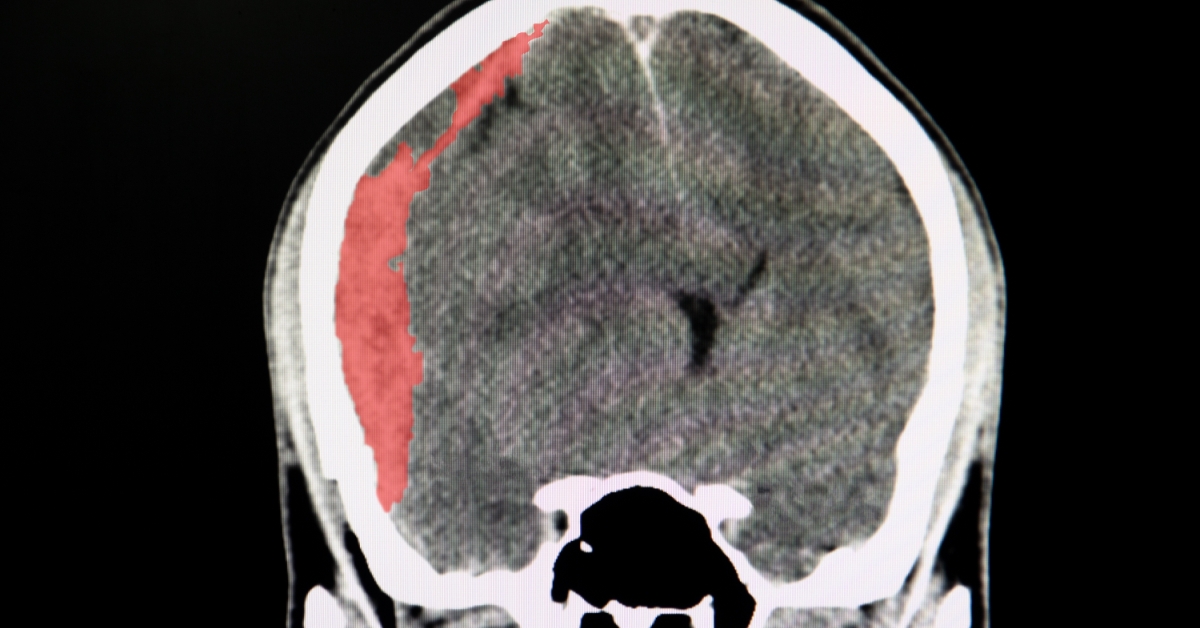
CADASIL (Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the degeneration of small blood vessels in the brain, primarily due to mutations in the NOTCH3 gene.
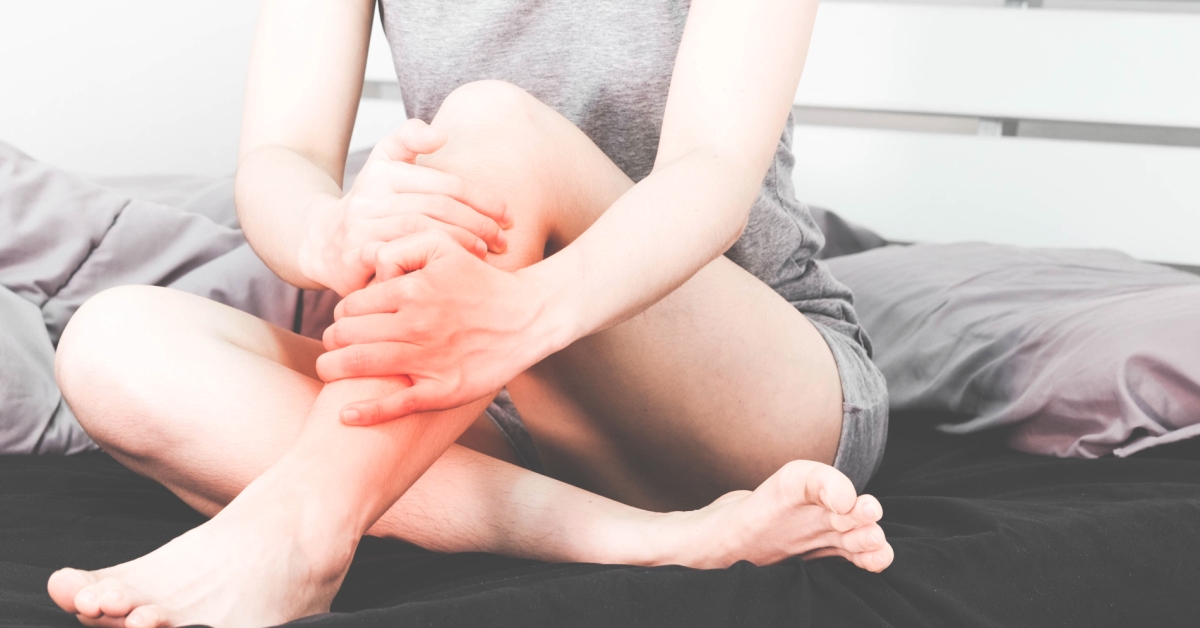

Bursitis is the inflammation of small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion joints, often causing pain and restricted movement.
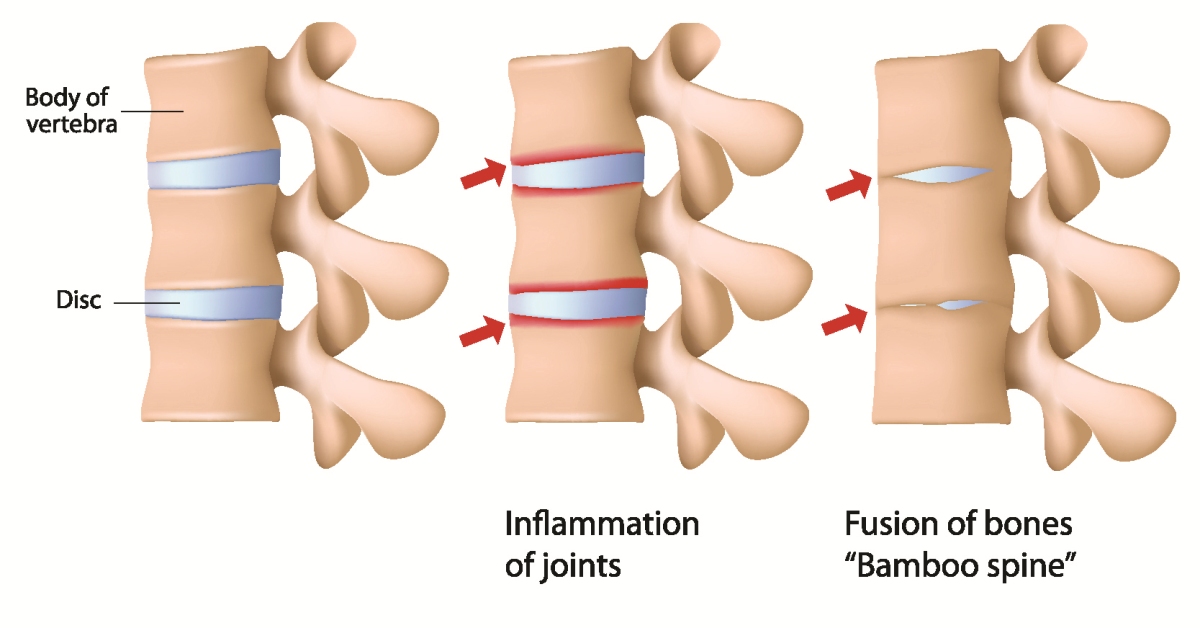
A bulging disk occurs when an intervertebral disk protrudes beyond its normal boundary, often due to age-related degeneration, injury, or repetitive stress.
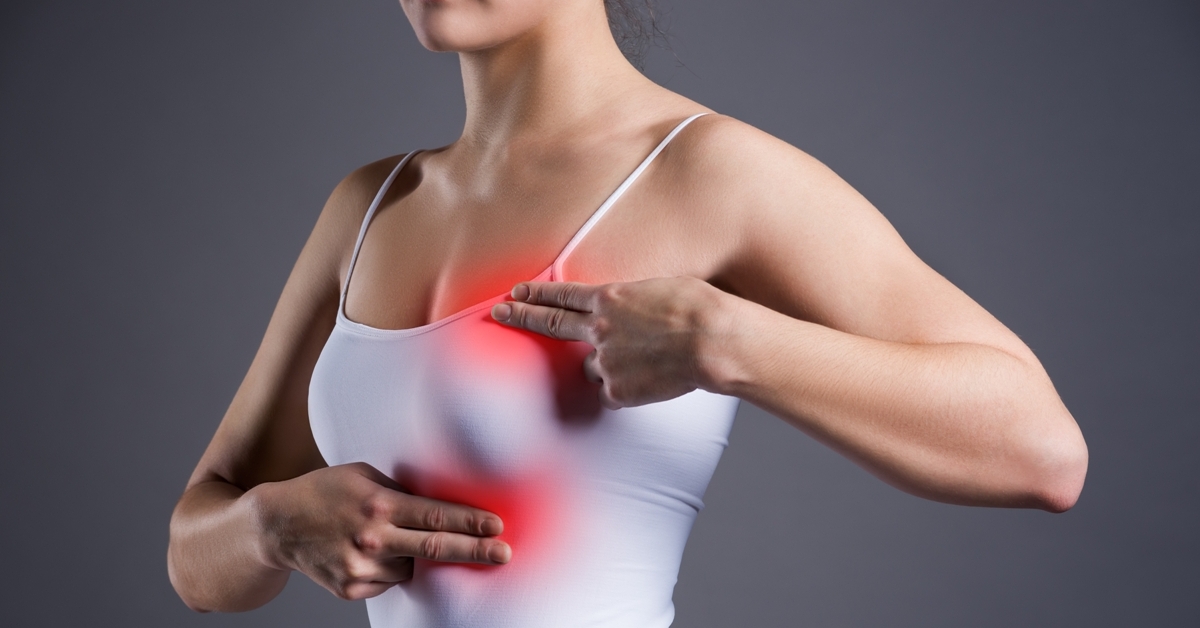

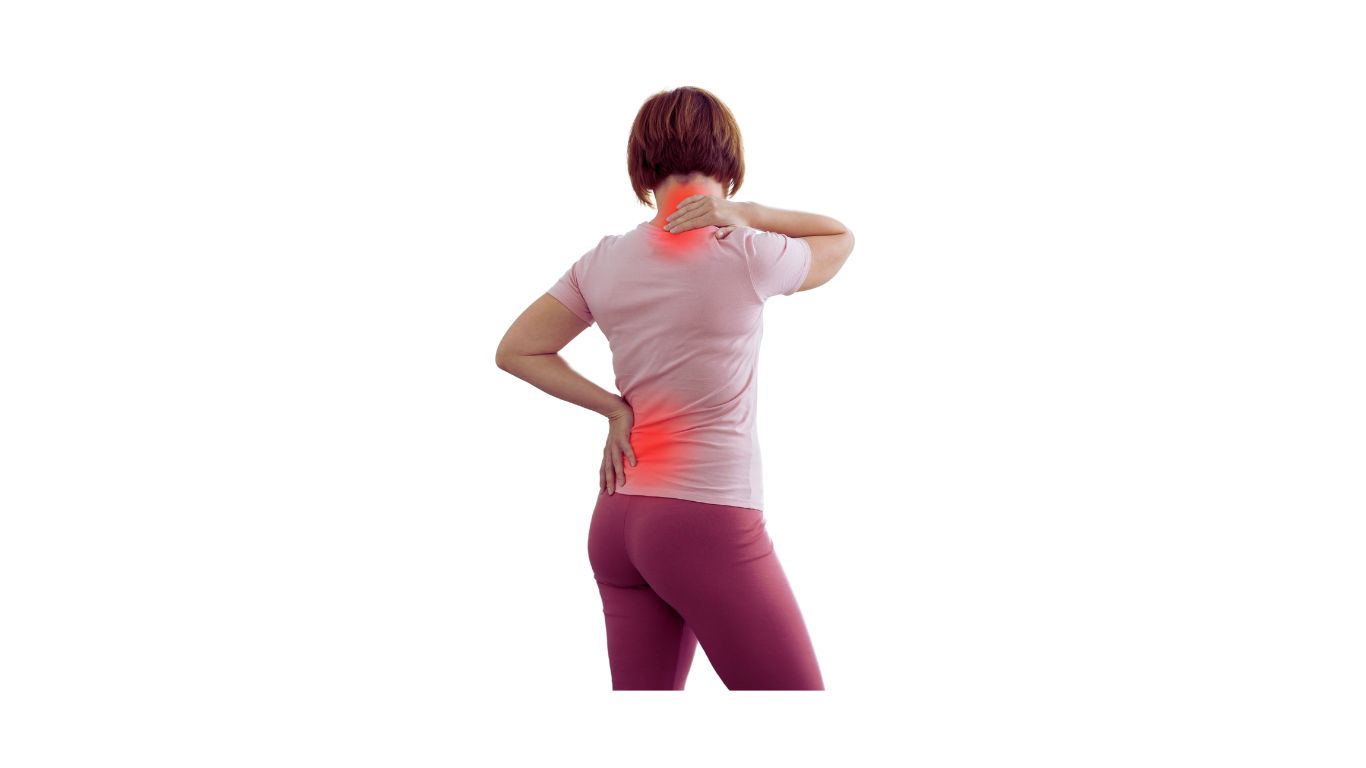
Breast pain, or mastalgia, is a common condition that can affect individuals of all ages. It may result from hormonal changes, such as those occurring during the menstrual cycle, or from factors like injury, infection, or certain medical conditions.
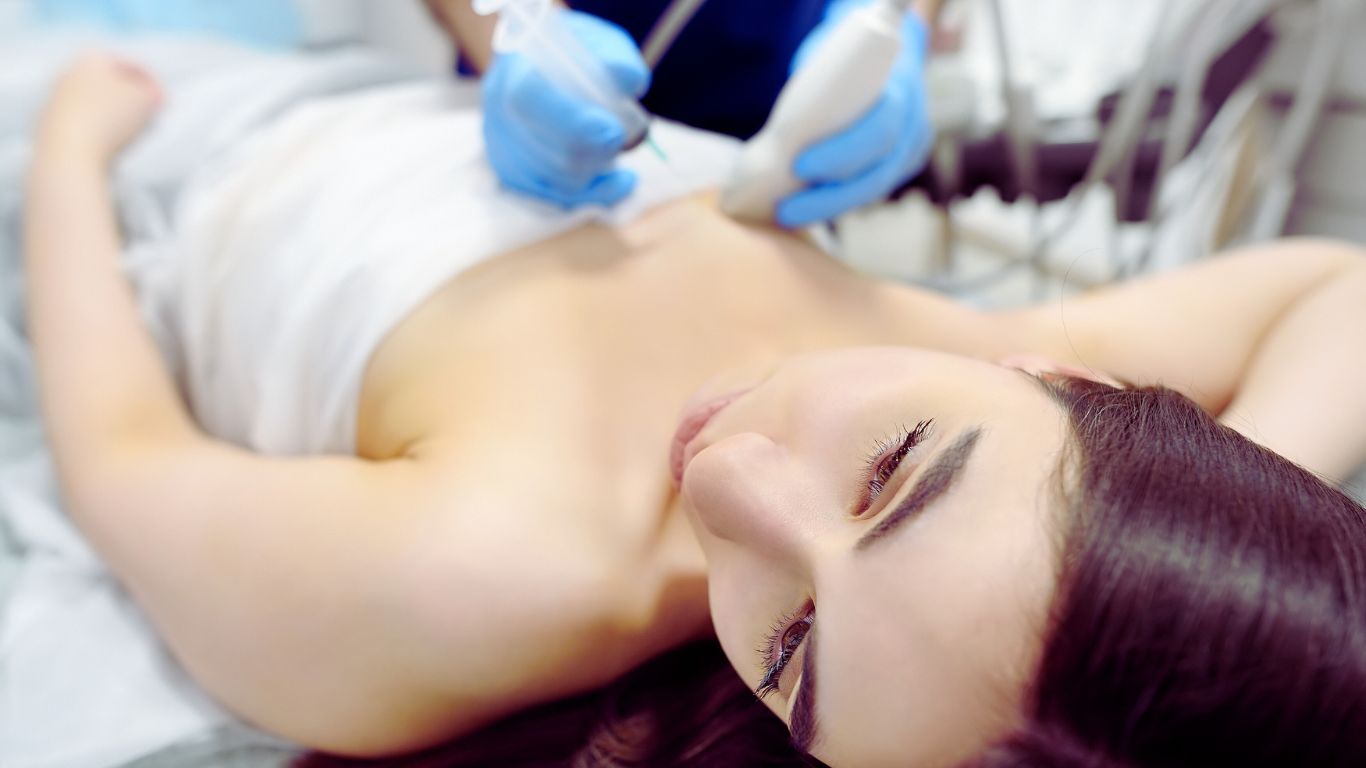
A breast biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of breast tissue is removed for examination under a microscope.
Chat on WhatsApp!
*Please note: As of now, we are only assisting international patients who plan to come to India for medical treatment.