Cervical Cancer
Cancer occurs when the cells grow abnormally and also invade nearby tissues and eventually spreading to other organs in the body through the bloodstream or the lymph nodes.
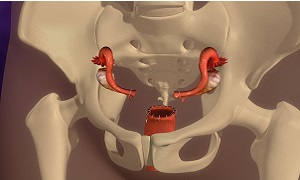
Cervical cancer is the cancer of cervix. It the lowest part of uterus and connects the uterus with vagina. Cervical cancer is invasive, it effects the deeper tissues of the cervix and may also effect other part of the body like the lungs, liver, rectum and vagina.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
- Infection caused by Human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Weak immune system
- Smoking
- Having sex at an early age increases the risk of HPV.
- Intake of oral contraceptive pills for more than 5 years
Signs & Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
- Unusual vaginal bleeding like bleeding after menopause, bleeding between regular menstrual periods
- Pain in pelvis
- Frequent urination
- Pain during urination
- Heavy or unusual discharge that may be watery, thick, and possibly have a foul odour
Stages of Cervical Cancer
- Stage I: Cancer is present in the cervix.
- Stage II: Cancer is present in the cervix as well the lower part of the vagina.
- Stage III: Cancer is present in the cervix as well the lower & upper part of the vagina.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to nearby organs, like the bladder or rectum & it may have spread to other areas of the body, such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Pap Test
HPV DNA Test
Punch biopsy
Endocervical curettage
Electrical wire loop
Cone Biopsy
Treatment of Cervical Cancer
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is surgical removal of the uterus. Hysterectomy may be:
Simple hysterectomy: Surgical removal of cervix and uterus along with the removal of cancer, or
Radical hysterectomy: Surgical removal of cervix, uterus, part of the vagina and lymph nodes in the affected area.
Chemo Treatment
Chemo treatment is the use of anti-cancer drug that helps to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells that cause cancer. It prevents the growth of rapidly dividing cells by killing the dividing cells.
Despite its side effects, chemo is still the most widely used cancer treatment option. Unlike radiation and surgery which treats cancer cells at particular locations, chemo drugs can kill cancer cells that have metastated (spread) to different organs in the body.
Radiation Treatment
Radiation Treatment is a kind of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation beams to kill cancer cells to shrink the tumors. Radiation kills the cancer cells by destroying the DNA. Cancer cells with damaged DNA fail to multiply and die. They are then removed by the body’s mechanism.
Targetd Drug Treatment
Targeted treatment is a type of cancer treatment that uses cancer drugs. However, it is different from traditional chemo treatment, which also uses drugs to kill cancer cells. In Targeted treatment, the cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival are targeted. Targeted treatment is generally used with chemo and other interventions.
Immuno Treatment
Immuno treatment (also called biologic treatment) is a new type of cancer treatment where the body’s immune system is boosted to help the body fight cancer by itself. Immuno treatment uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function.
FAQs
What is the survival rate for cervical cancer?
- The survival rate for cervical cancer is about 92%, if detected early.
How long does it take cervical cancer to spread?
- It typically takes 10-15 years before invasive cervical cancer develops.
How is cervical cancer detected?
- A Pap test can detect cancerous cells in the cervix.
What is the most common age for cervical cancer?
- Frequently diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 44.