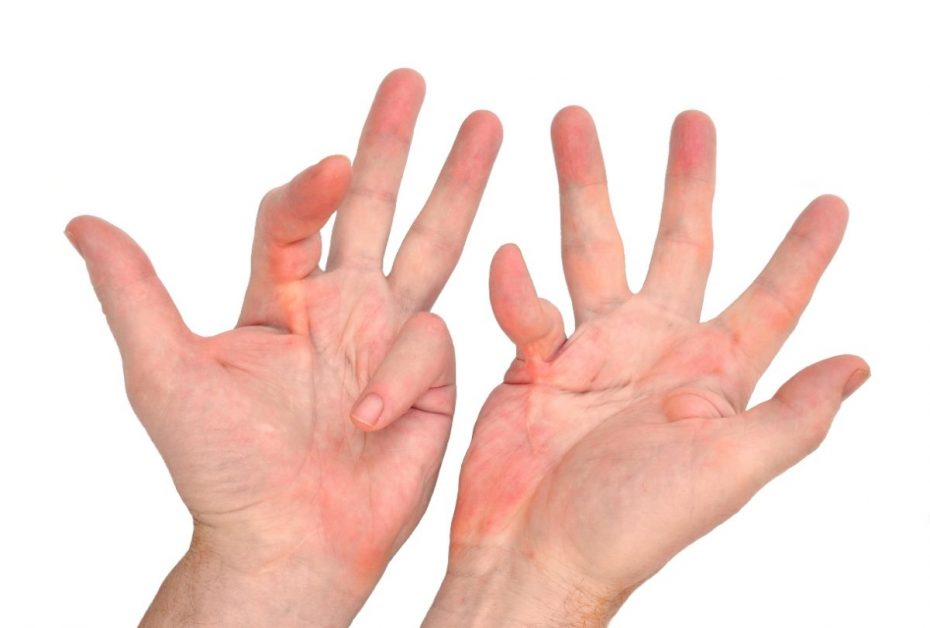

Dupuytren’s Contracture
Dupuytren’s Contracture is a condition where one or more fingers bend toward the palm due to thickening and shortening of the connective tissue in the hand.

Dupuytren’s Contracture is a condition where one or more fingers bend toward the palm due to thickening and shortening of the connective tissue in the hand.
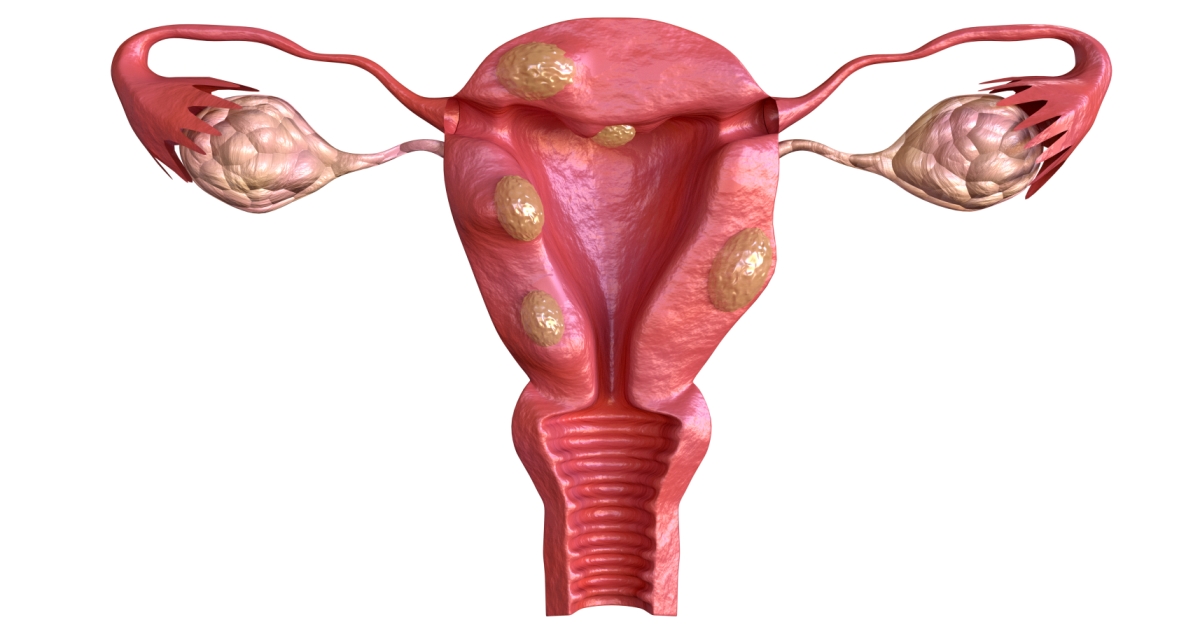
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years.
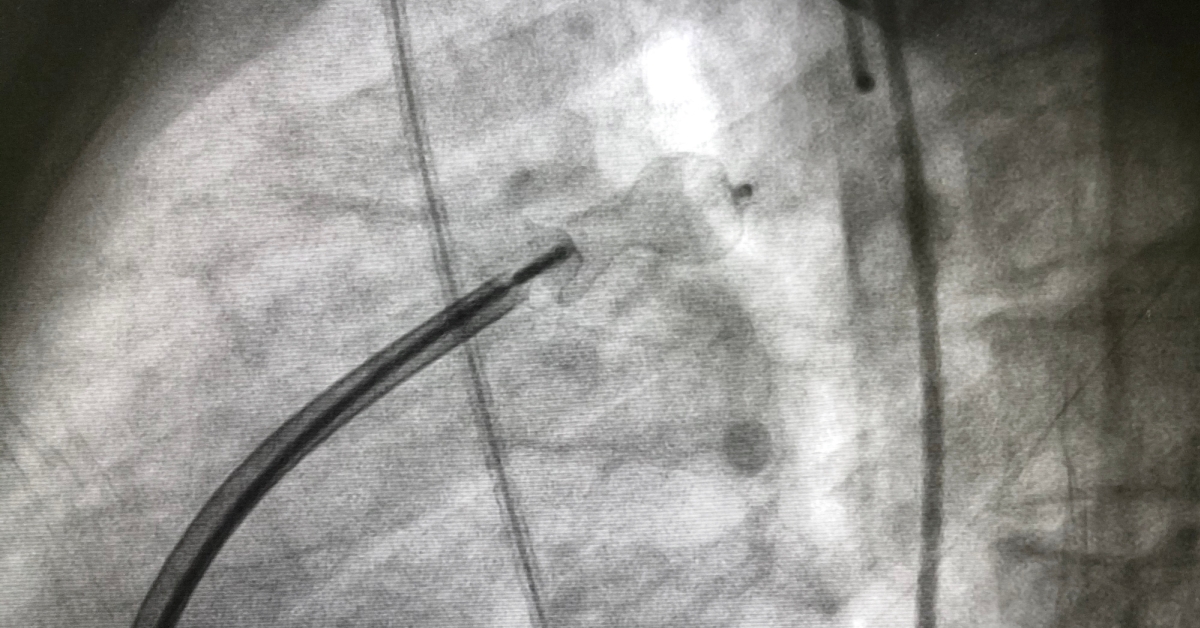
: Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth, potentially leading to heart complications.
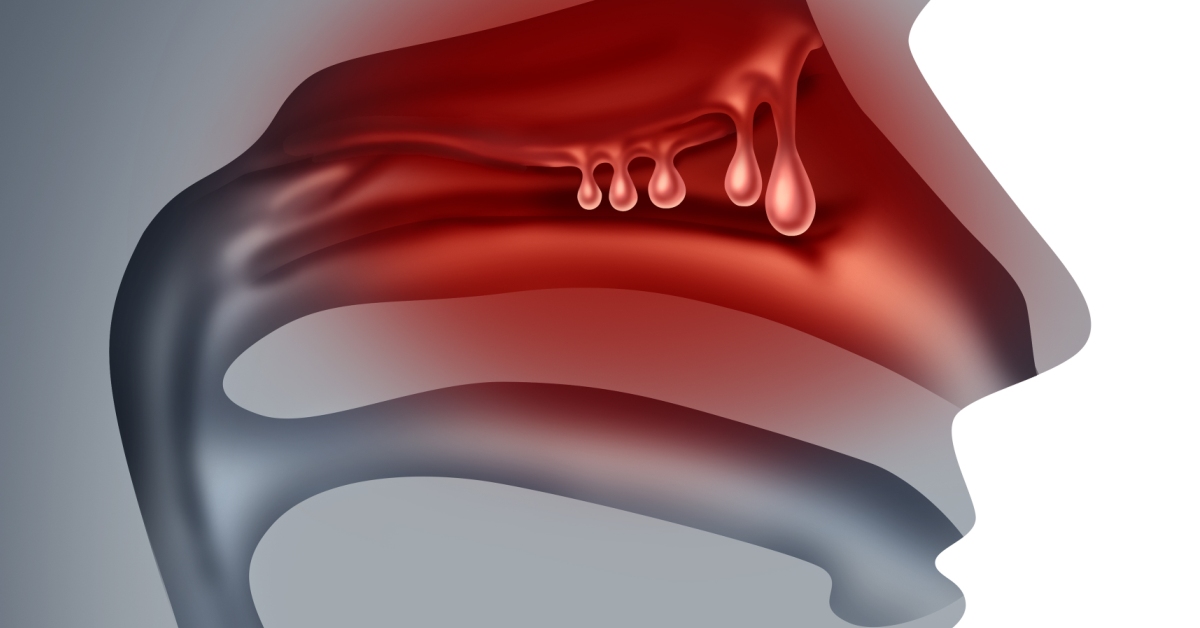
Nasal polyps are soft, noncancerous growths that develop in the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses, often resulting from chronic inflammation.
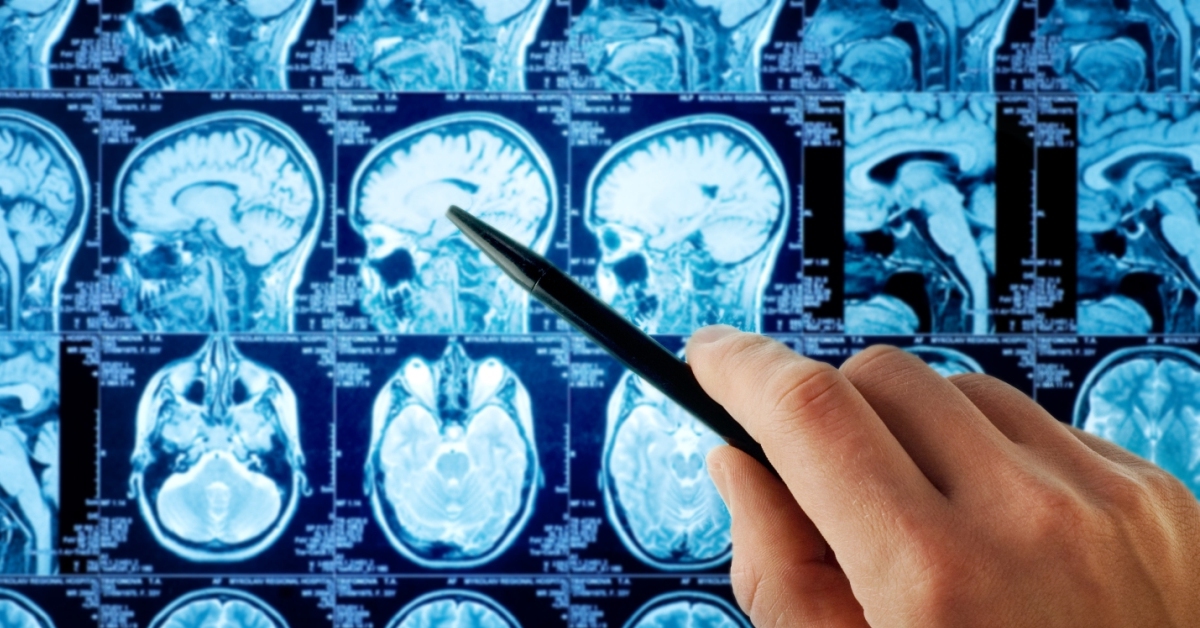
Meningioma is a type of tumor that arises from the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
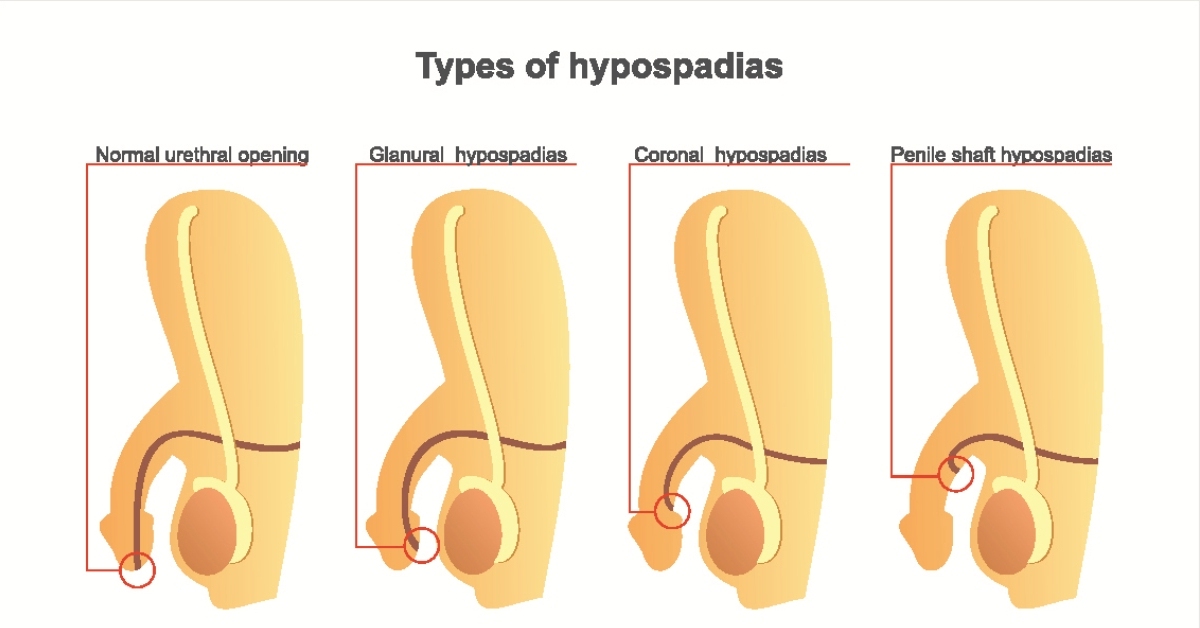
Hypospadias is a congenital condition where the urethral opening is located on the underside of the penis instead of at the tip.
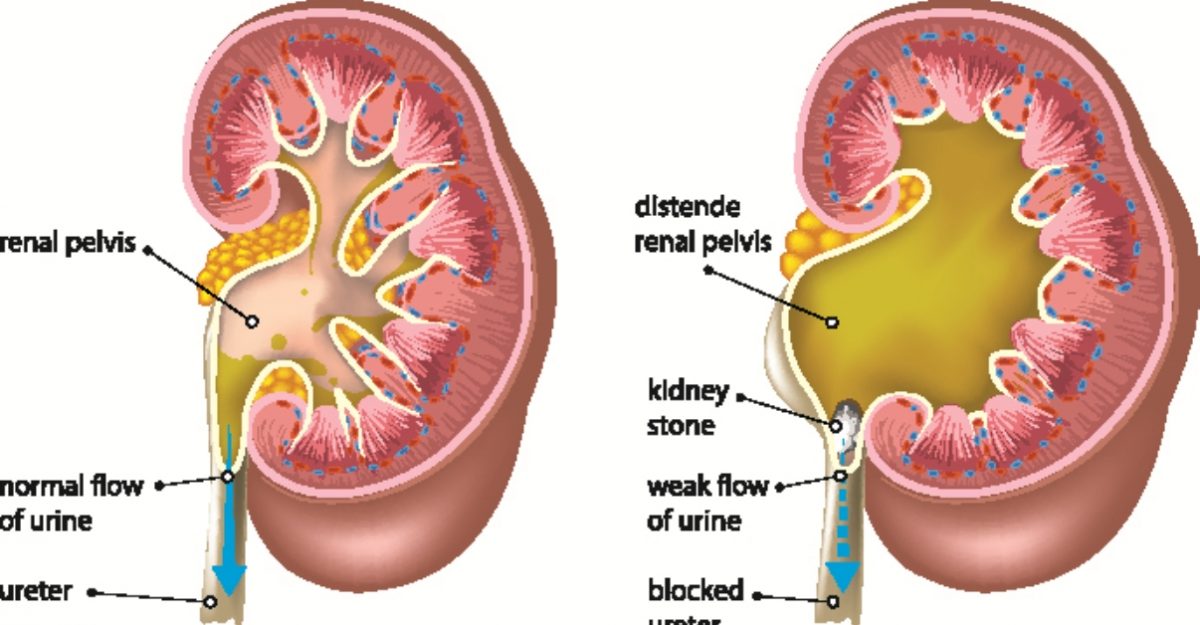
Hydronephrosis is a condition characterized by the swelling of a kidney due to the buildup of urine, often caused by an obstruction in the urinary tract.
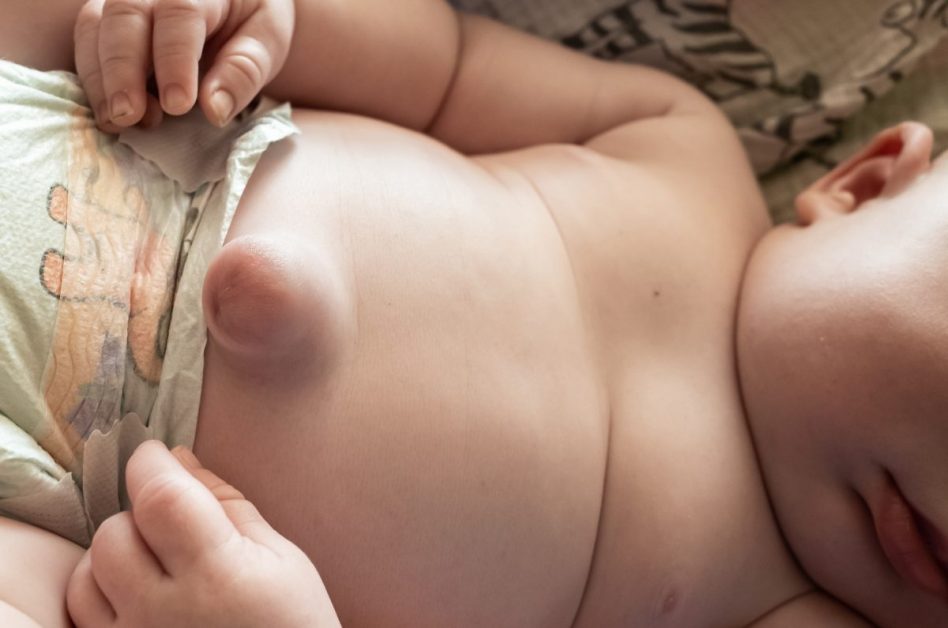

An umbilical hernia occurs when tissue protrudes through an opening in the abdominal muscles near the belly button, often presenting as a soft lump.
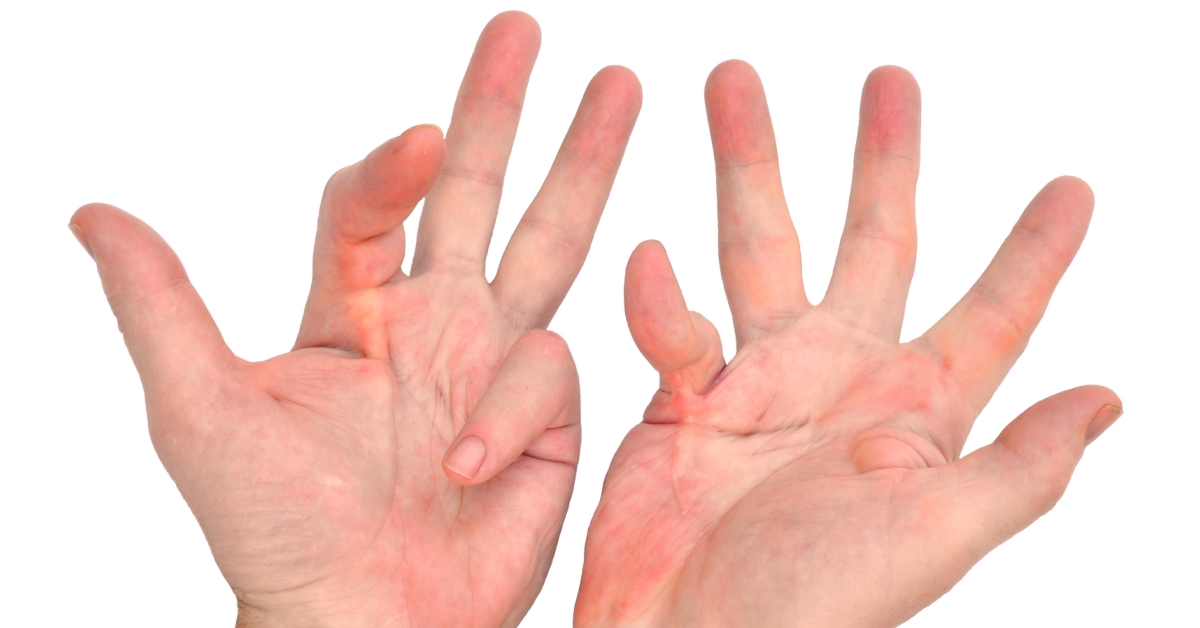

Trigger Finger is a condition characterized by the catching or locking of a finger or thumb in a bent position due to inflammation of the tendons.
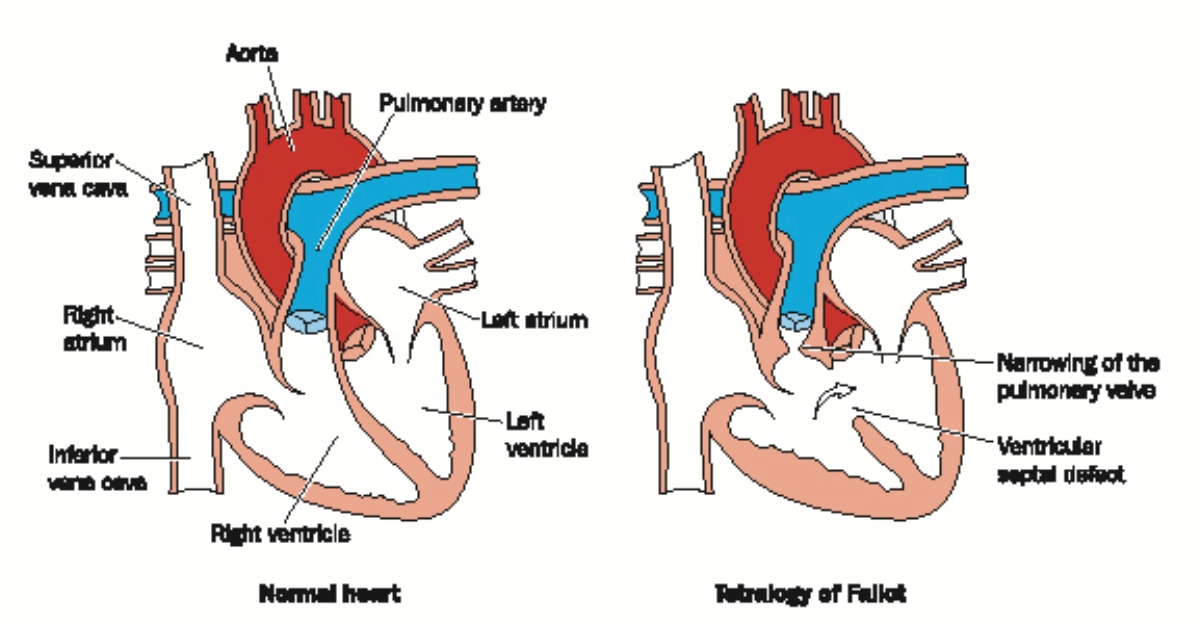
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific heart malformations that lead to insufficient oxygen in the bloodstream.
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, often caused by viral infections, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to certain toxins.
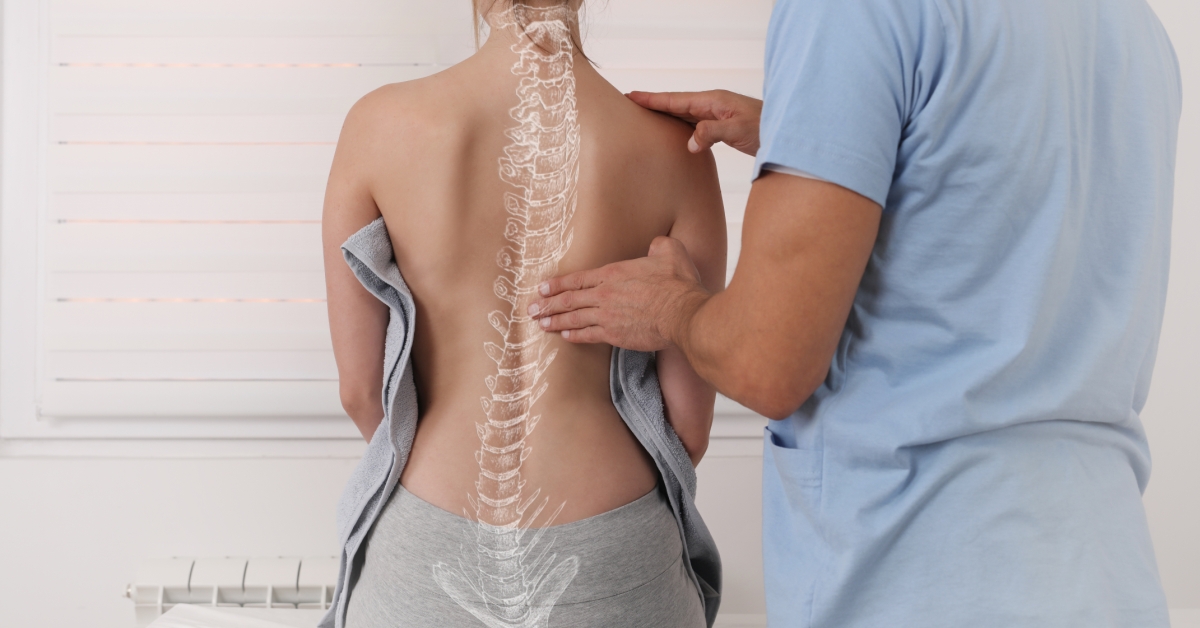
Kyphosis is a condition characterized by an excessive outward curvature of the spine, leading to a hunched back appearance.

An ear infection, or otitis media, occurs when germs infect the middle ear, often causing pain, fever, and irritability.
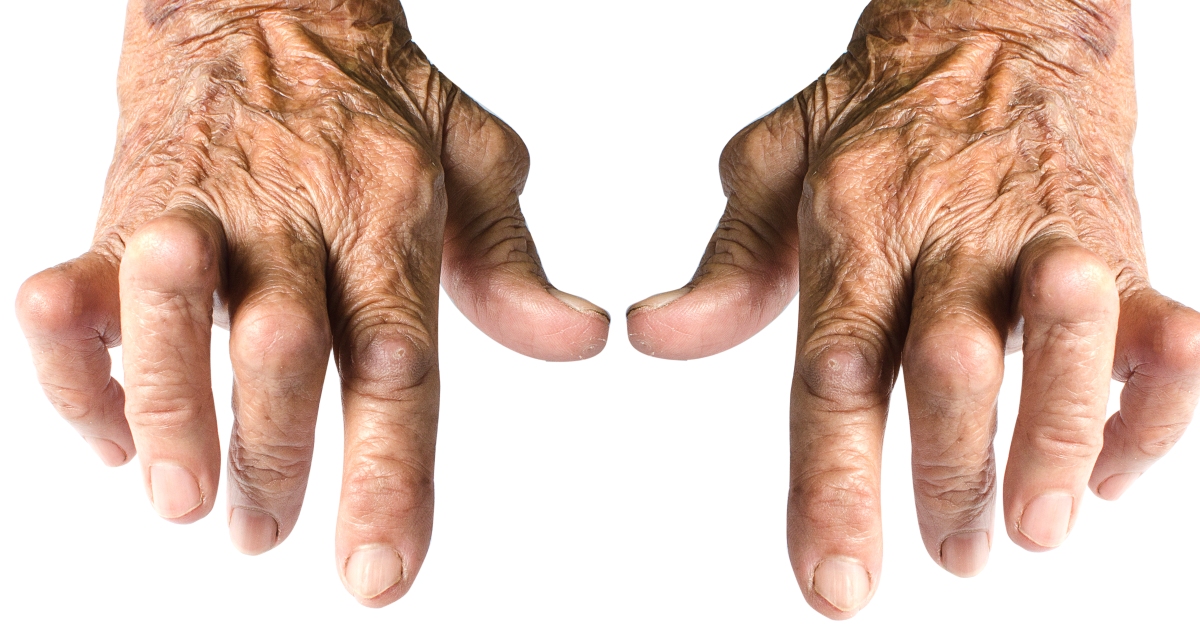
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition resulting from damage to the peripheral nerves, often causing symptoms like pain, tingling, and weakness in the limbs.
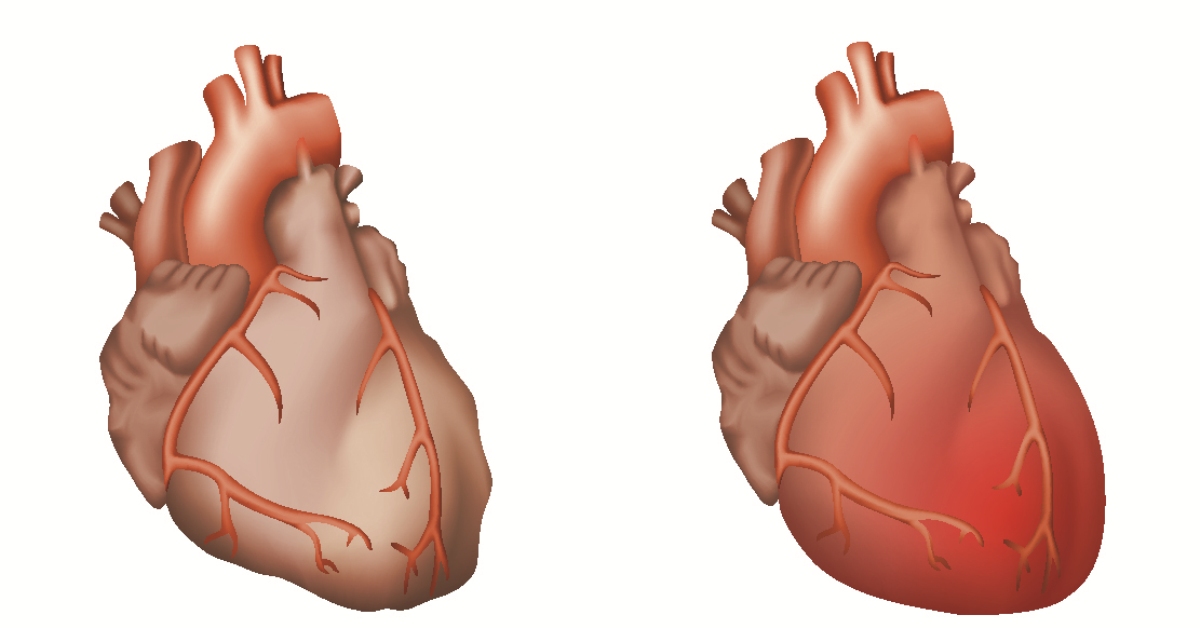
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart, often leading to chest pain and discomfort.
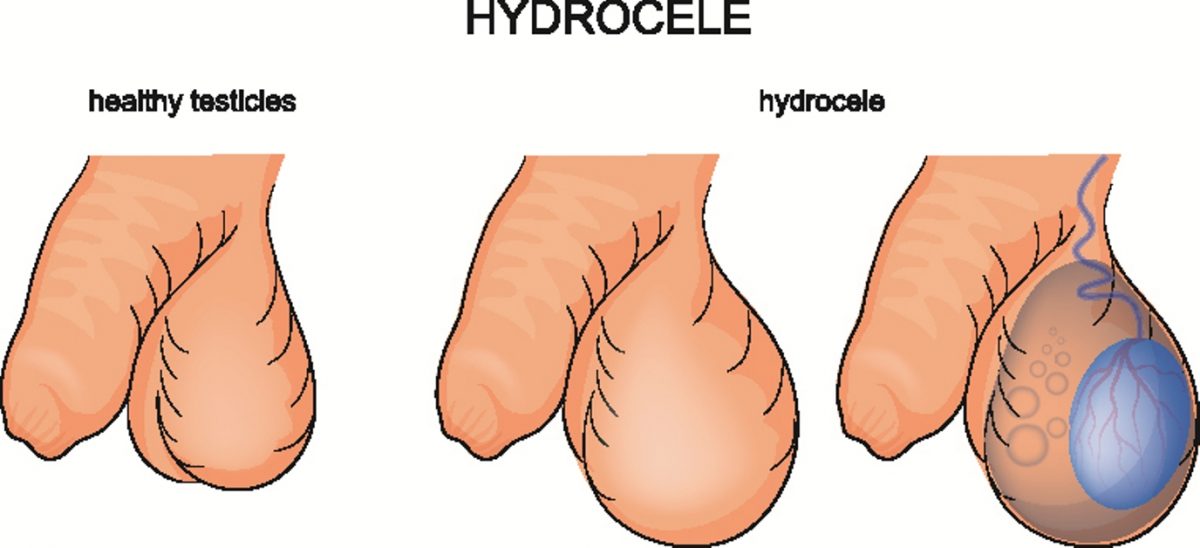
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac surrounding a testicle, often causing swelling in the scrotum.
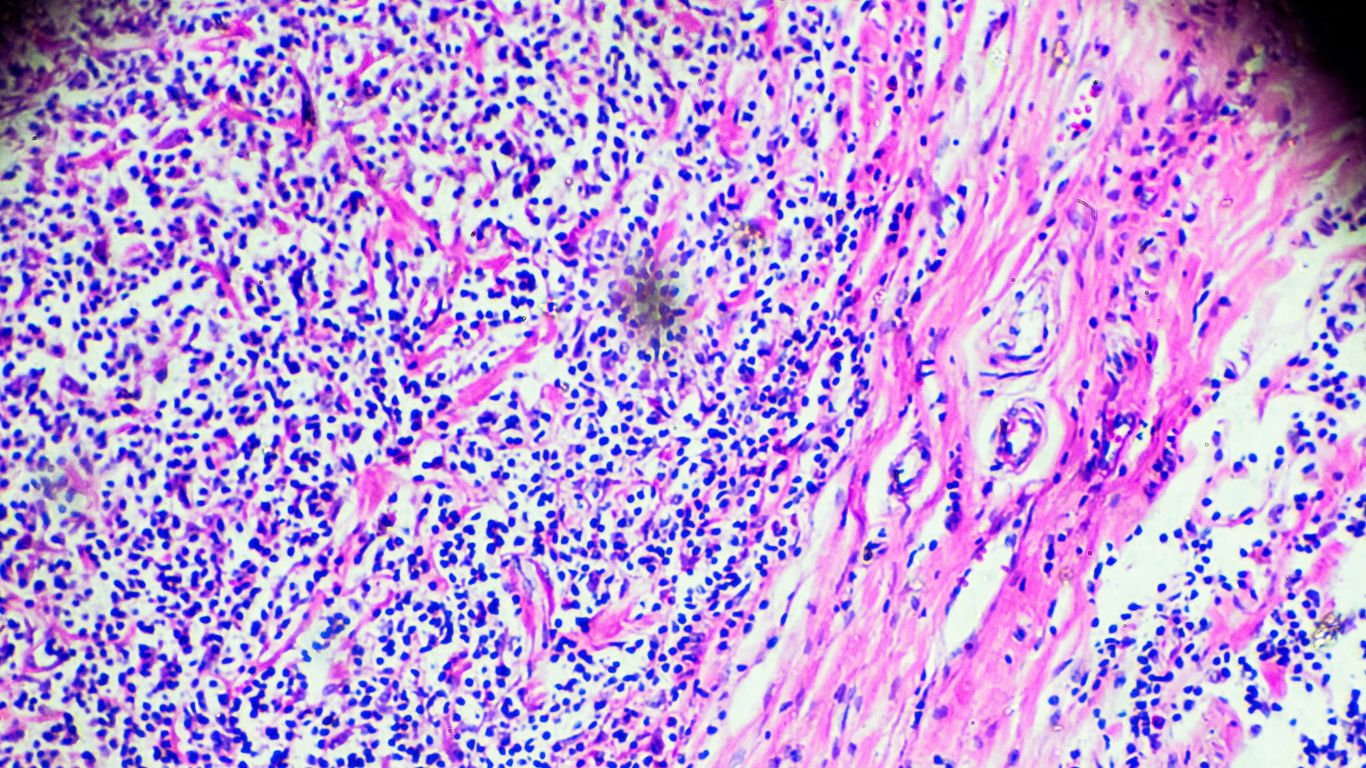
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (HL) is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells.
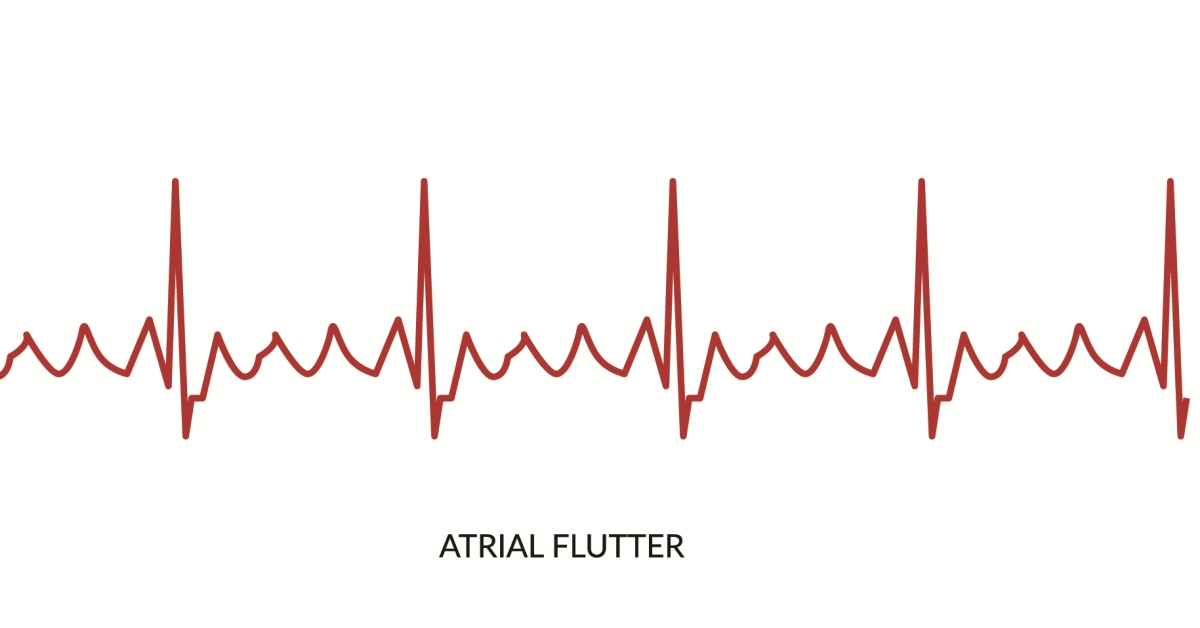
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a fast, abnormal heart rhythm originating from the ventricles, which can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
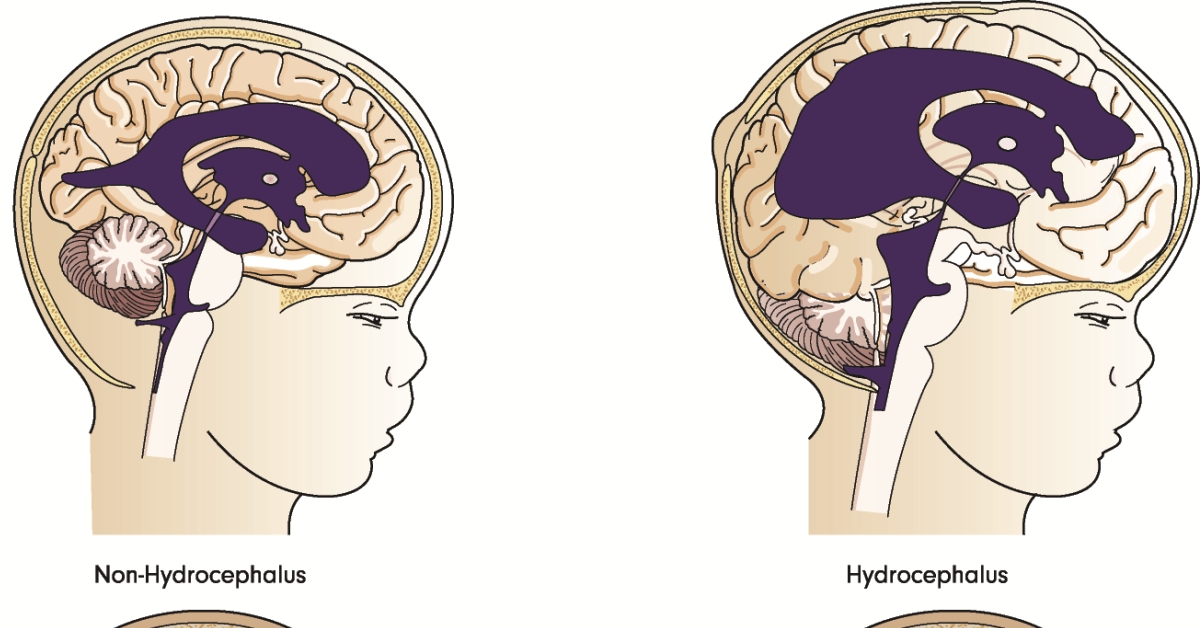
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain’s ventricles, leading to increased intracranial pressure.
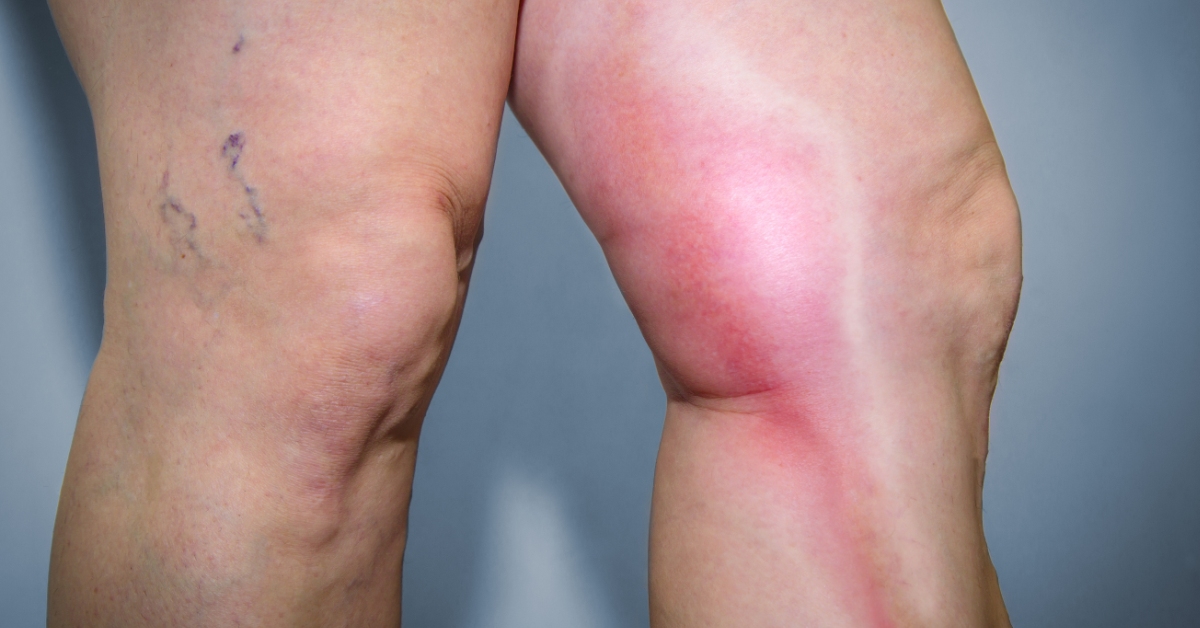
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs, which can lead to swelling, pain, and serious complications if not treated.
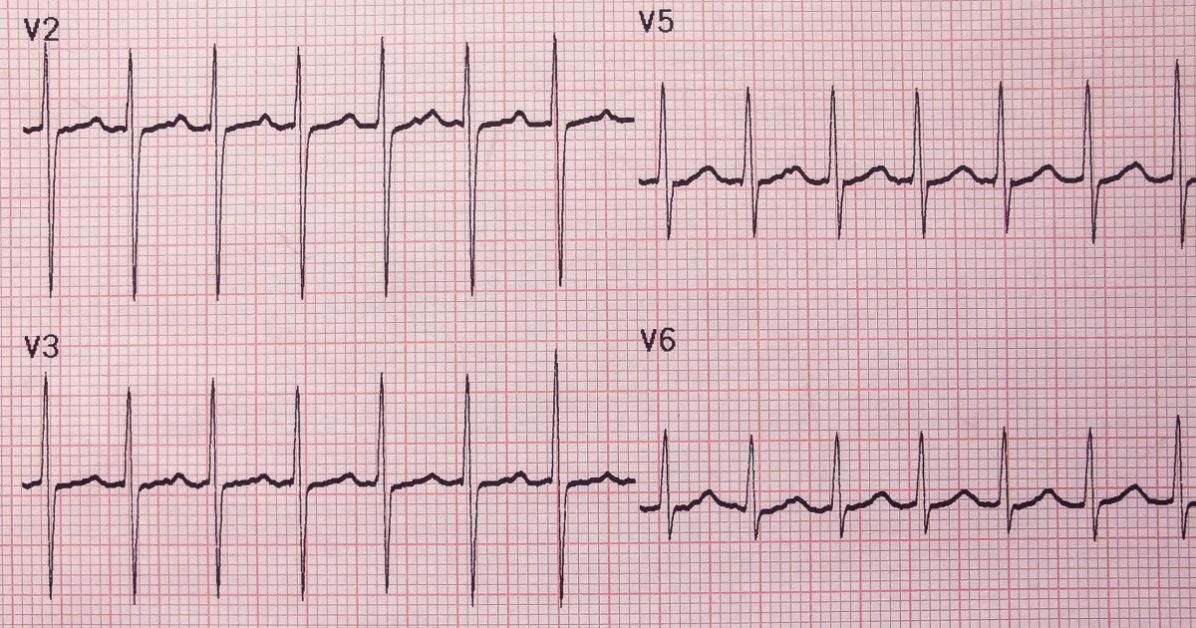
Tachycardia is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, typically exceeding 100 beats per minute, which can lead to various symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
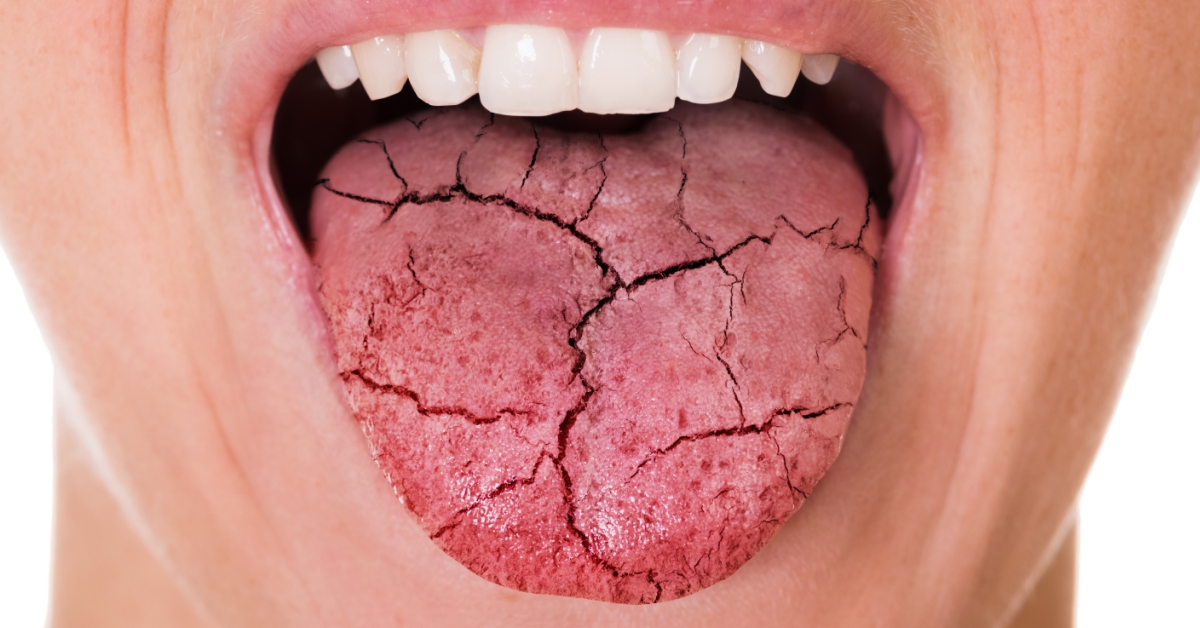
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder characterized by dry mouth and dry eyes due to the body’s immune system attacking the glands that produce saliva and tears.

Laryngeal cleft is a congenital condition characterized by an abnormal separation between the larynx and the esophagus, which can lead to difficulties in breathing and swallowing.
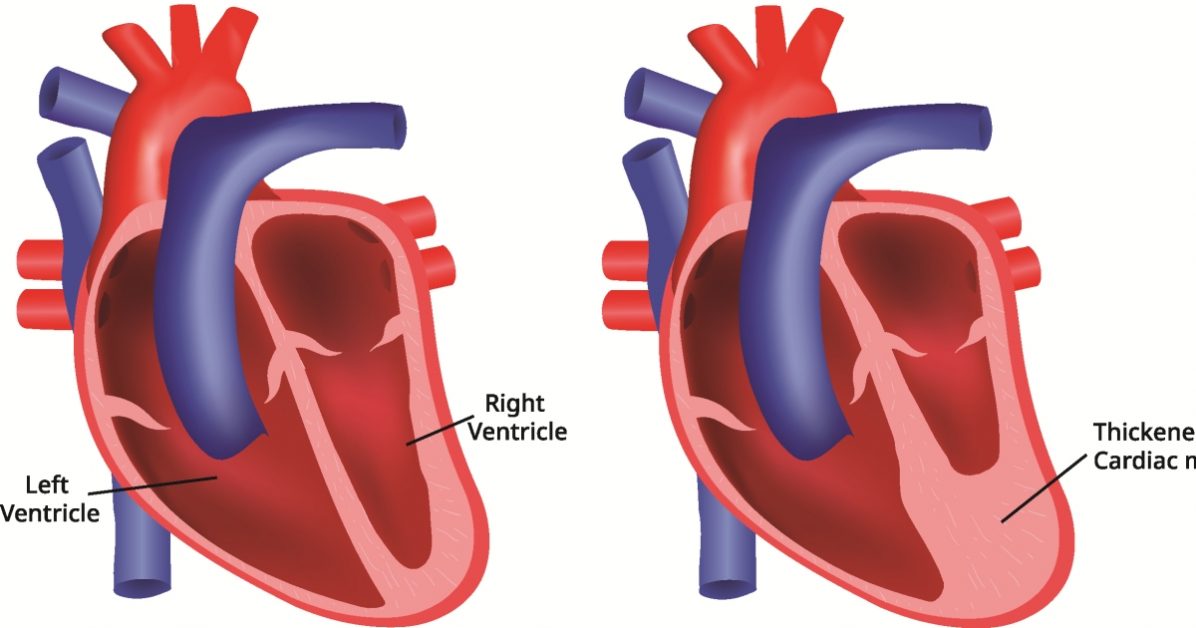
Vascular rings are congenital heart defects characterized by abnormal blood vessel formations that encircle and compress the trachea and esophagus, potentially causing respiratory and swallowing difficulties.

Degenerative disc disease is a condition characterized by the gradual deterioration of intervertebral discs, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
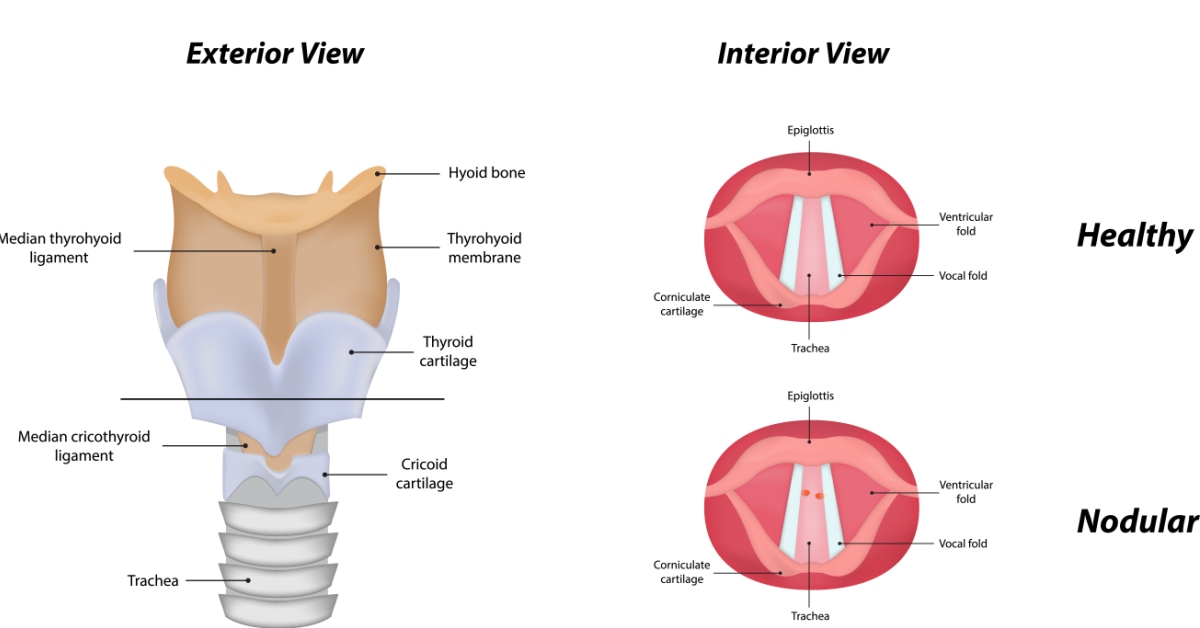
Vocal cord polyps are benign growths on the vocal cords that can cause hoarseness, breathiness, and vocal strain.

Cleft lip and cleft palate are congenital conditions characterized by openings or splits in the upper lip and/or the roof of the mouth, respectively, affecting facial structure and function.
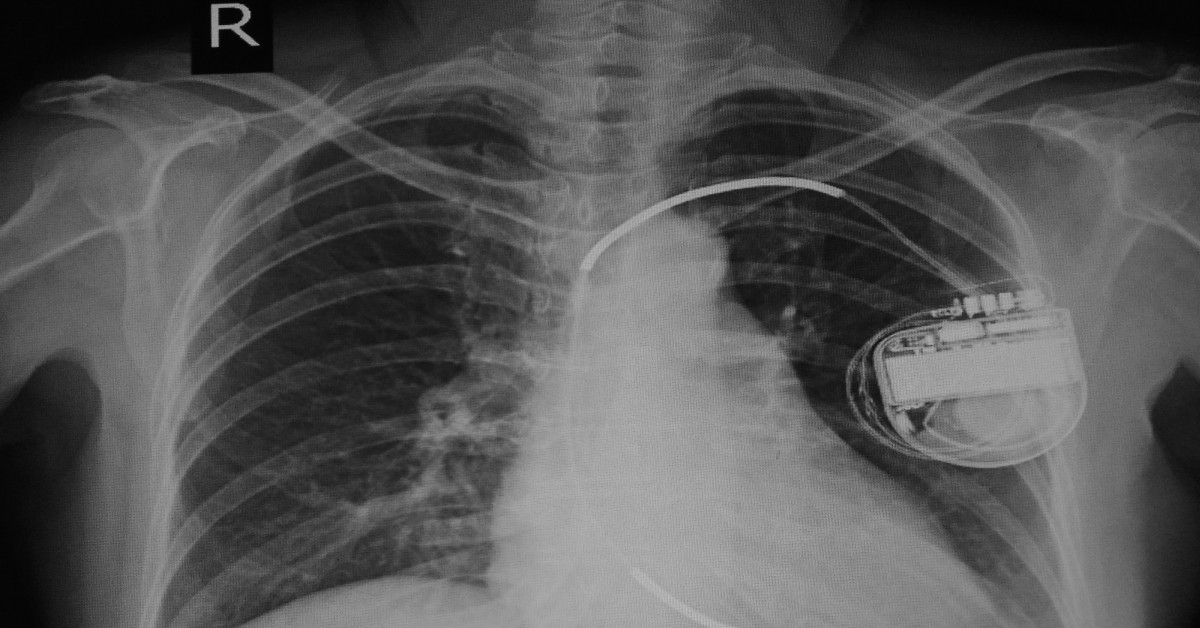
Tracheal stenosis is a narrowing of the trachea that can obstruct airflow, often resulting from congenital factors, trauma, or prolonged intubation.
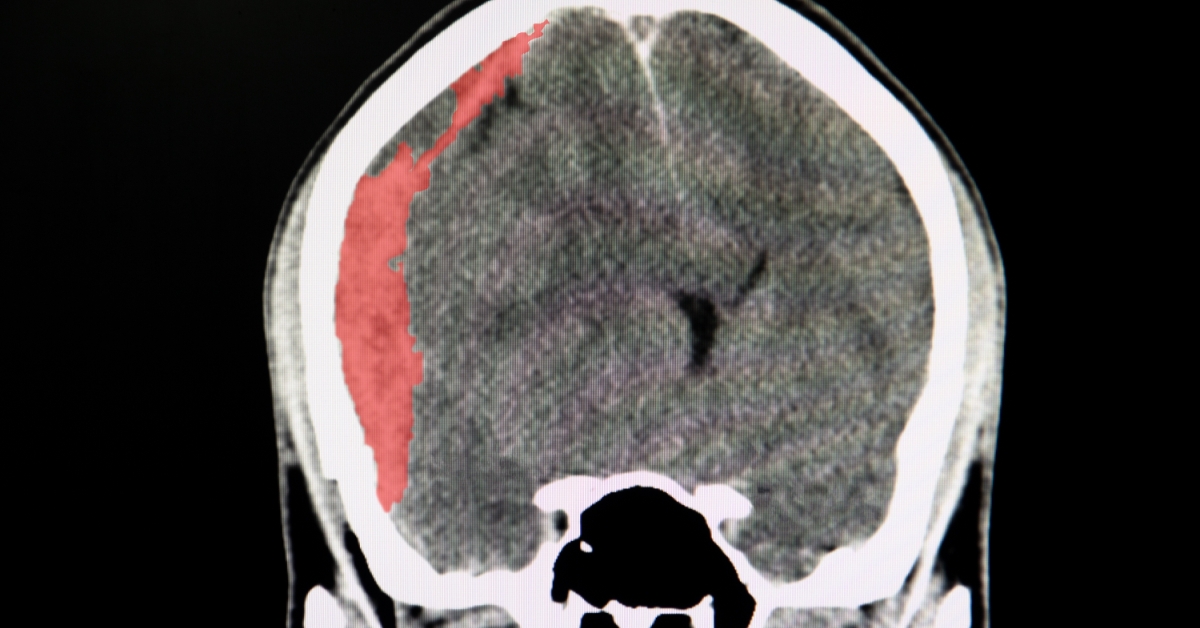
Retroperitoneal fibrosis is a rare condition characterized by the abnormal growth of fibrous tissue in the retroperitoneal space, often leading to compression of surrounding organs such as the kidneys and ureters.
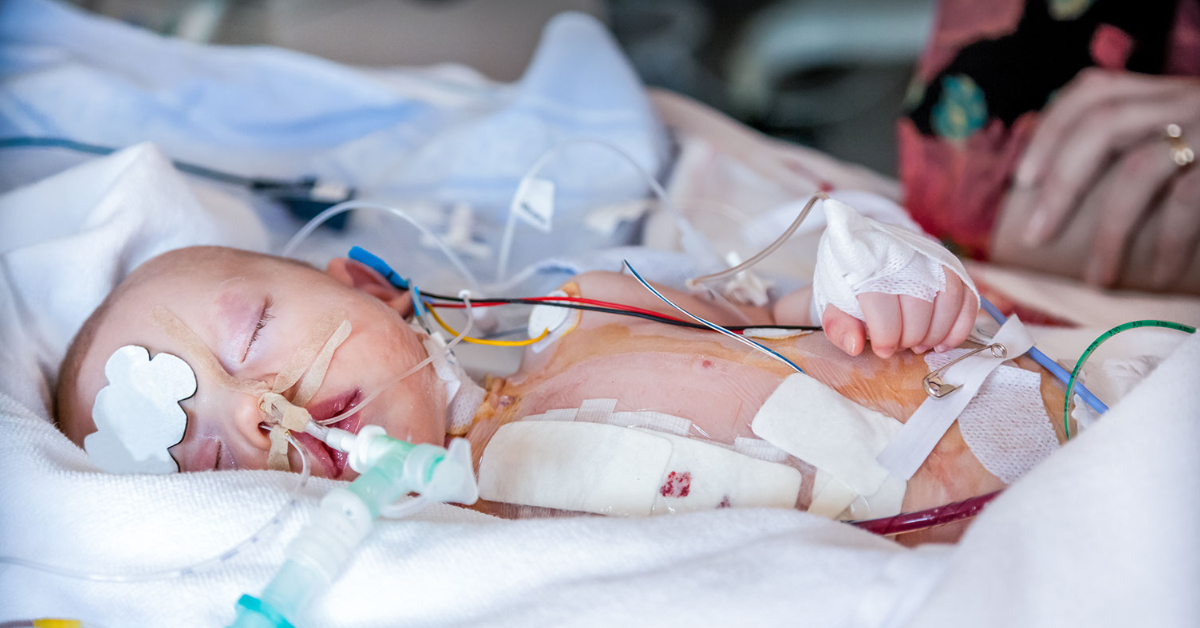
Pulmonary atresia is a congenital heart defect where the pulmonary valve does not form properly, obstructing blood flow from the heart to the lungs.
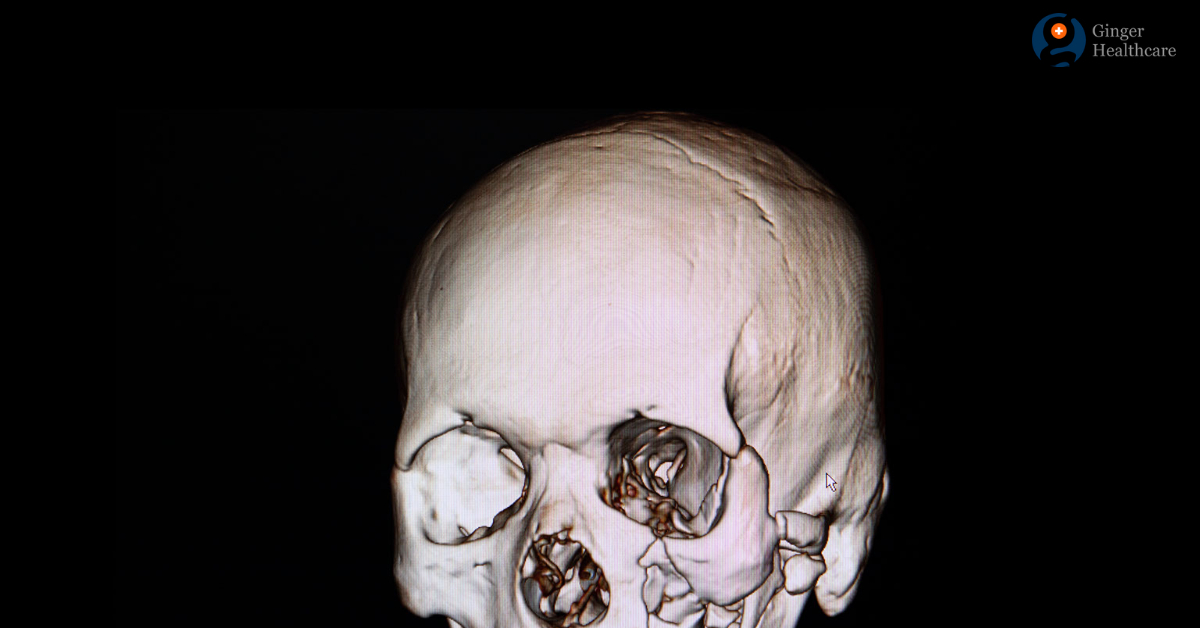
An orbital fracture involves a break in the bones surrounding the eye, often resulting from trauma, leading to symptoms such as swelling, bruising, and impaired vision.
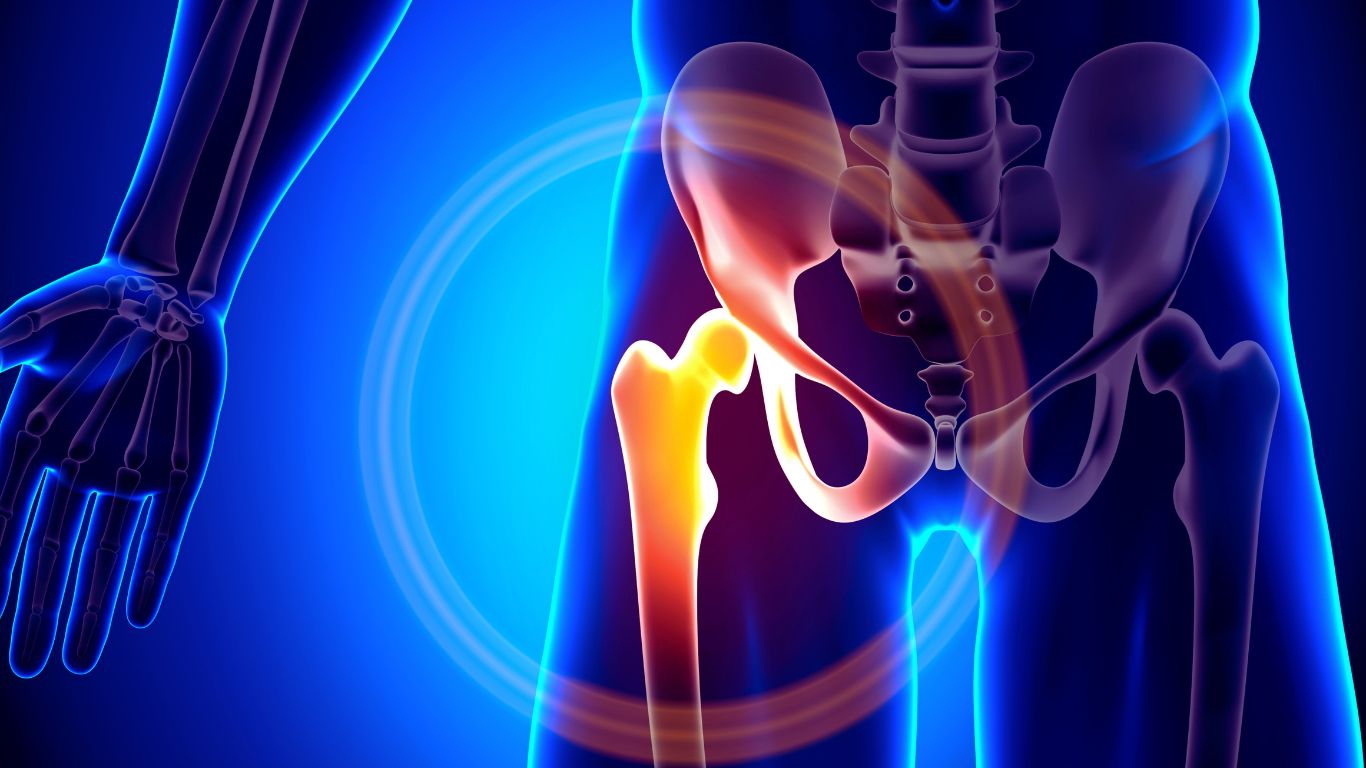
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease is a childhood condition characterized by the temporary loss of blood supply to the hip joint, leading to bone necrosis and potential deformity.

Skeletal dysplasia refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the size and shape of bones, leading to abnormal skeletal development.
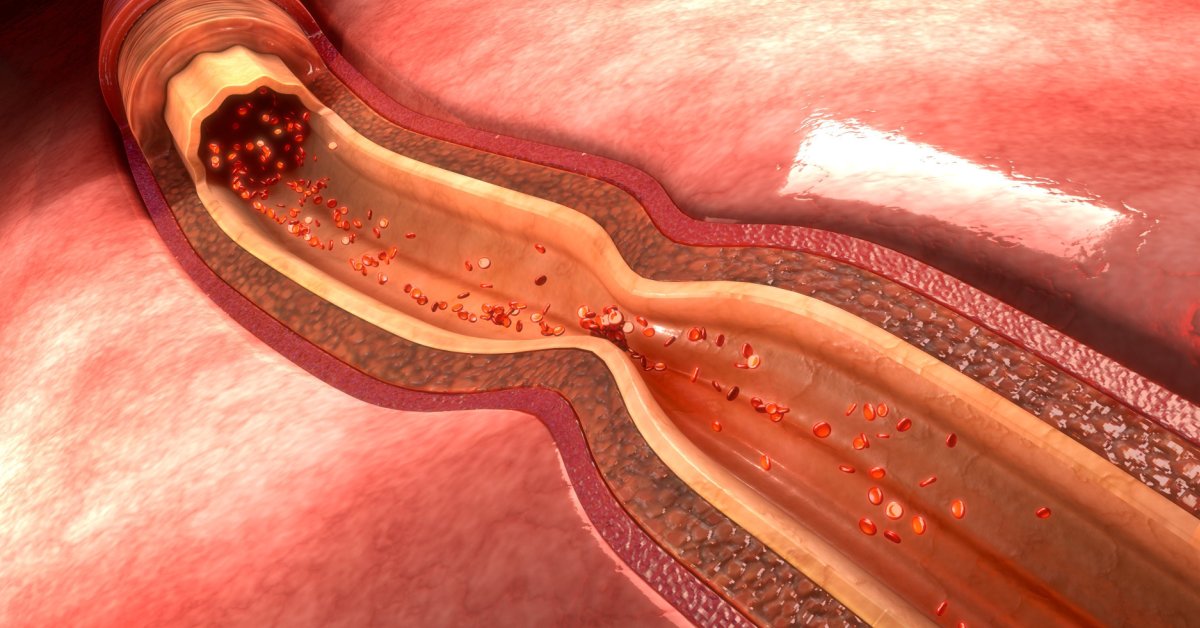
Vertebral artery dissection is a tear in the inner lining of the vertebral artery, which can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain and potentially cause stroke-like symptoms.
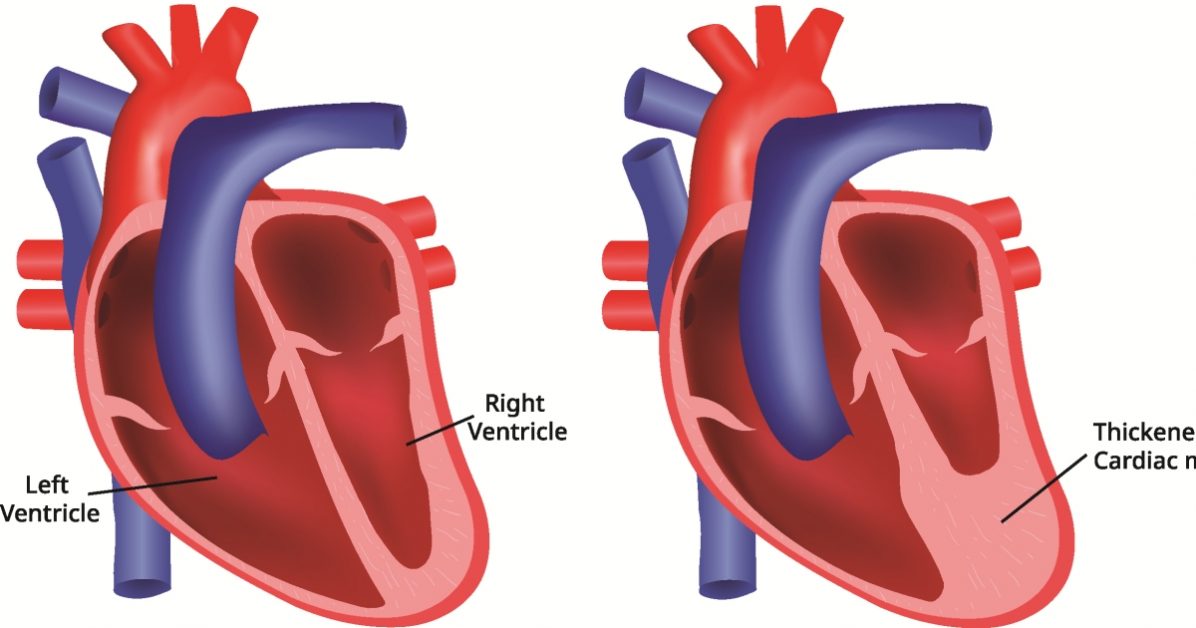
Tricuspid atresia is a congenital heart defect characterized by the absence of the tricuspid valve, obstructing blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
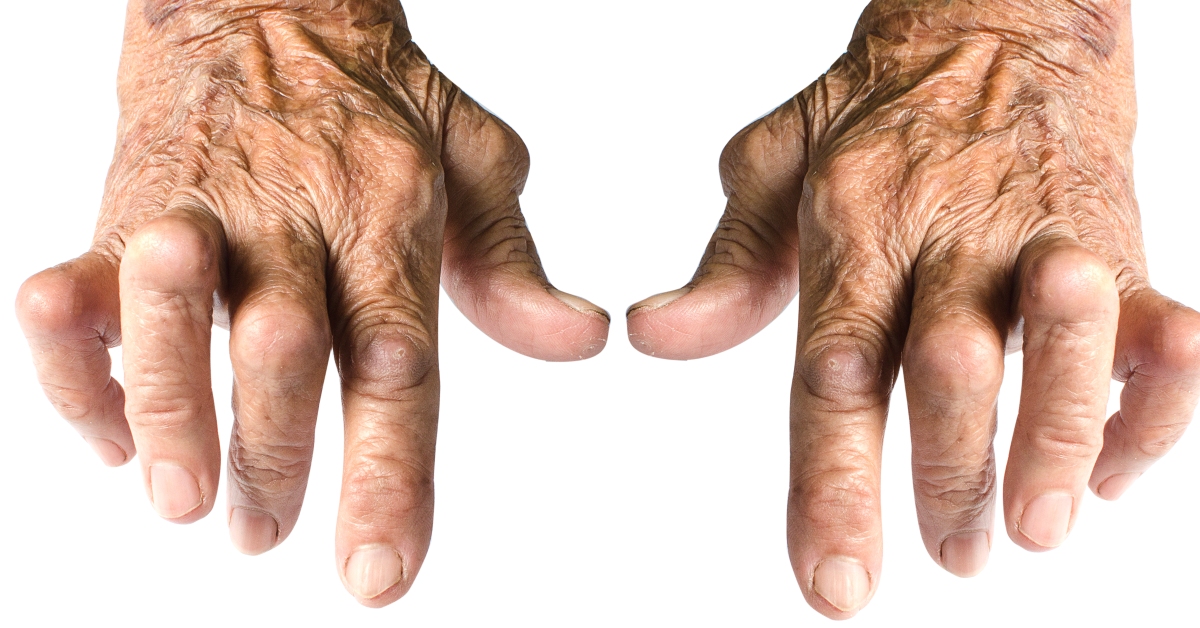
Inflammatory arthritis is a group of disorders characterized by joint inflammation, leading to pain, swelling, and potential joint damage.
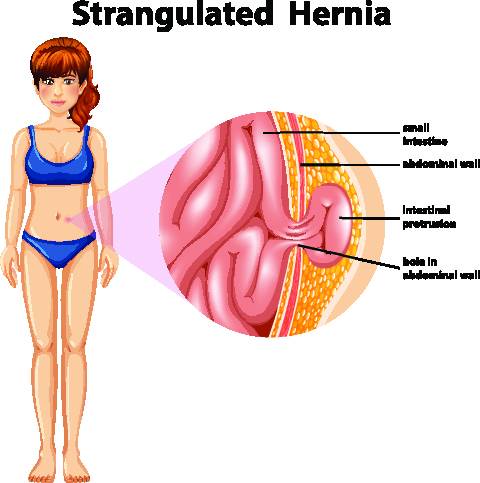
A strangulated hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine is trapped in the abdominal wall, cutting off its blood supply and leading to severe pain and potential complications.

A hip labral tear involves damage to the cartilage surrounding the hip joint, leading to pain, instability, and difficulty with movement.
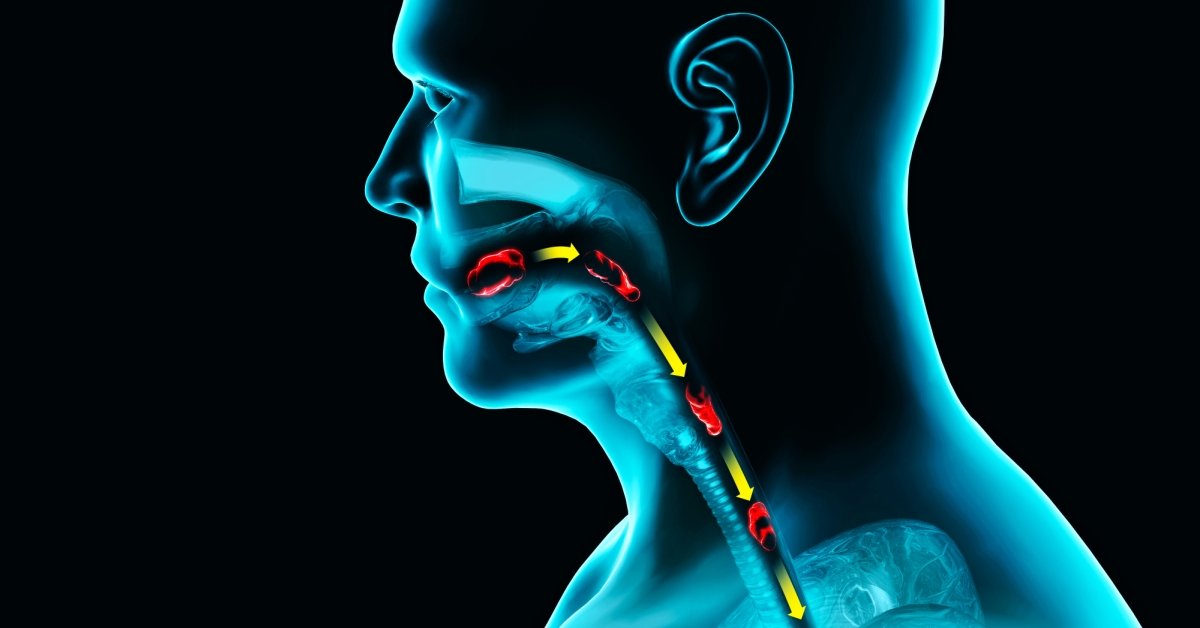
Esophageal spasms are involuntary contractions of the esophagus that can cause chest pain and difficulty swallowing.
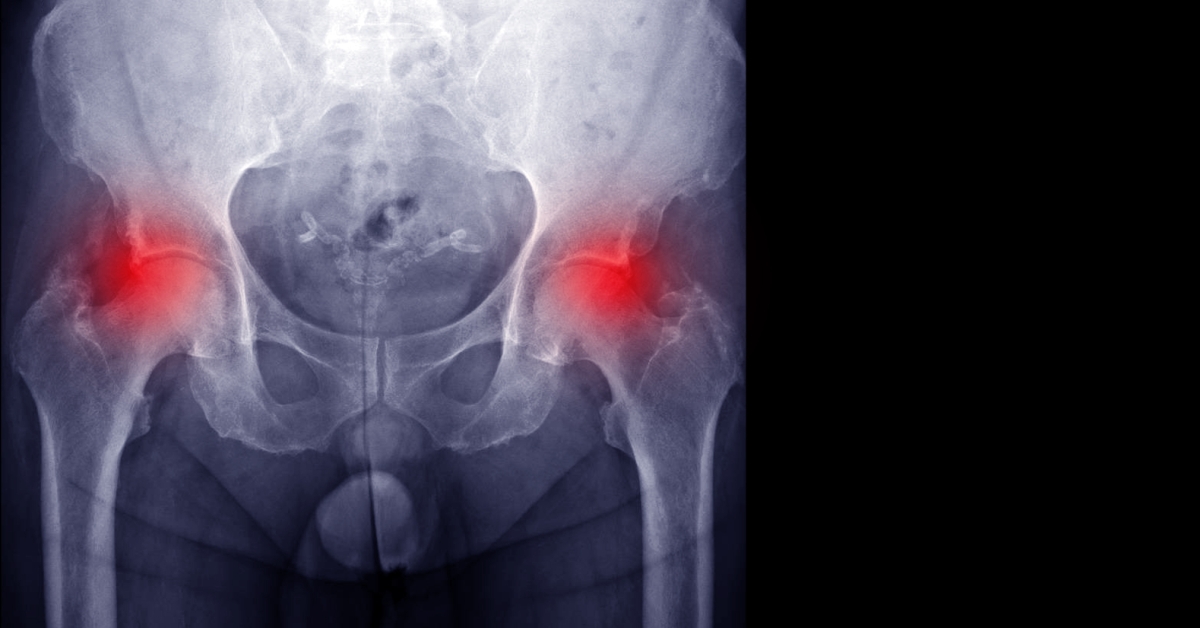
Hip impingement, or femoroacetabular impingement, occurs when the hip joint is not shaped properly, leading to pain and restricted movement.

Double vision, or diplopia, is a visual disturbance where a person sees two images of one object, which can result from various underlying conditions affecting the eyes or the brain.

Overactive bladder is a condition characterized by a sudden and uncontrollable urge to urinate, often leading to frequent urination and, in some cases, urinary incontinence.

Lumbar spondylosis is a degenerative condition of the spine that occurs due to age-related changes, leading to pain and stiffness in the lower back.
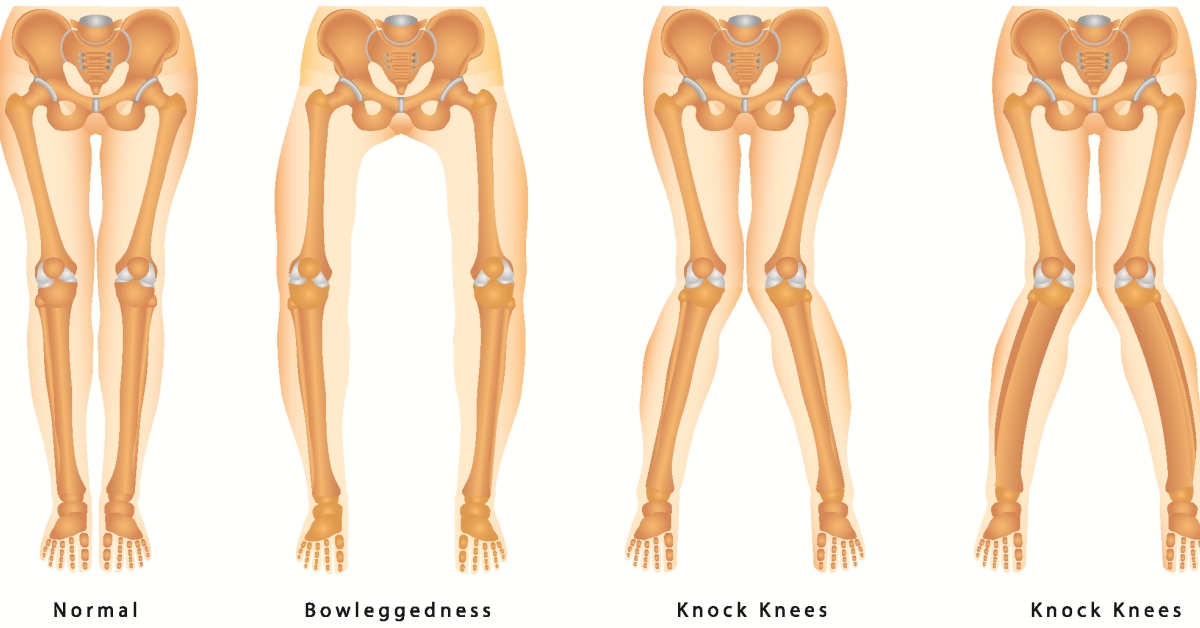
Knock-knees, or genu valgum, is a condition where the knees angle inward, causing the lower legs to be spaced apart when standing.

A slipped disc, or herniated disc, occurs when the soft material inside a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the outer layer, often causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
A deviated septum occurs when the cartilage and bone that divide the nasal cavity are displaced, leading to breathing difficulties and nasal congestion.

Cluster headaches are excruciating, recurring headaches that occur in cyclical patterns, often described as sharp, intense pain around one eye.
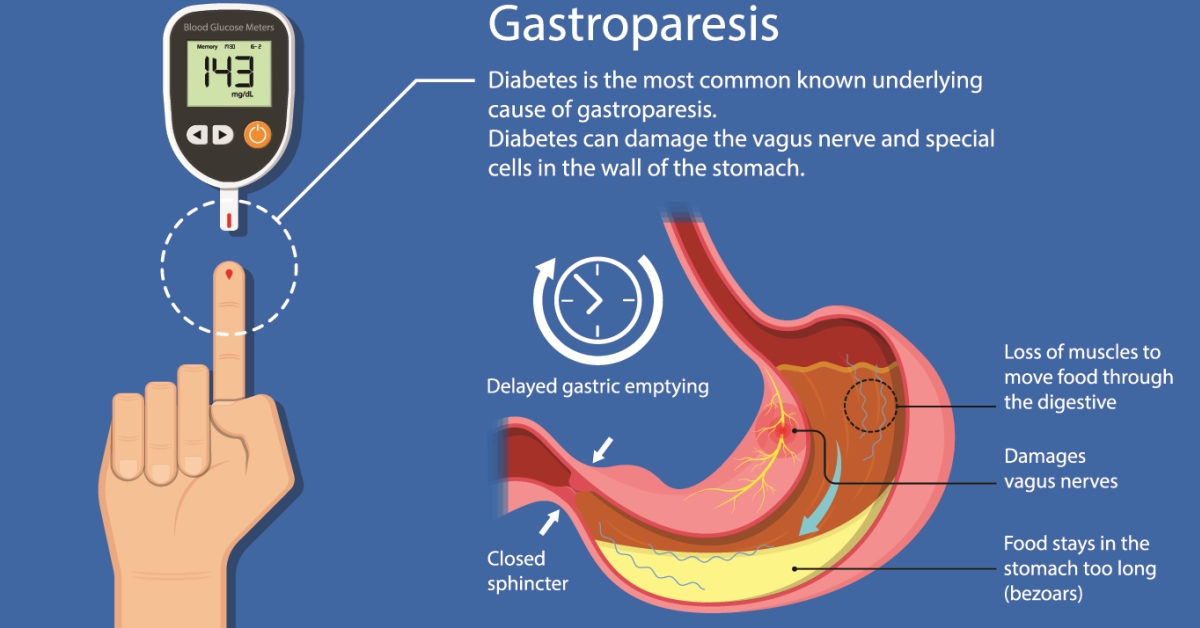
Gastroparesis is a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying, where the stomach takes too long to empty its contents, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
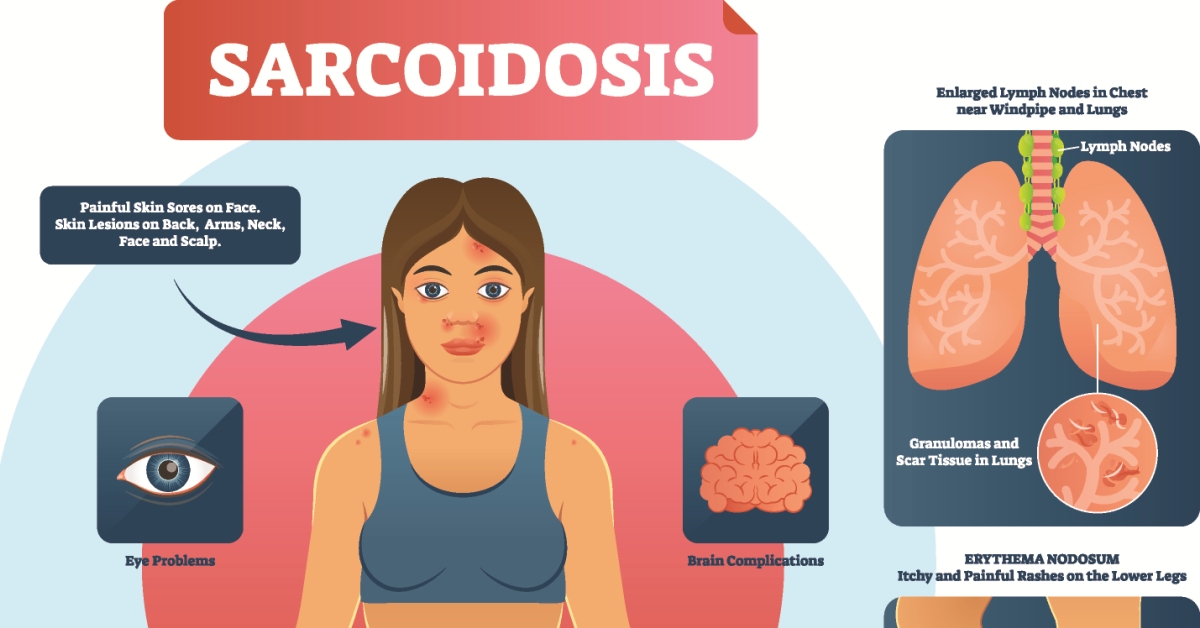
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of tiny clumps of inflammatory cells, known as granulomas, in various organs, most commonly the lungs and lymph nodes.
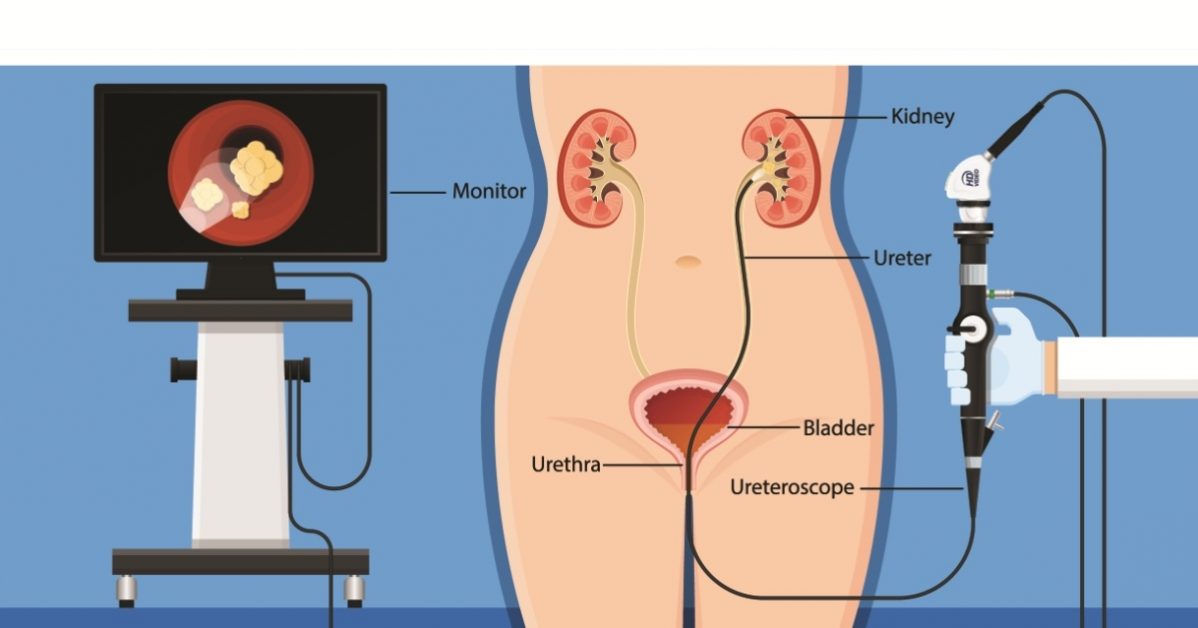
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries, often causing no symptoms but potentially leading to pain or complications.

Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, is a refractive error where distant objects appear blurry while close objects can be seen clearly.
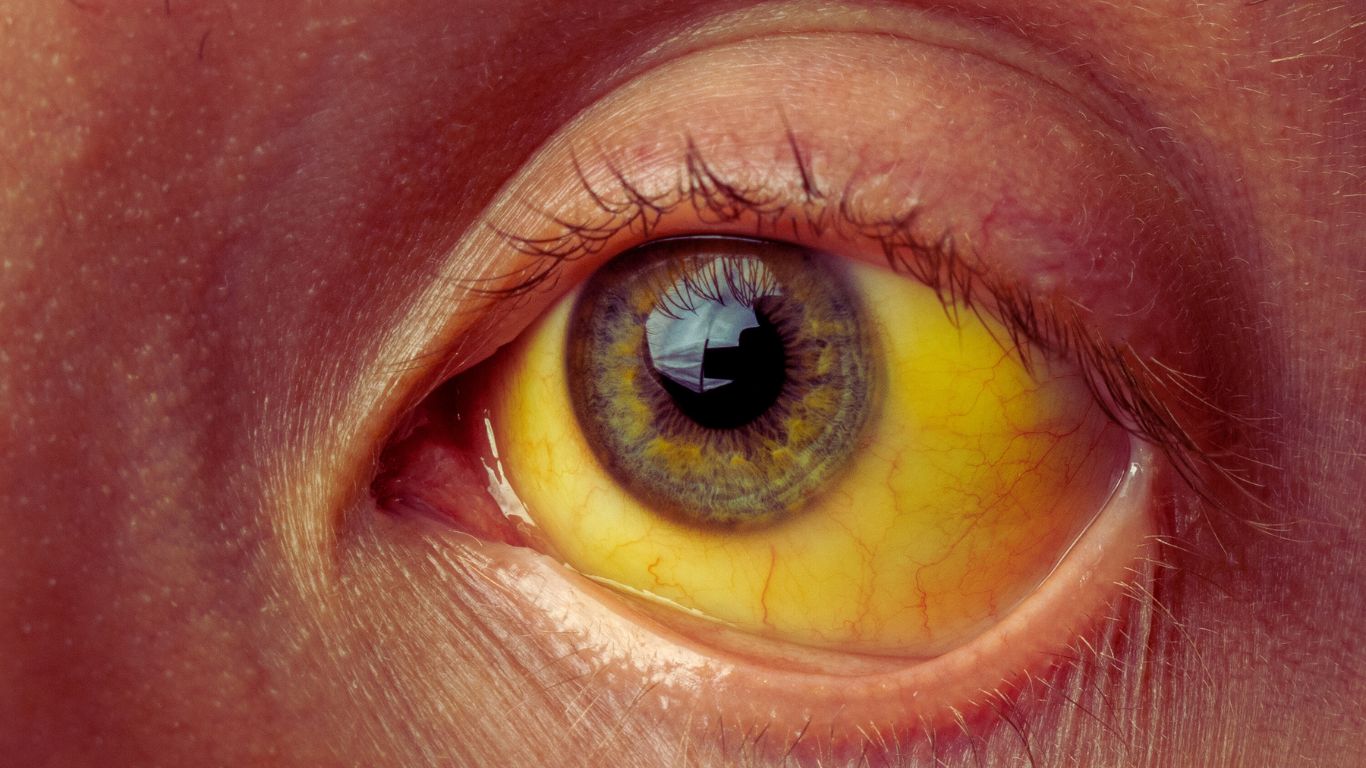
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, causing symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and jaundice.
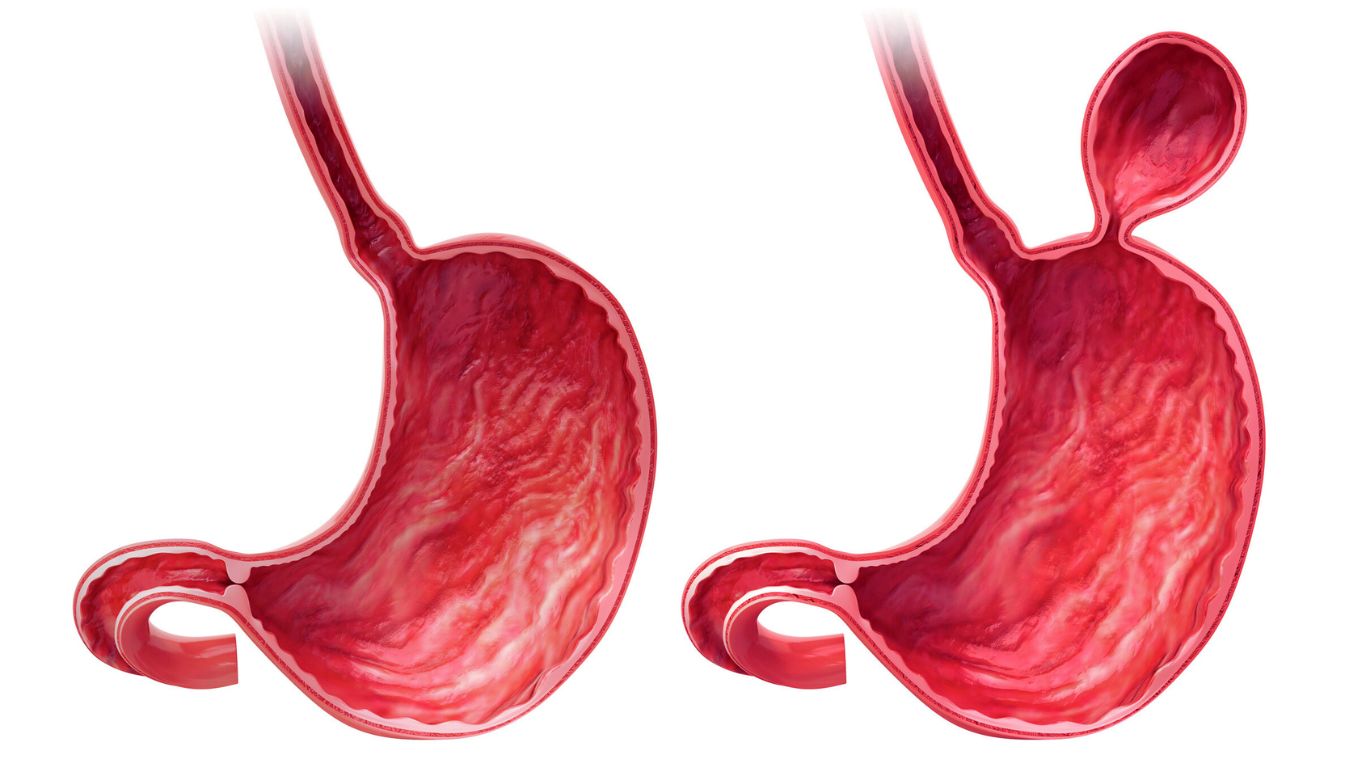
A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, often leading to symptoms like heartburn and difficulty swallowing.

Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in affected joints.
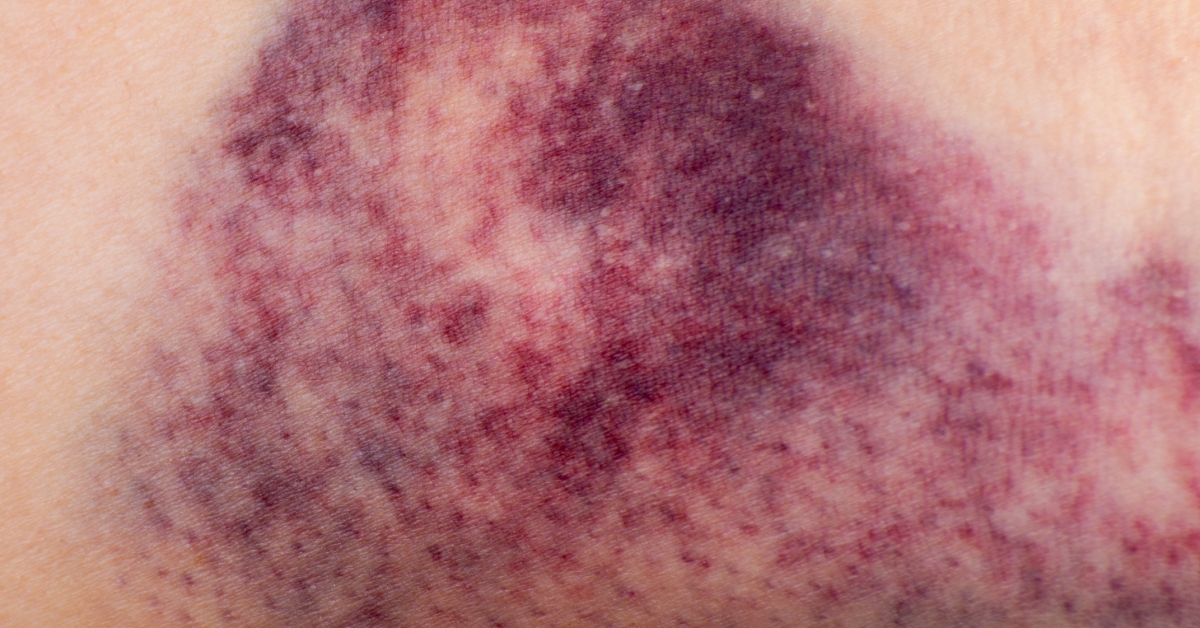
A hematoma is a localized collection of blood outside blood vessels, often resulting from injury, that can cause swelling and pain in the affected area.

Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement, leading to symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and balance issues.
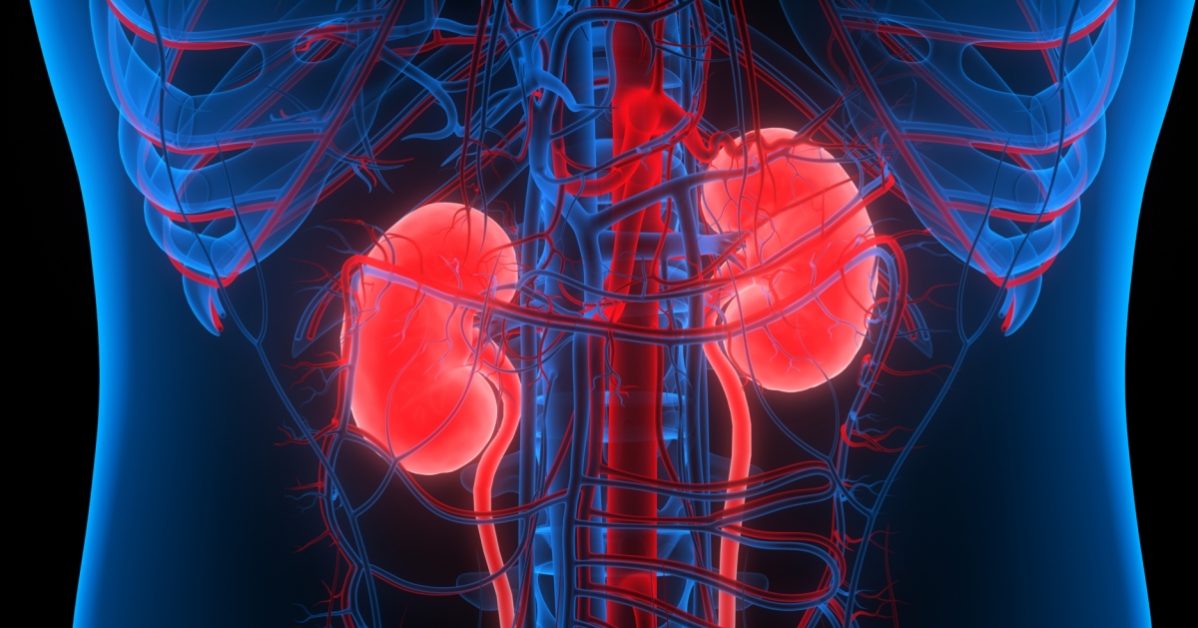
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys, causing severe pain and discomfort when passing through the urinary tract.

Vertigo is a sensation of spinning or dizziness, often caused by inner ear disorders or issues with the vestibular system.
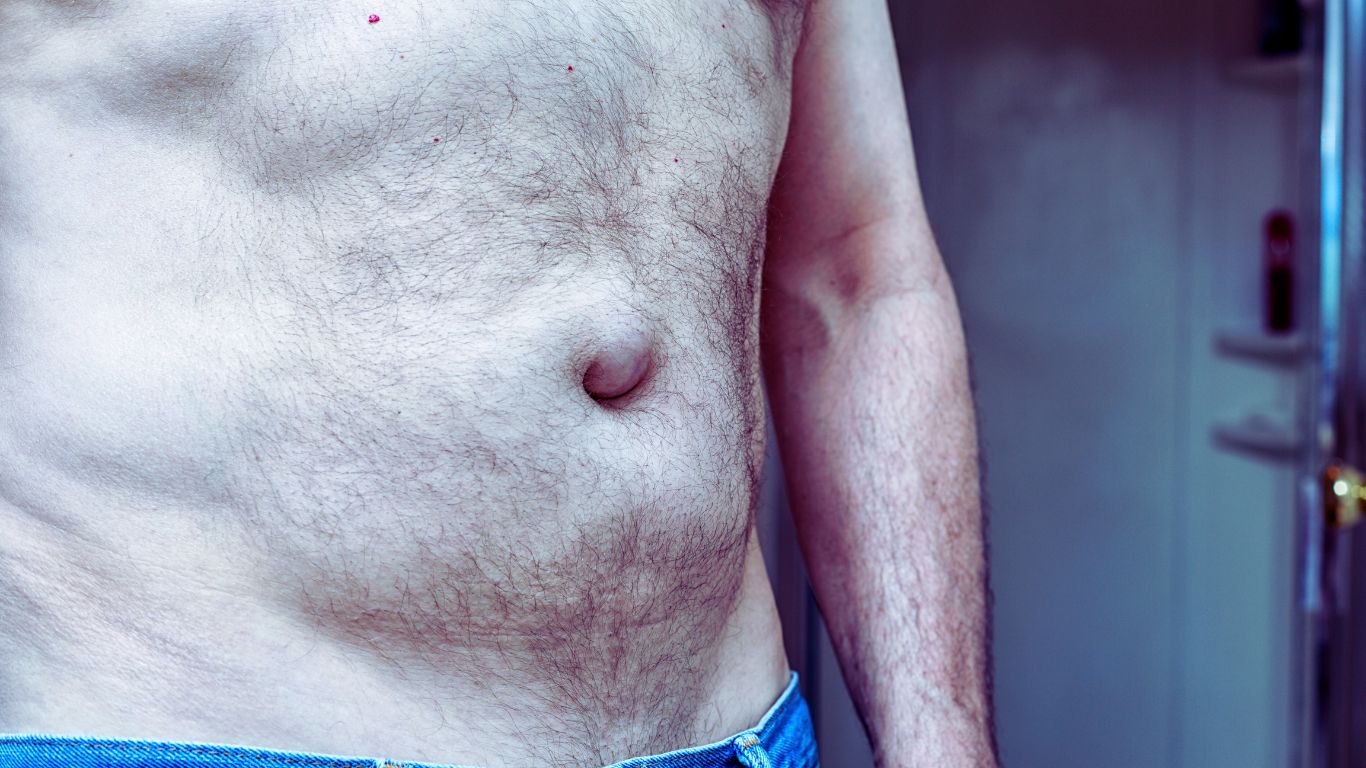
A hernia occurs when an internal organ pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or tissue, often causing discomfort or pain.

Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, characterized by high blood sugar levels that can affect both the mother and baby.

A ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump filled with jelly-like fluid that commonly forms near joints or tendons, particularly in the hands and wrists.
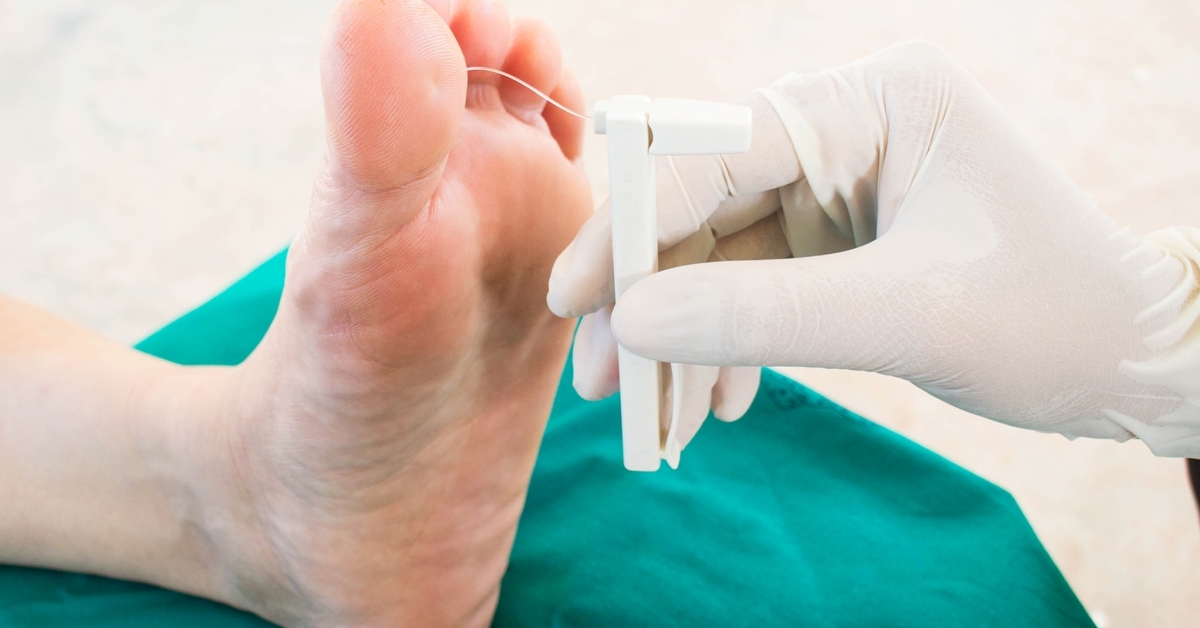
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes, leading to symptoms like pain, tingling, or numbness, particularly in the extremities.

High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common condition where the force of blood against artery walls is consistently too high, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
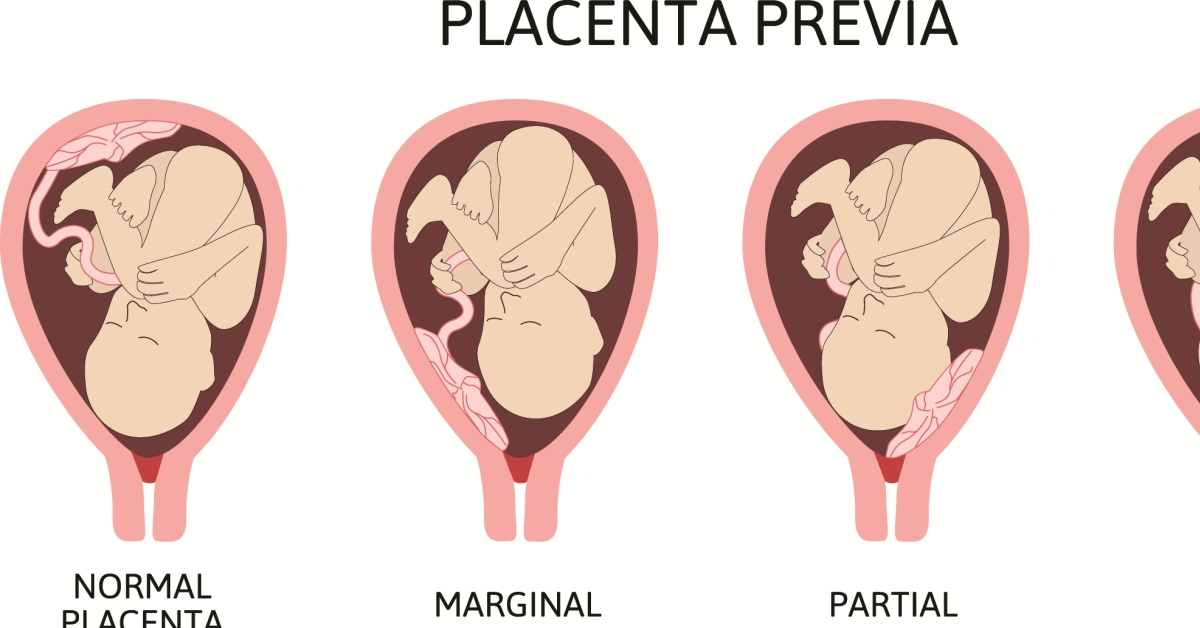
Placenta previa is a condition during pregnancy where the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix, potentially leading to complications during delivery.
Thymoma is a rare type of cancer originating in the thymus gland, often associated with autoimmune disorders.
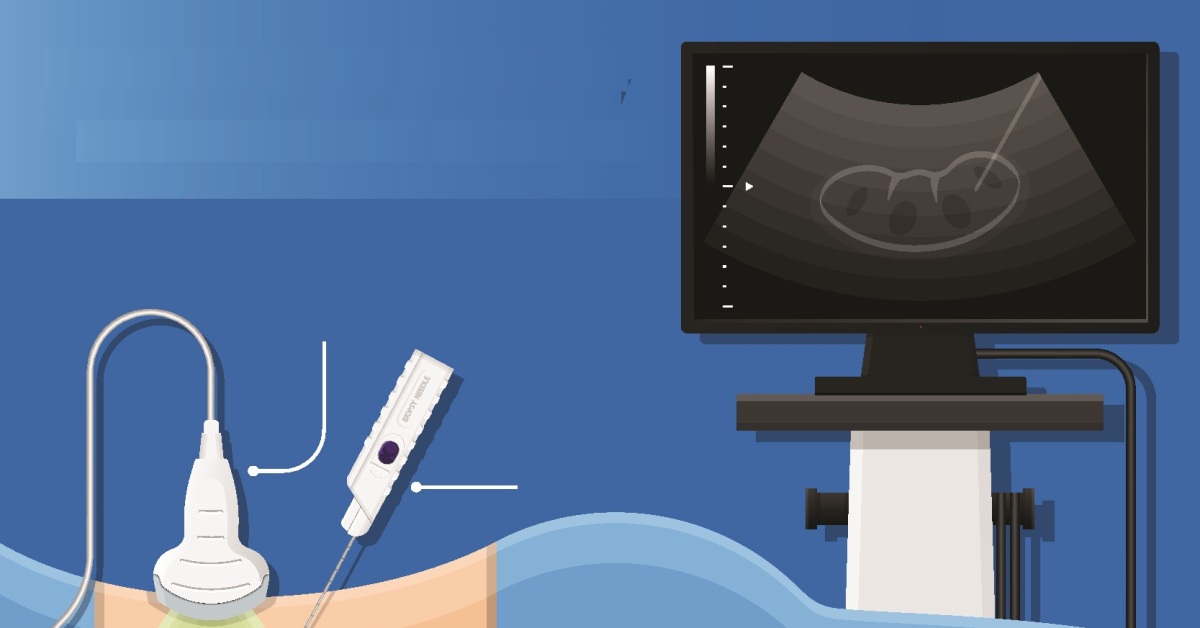
Renal vein thrombosis is a condition where a blood clot forms in the renal vein, which can lead to kidney damage and impaired function.
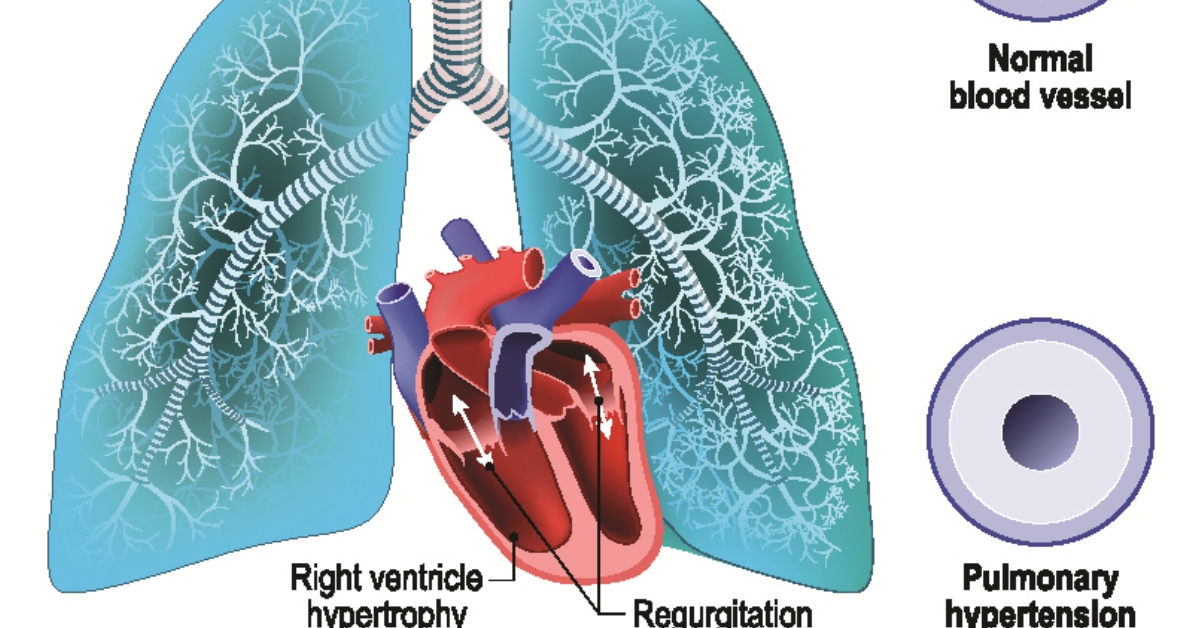
Pulmonary regurgitation is a heart condition where blood flows backward from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle due to an imperfectly closing pulmonary valve.
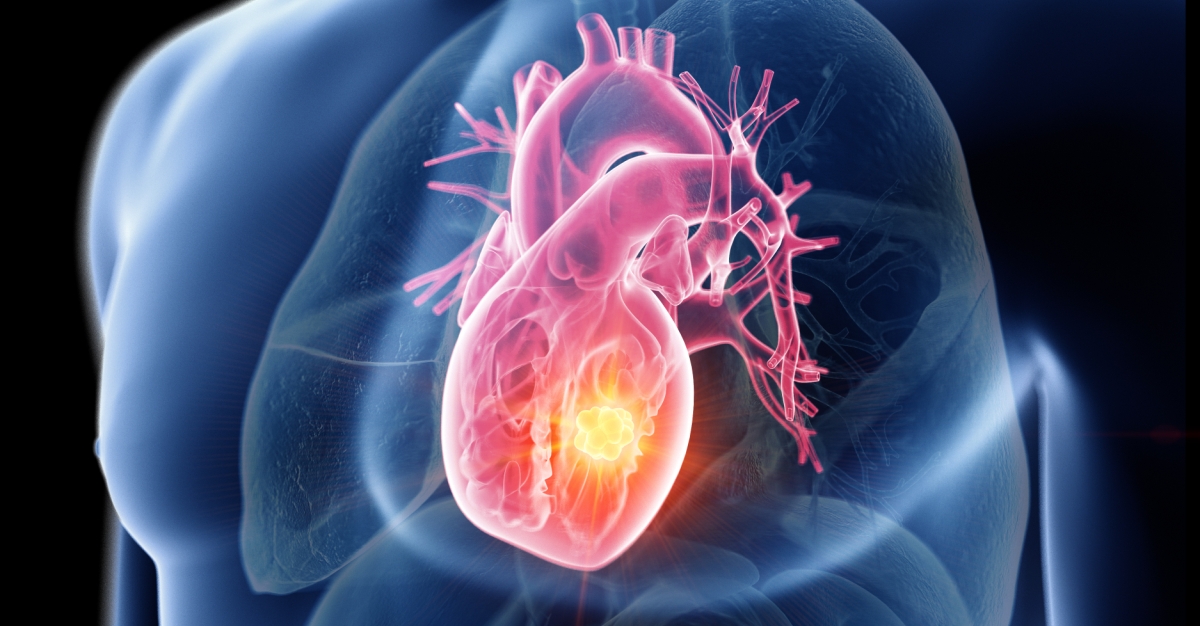
Heart tumors are abnormal growths that can develop in or on the heart, which can be either benign or malignant.
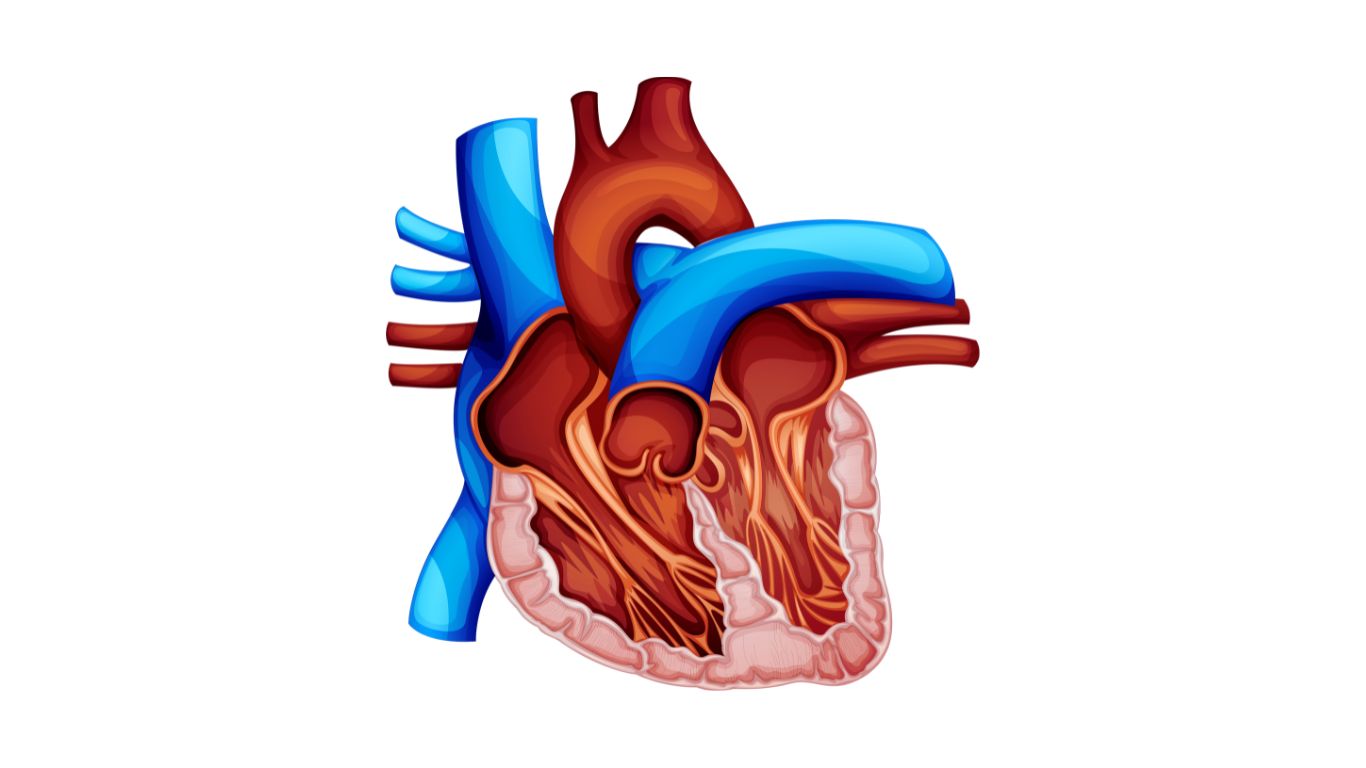
Double Outlet Right Ventricle (DORV) is a congenital heart defect where both the aorta and pulmonary artery connect to the right ventricle, leading to inefficient blood circulation.
Congenital heart defects are structural abnormalities of the heart present at birth, affecting normal blood flow and potentially leading to various health complications.
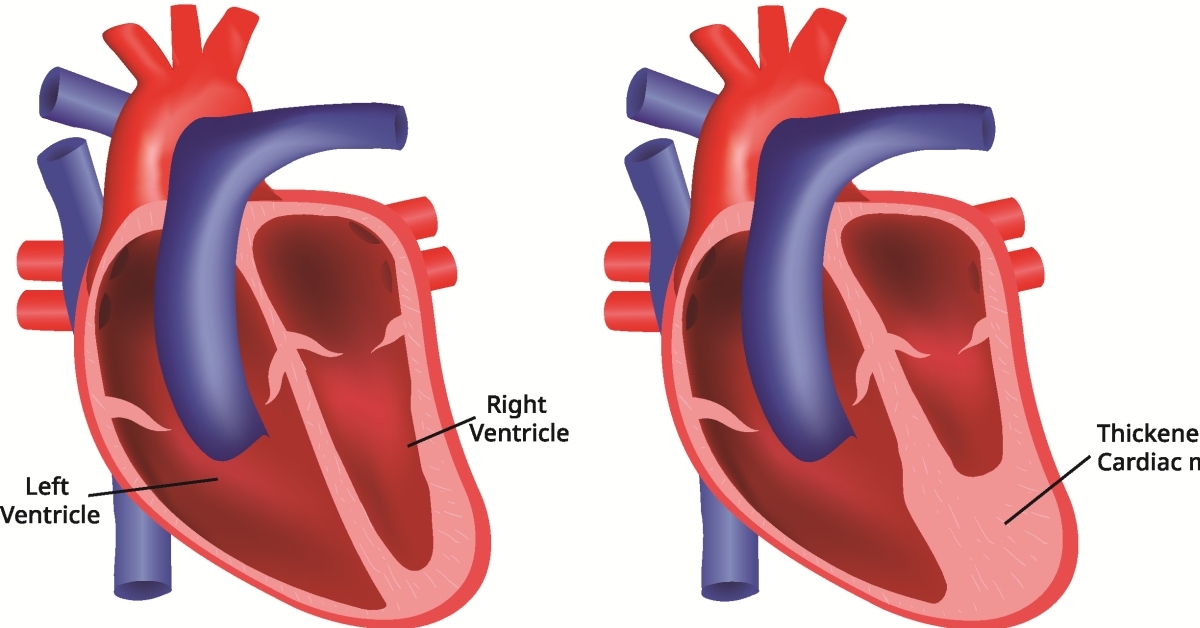
Mitral valve stenosis is a narrowing of the mitral valve opening, which can obstruct blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, leading to various cardiovascular complications.

A vaginal fistula is an abnormal connection between the vagina and another organ, often resulting in incontinence or discomfort.
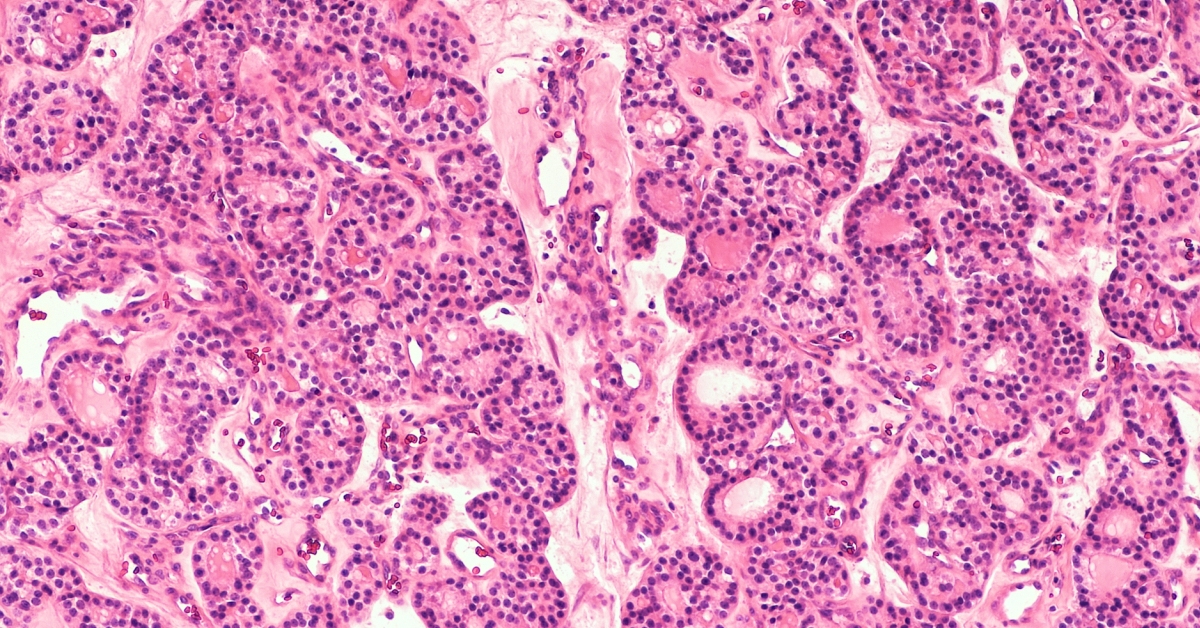
Parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid glands, often leading to hyperparathyroidism and elevated calcium levels in the blood.
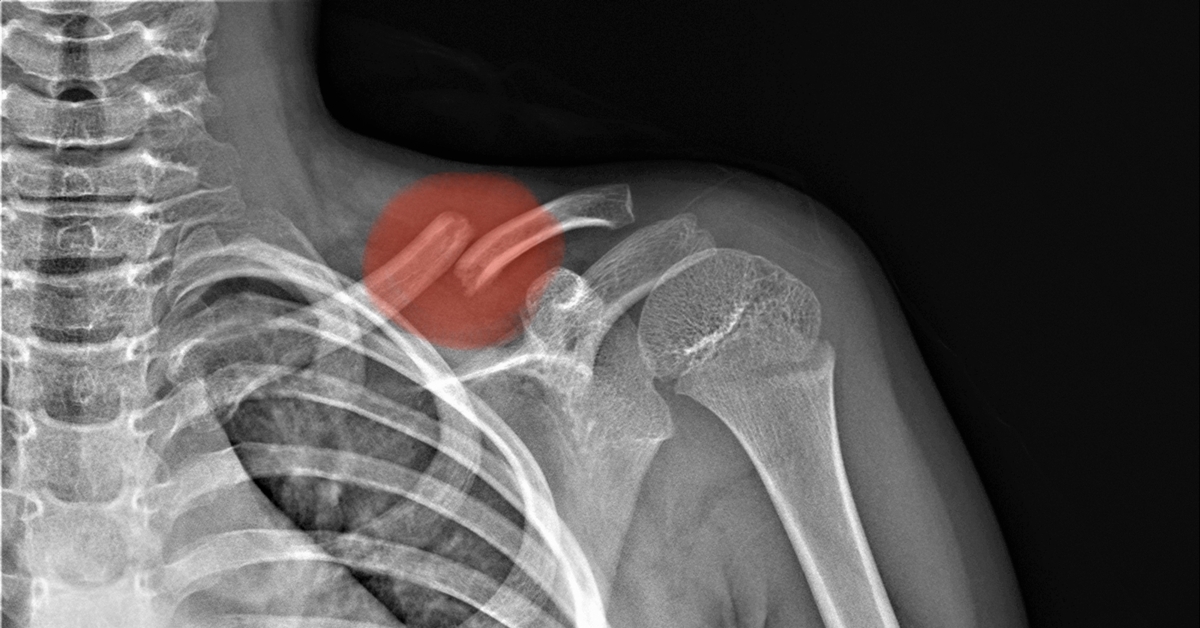
Osteoblastoma is a rare, benign bone tumor characterized by the proliferation of osteoblasts, leading to pain and swelling, primarily occurring in the spine and long bones.
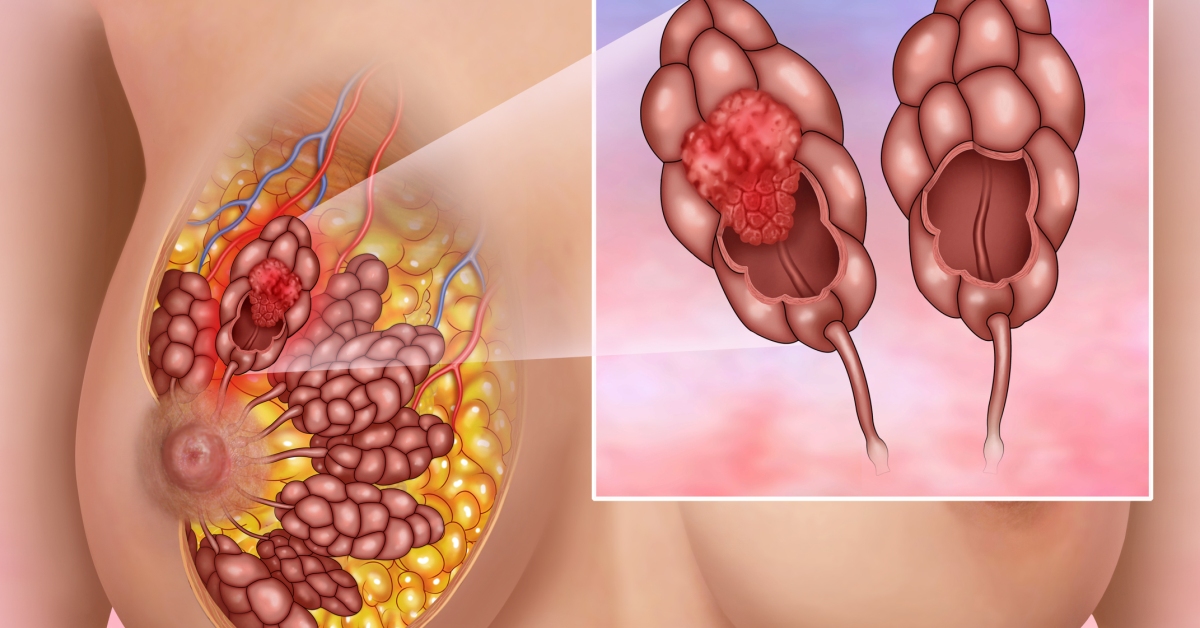
Invasive lobular carcinoma is a type of breast cancer that begins in the lobules, the glands responsible for milk production, and is known for its unique growth pattern, often resulting in subtle thickening or changes in breast tissue.
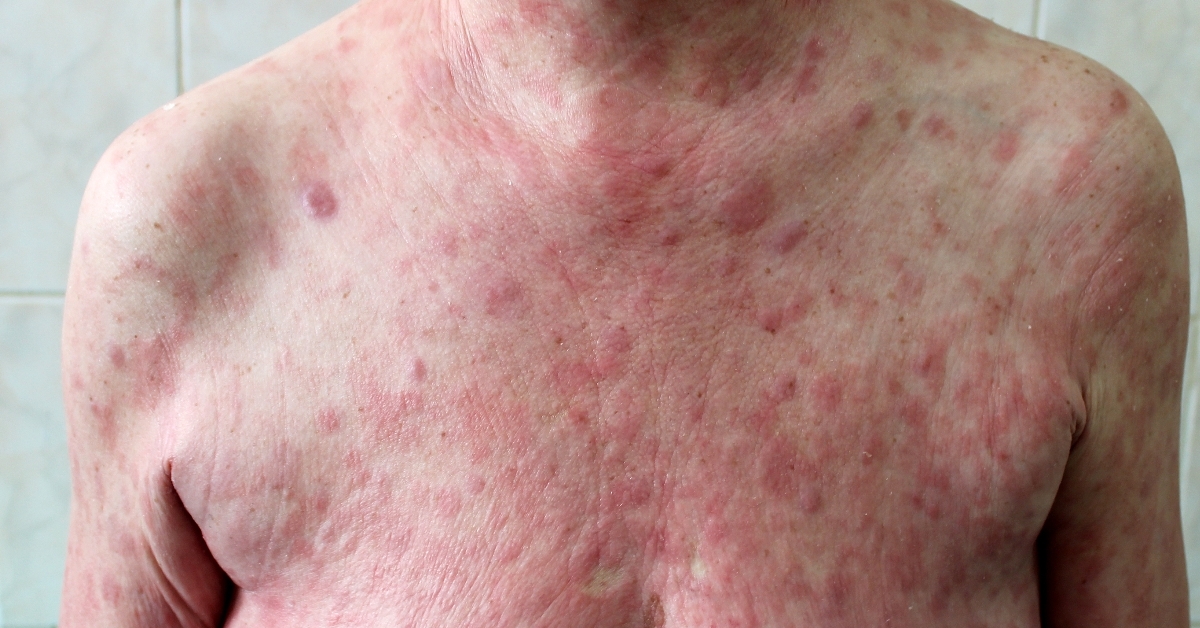
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the skin, characterized by the abnormal proliferation of T-cells.
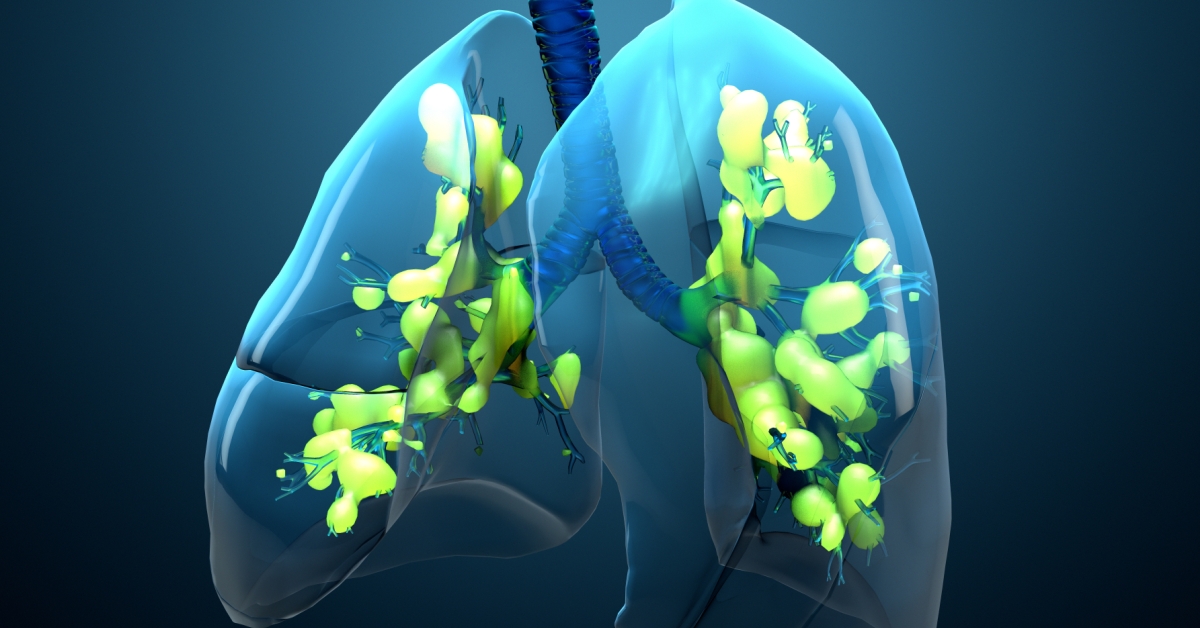
Renal artery stenosis is a narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys, which can lead to high blood pressure and kidney damage.

Male infertility refers to the inability of a man to contribute to conception, often due to issues with sperm production, motility, or delivery.

A hip fracture is a serious injury often resulting from a fall or trauma, leading to severe pain and limited mobility.
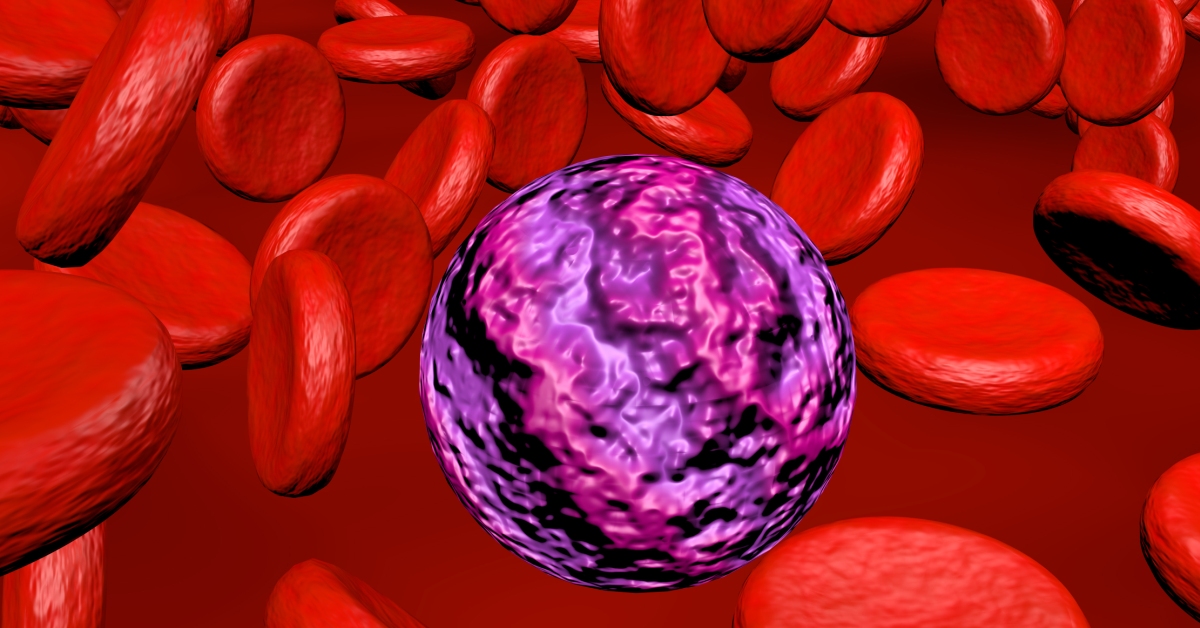
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, characterized by an overproduction of monocytes and a mix of myeloid and monocytic features.
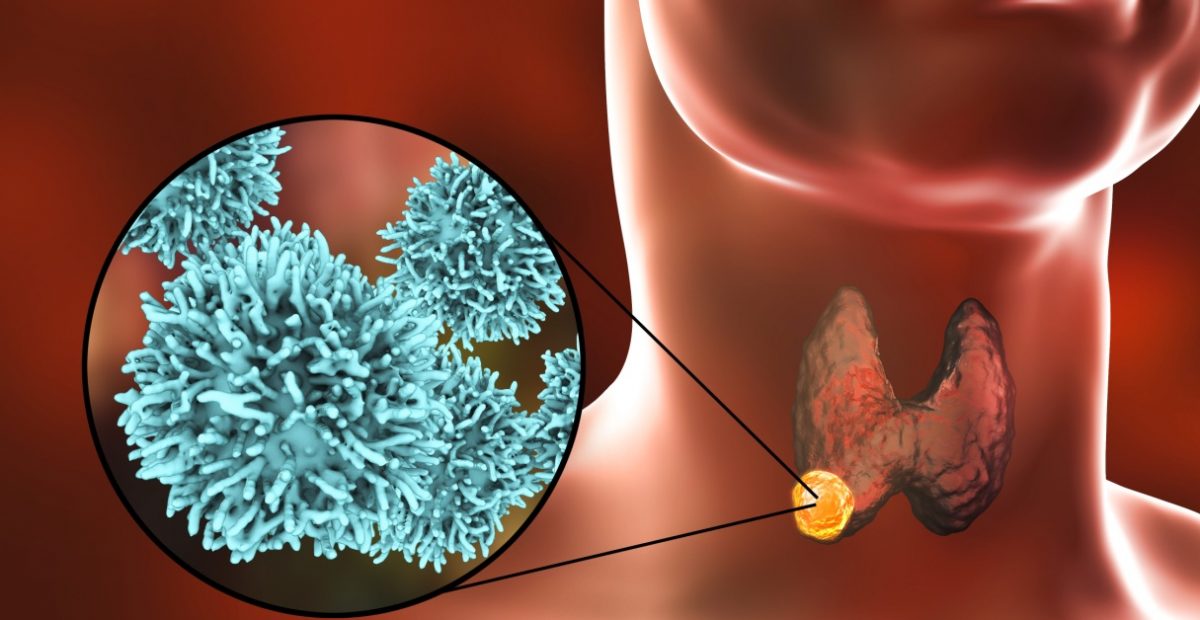
Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer, characterized by slow growth and often a favorable prognosis.
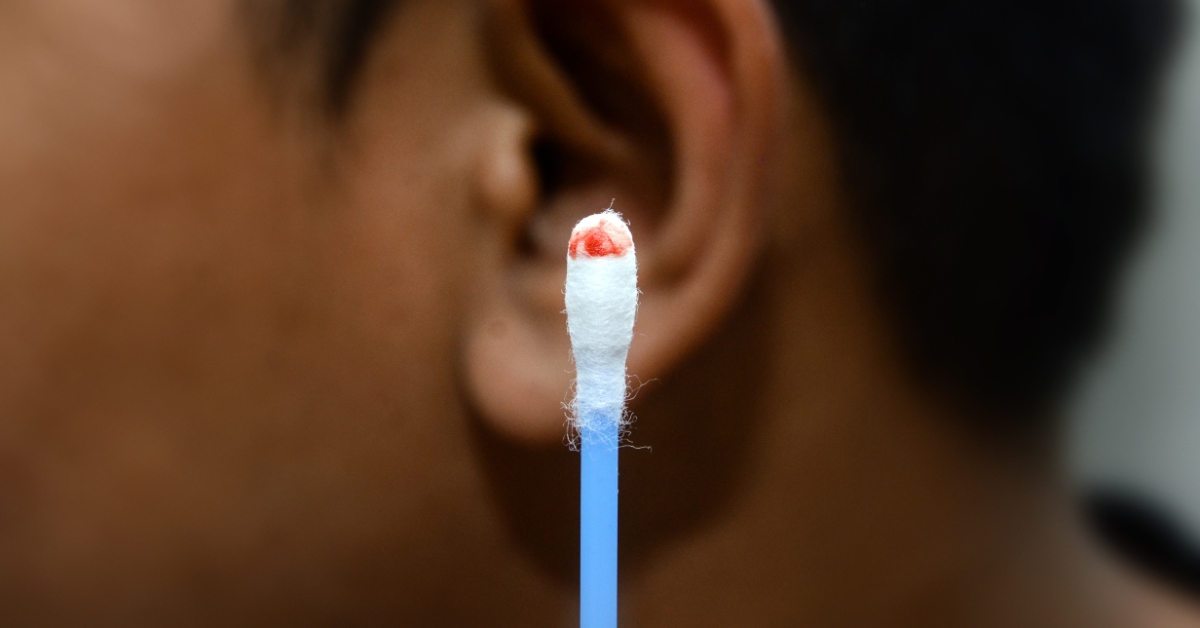
Ear cancer refers to malignant tumors that can develop in various parts of the ear, including the outer ear, middle ear, or inner ear.
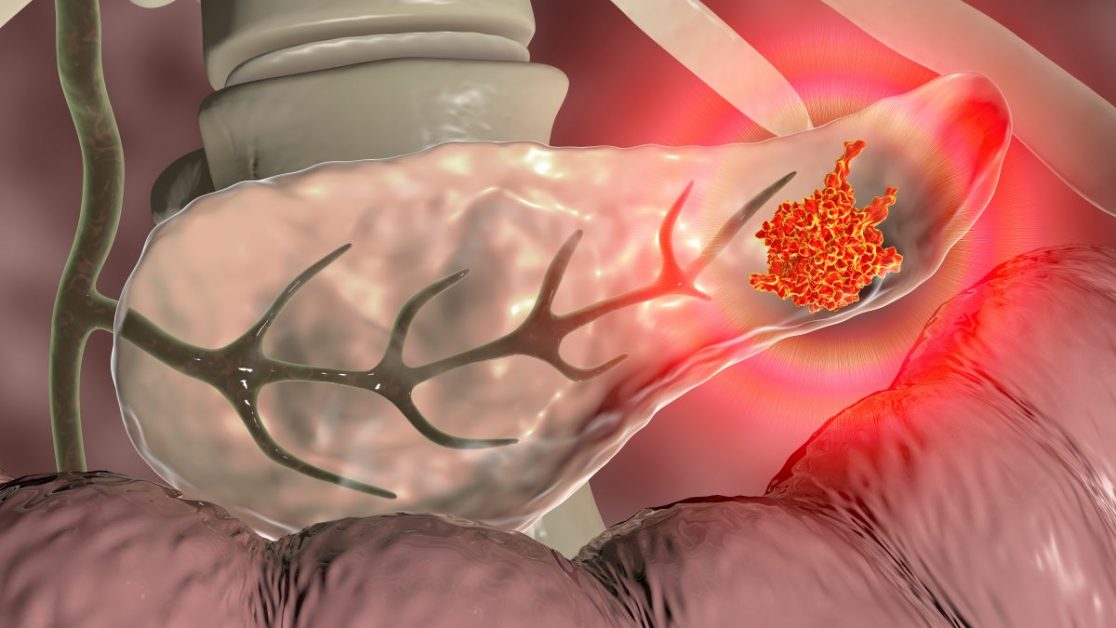
Pancreatic cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the pancreas, often detected incidentally during imaging studies for other conditions.

Nose cancer, or nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer, is a rare form of cancer that affects the tissues of the nasal passages and sinuses, often presenting symptoms like nasal obstruction, bleeding, and facial pain.
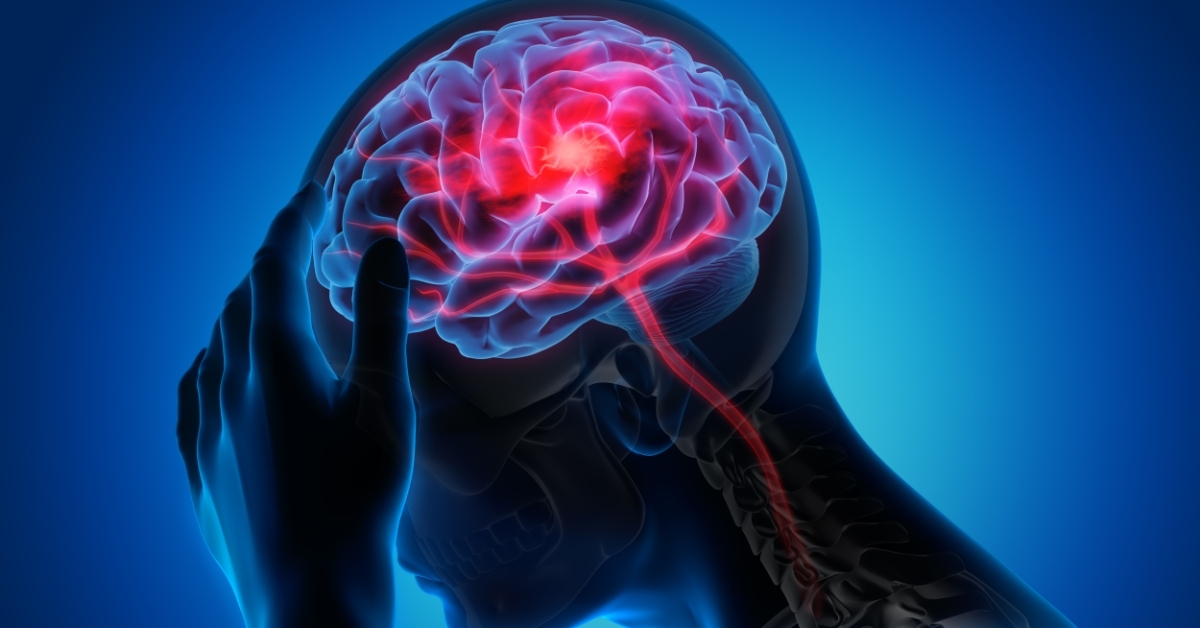
Intracerebral hemorrhage is a type of stroke that occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding within the brain tissue.
Hairy cell leukemia is a rare type of chronic blood cancer characterized by the proliferation of abnormal B cells that have a distinctive “hairy” appearance under the microscope.
Salivary gland cancer is a rare type of cancer that originates in the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva to aid digestion.
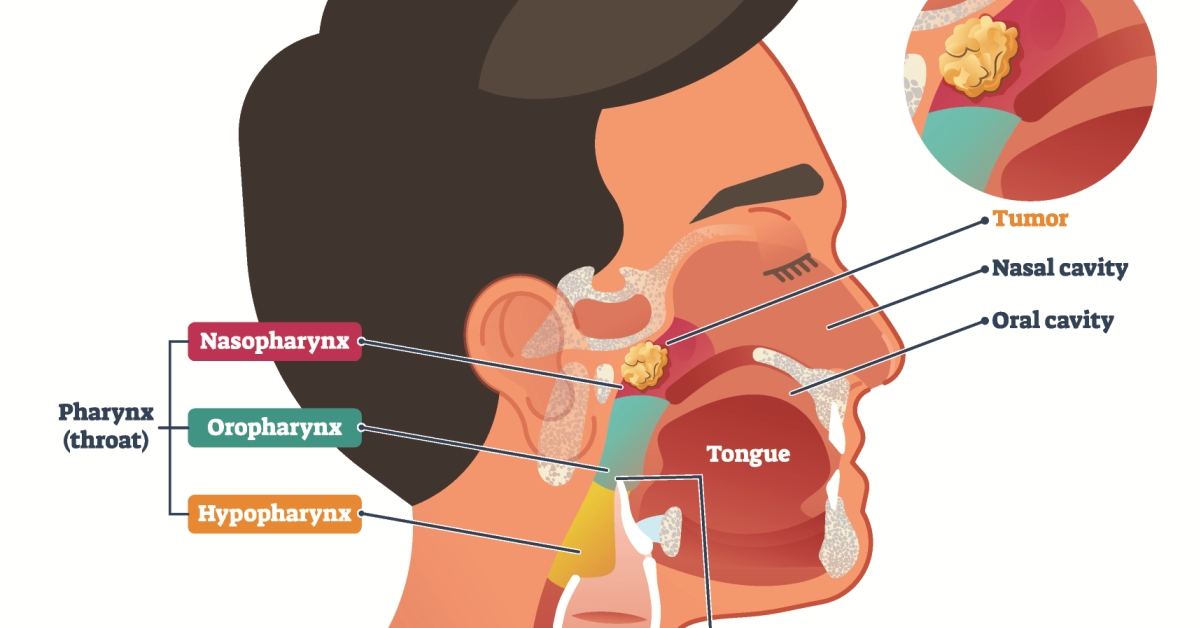
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that originates in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose.

Gallbladder cancer is a rare and aggressive malignancy that originates in the tissues of the gallbladder, often presenting with vague symptoms that can lead to late-stage diagnosis.
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) is the final stage of chronic kidney disease, where the kidneys can no longer function effectively, leading to the accumulation of waste products in the body.
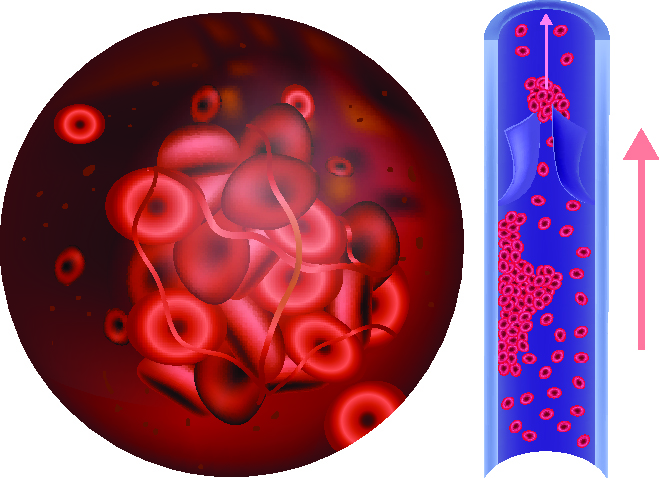
Thrombophilia is a blood disorder that increases the risk of abnormal blood clotting, potentially leading to conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
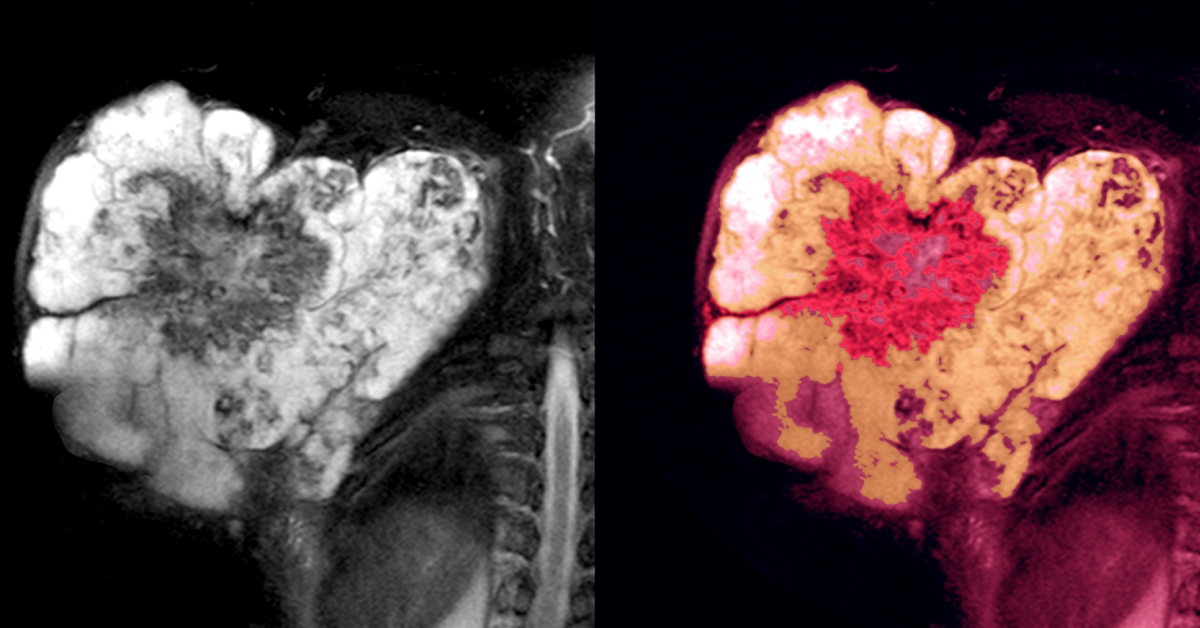
Soft tissue sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that arises in the connective tissues of the body, such as muscles, fat, nerves, and blood vessels.
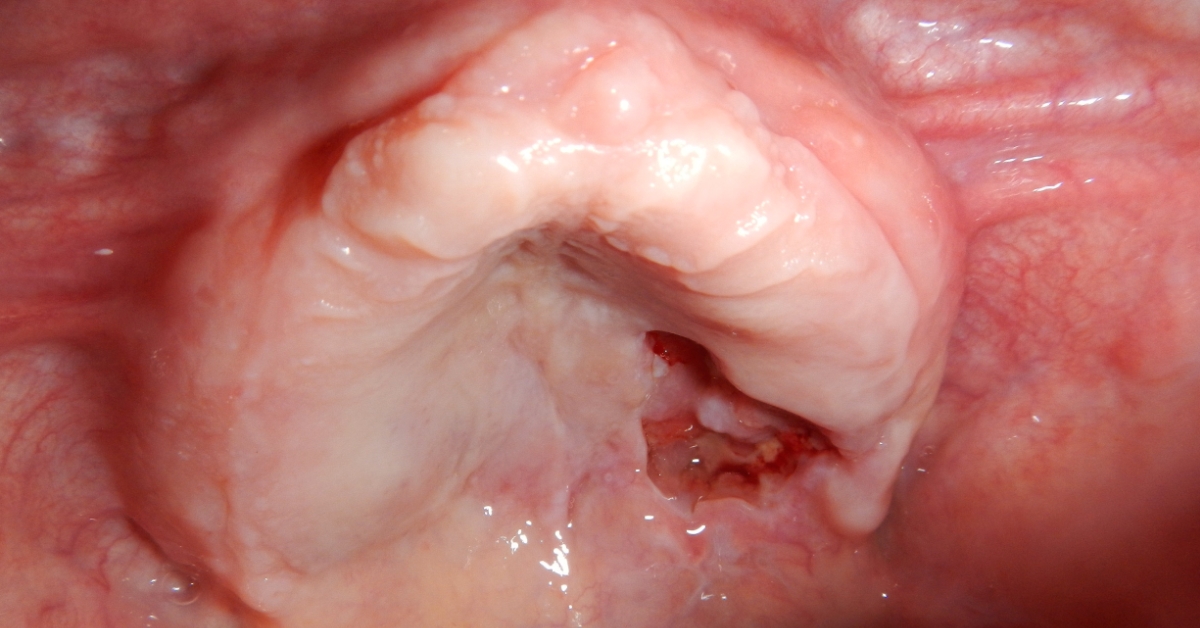
Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia is a rare type of blood cancer characterized by the overproduction of a specific antibody known as IgM, leading to various health complications.

Laryngeal cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the larynx (voice box), often linked to risk factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
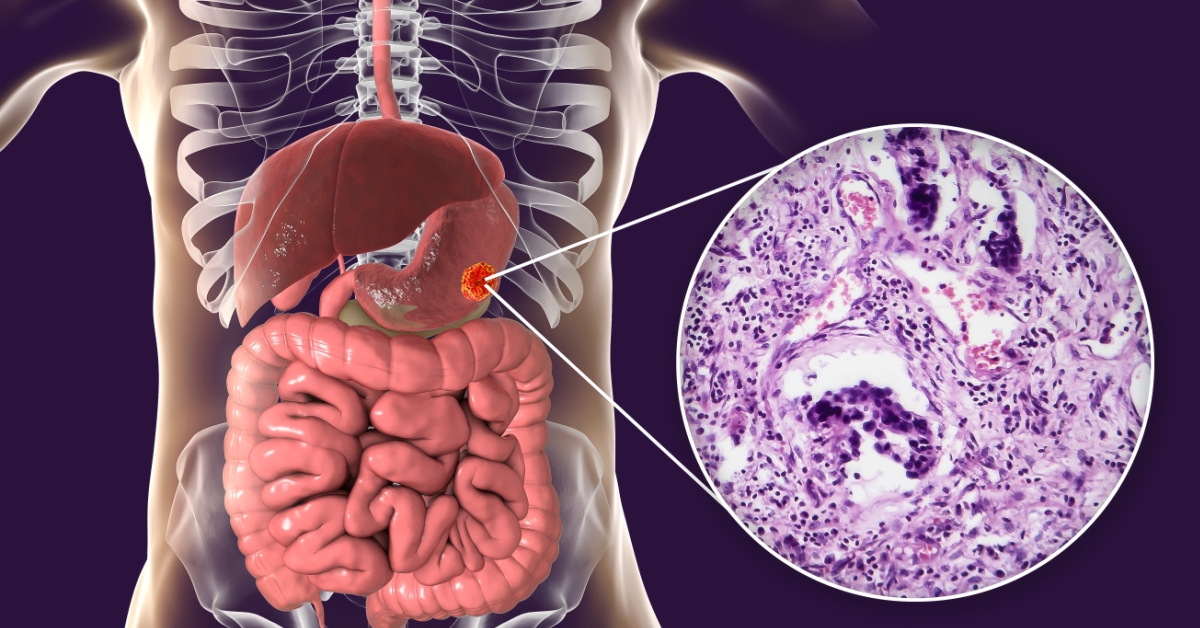
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a serious condition characterized by bleeding in the digestive tract, which can result from various causes such as ulcers, tumors, or inflammatory diseases.
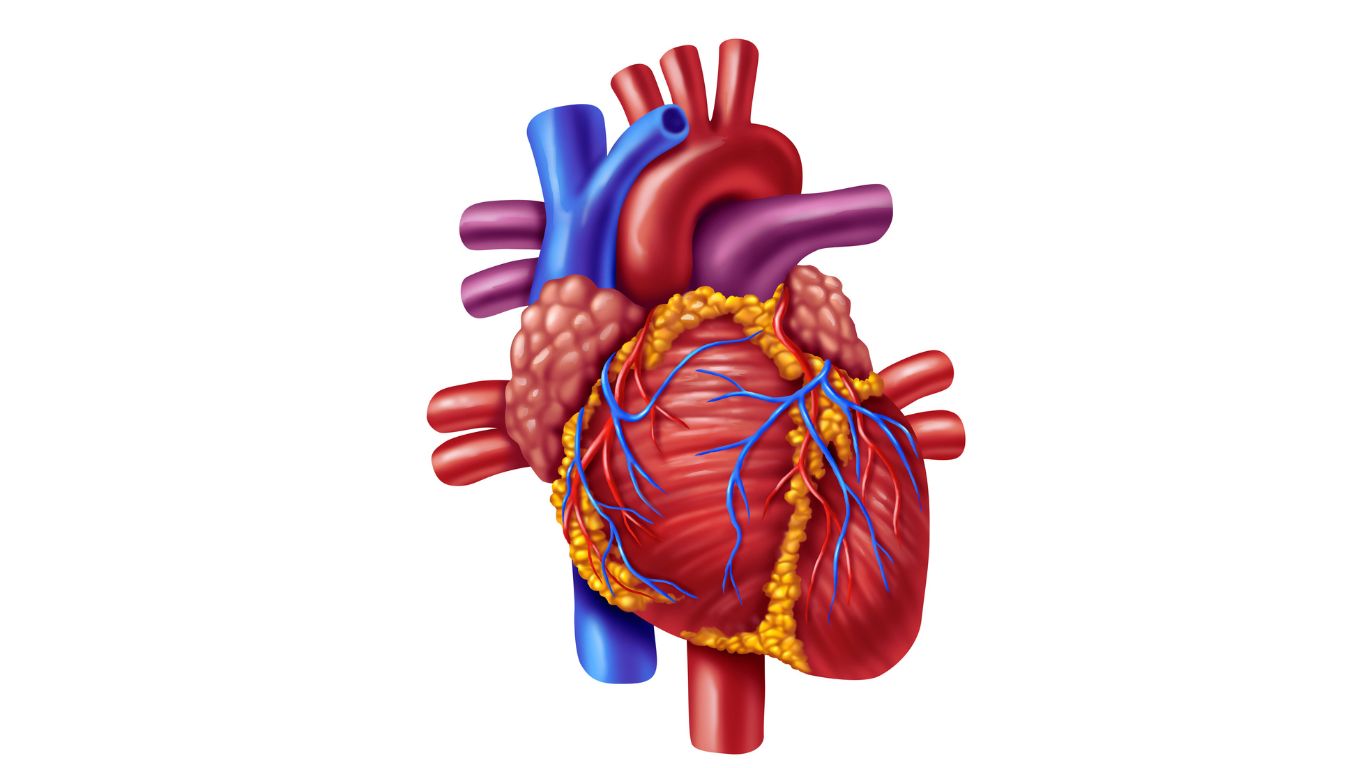
Rheumatic Heart Disease is a condition resulting from damage to the heart valves and heart muscle caused by rheumatic fever, often following untreated strep throat.
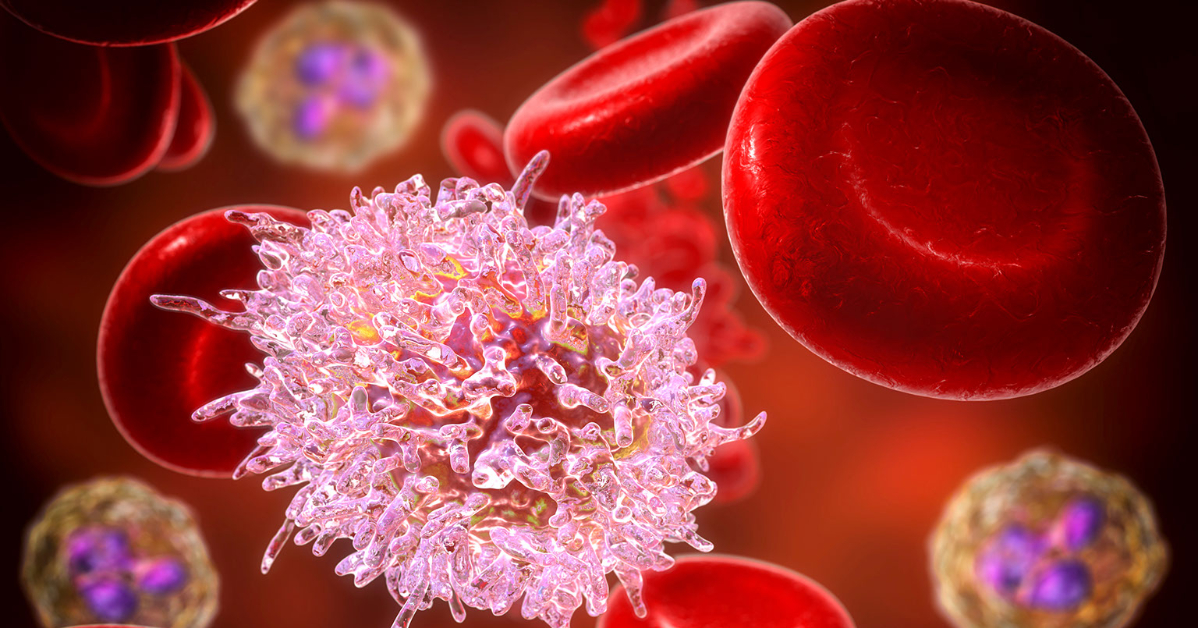
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the accumulation of abnormal lymphocytes.
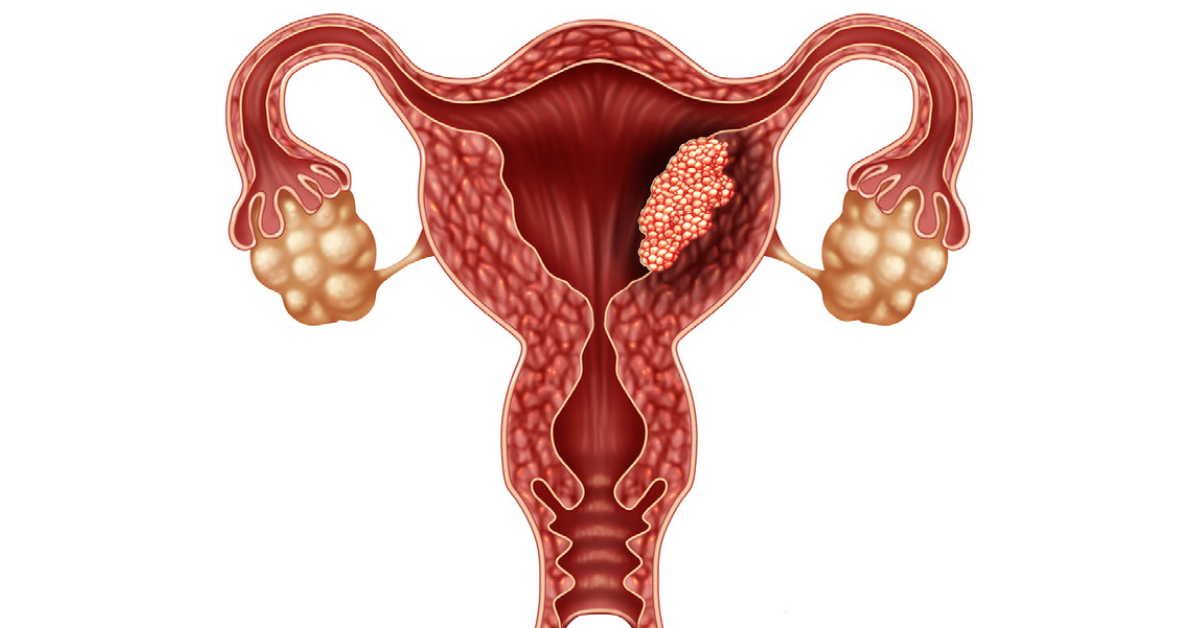
Uterine cancer primarily affects the lining of the uterus and can manifest as abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain.
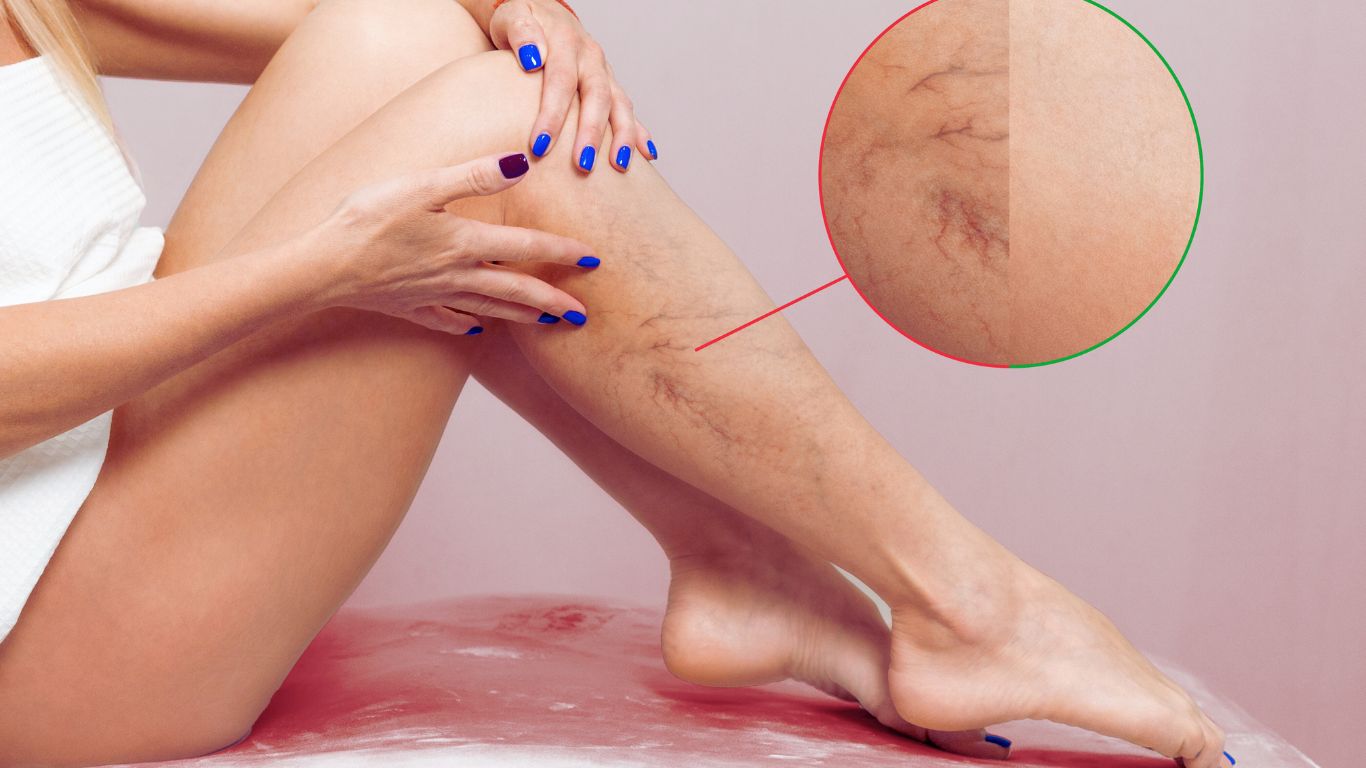
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition characterized by narrowed arteries, which reduces blood flow to the limbs, often causing pain and discomfort, particularly in the legs during physical activity.
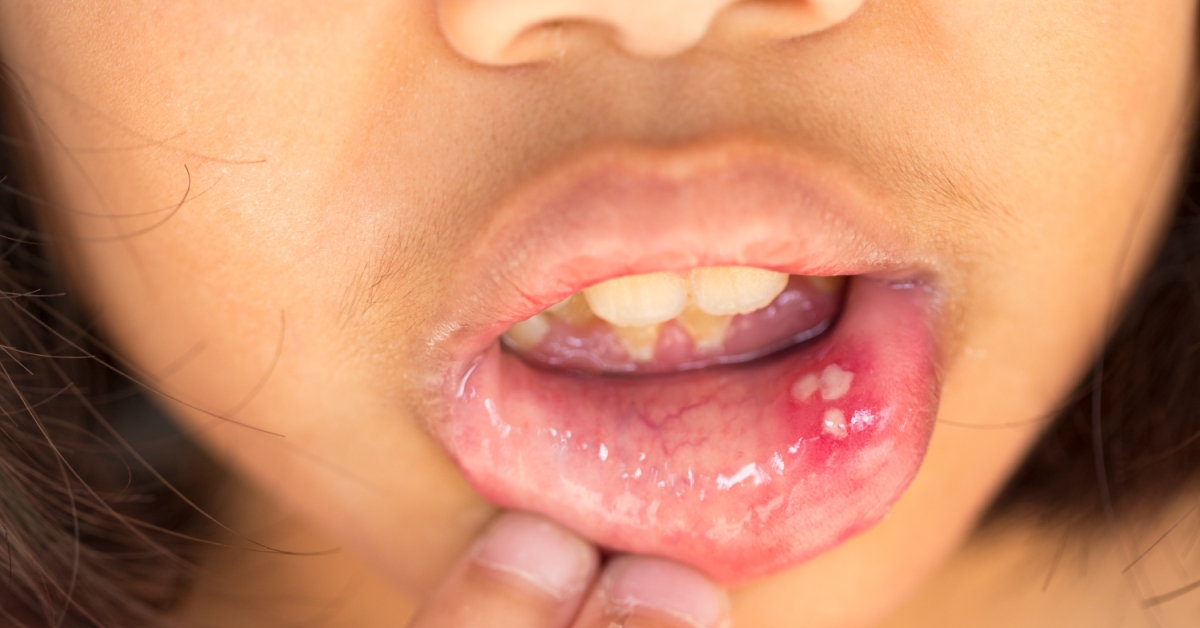
Lip cancer is a type of oral cancer that manifests as growths or lesions on the lip, often linked to sun exposure, tobacco use, and other risk factors.
Chat on WhatsApp!
*Please note: As of now, we are only assisting international patients who plan to come to India for medical treatment.