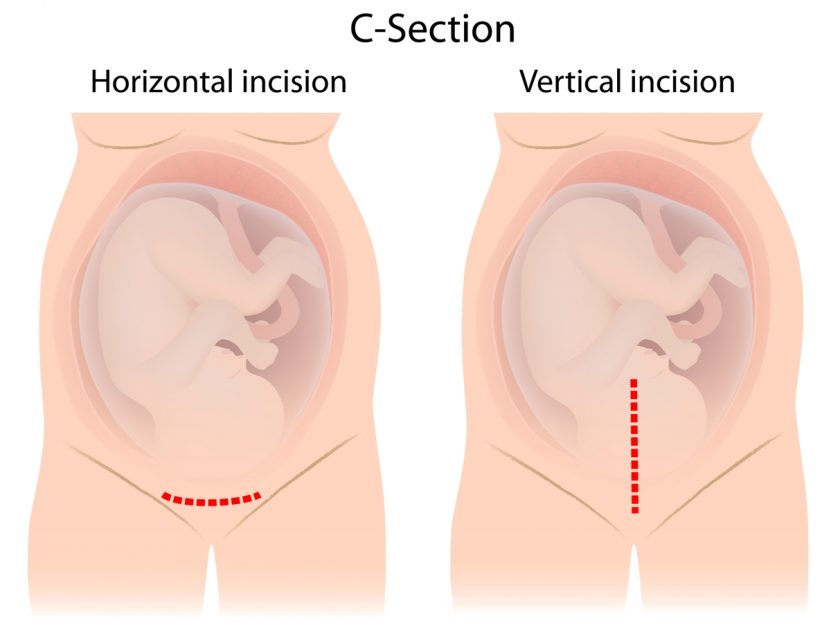
C-Section
A C-section, or cesarean section, is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus, typically when a vaginal delivery poses risks to the mother or child.

A C-section, or cesarean section, is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus, typically when a vaginal delivery poses risks to the mother or child.
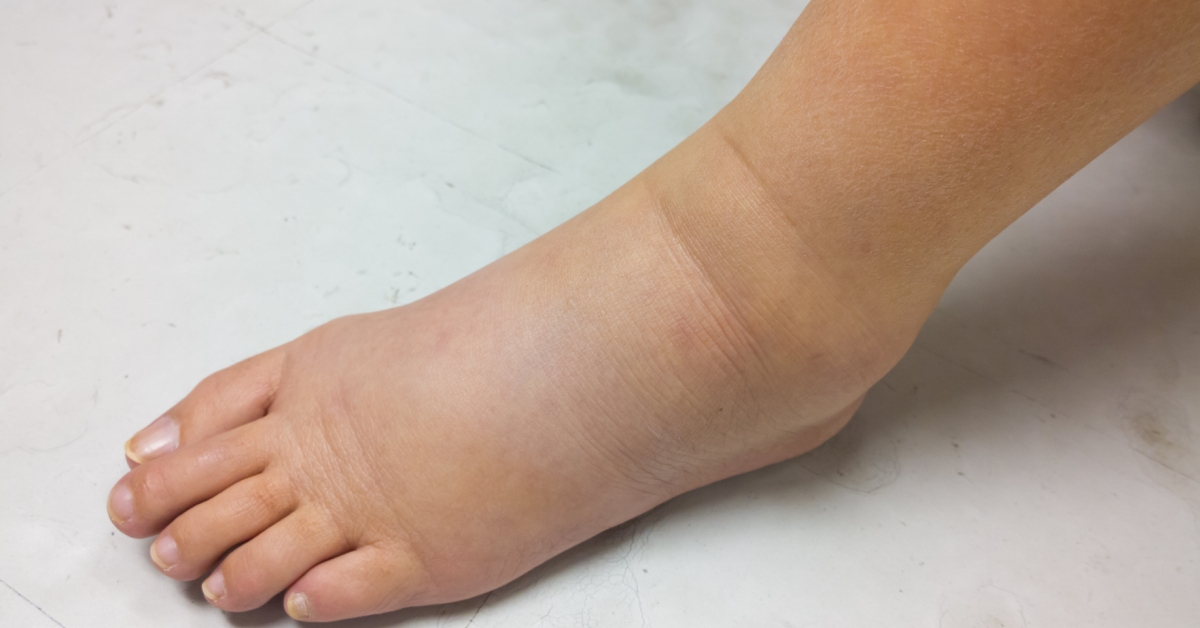
Dependent edema is a condition characterized by swelling in specific areas of the body, usually the legs or feet, due to fluid accumulation.
Coarctation of the aorta is a congenital condition characterized by a narrowing of the aorta, which can lead to high blood pressure and heart complications.
Vocal cord paralysis occurs when the nerves that control the vocal cords are damaged, leading to difficulties in speaking, breathing, or swallowing.
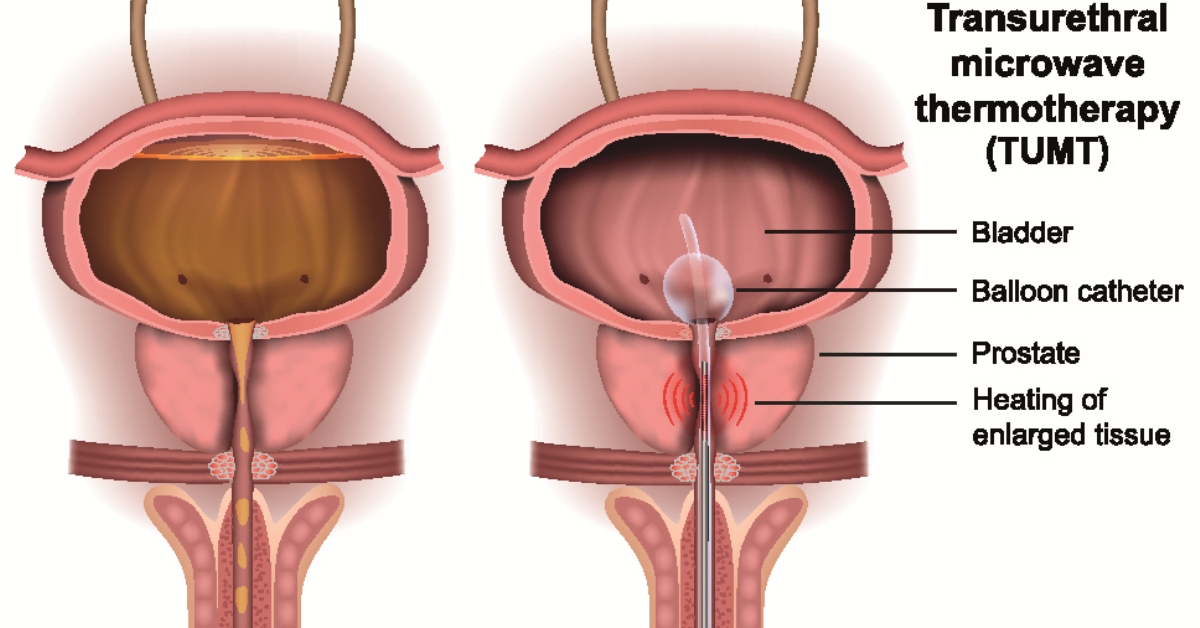
Urethral diverticulum is a condition characterized by the formation of a pouch or sac in the urethra, often leading to urinary issues and discomfort.
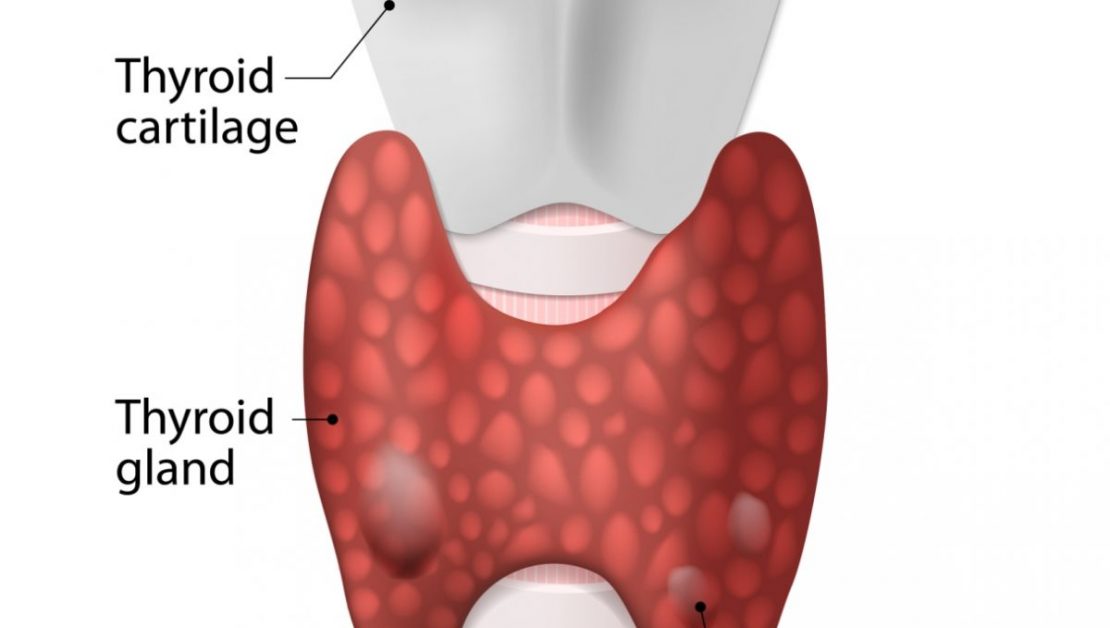
A thyroid cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms within the thyroid gland, often detected during imaging studies.
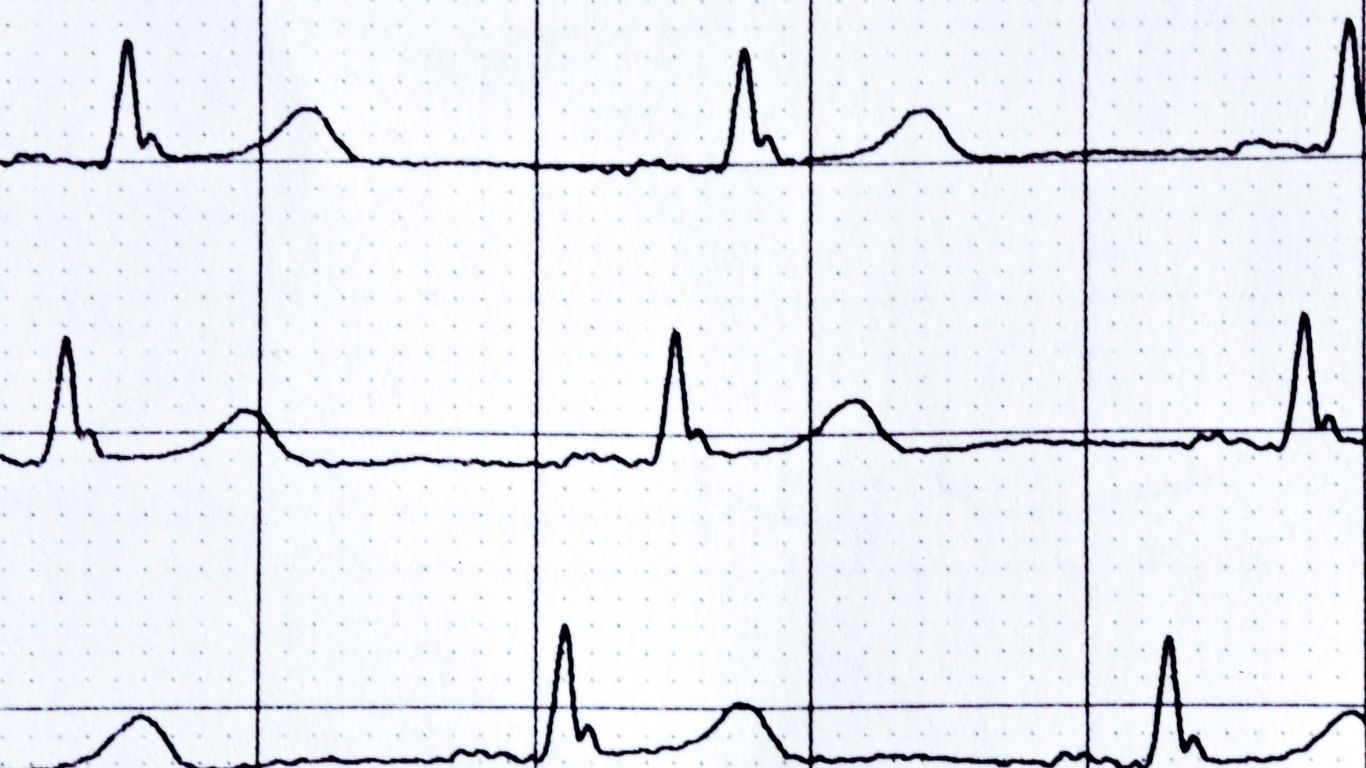
Tachy-brady syndrome is a condition characterized by alternating episodes of rapid and slow heart rates, often leading to symptoms like dizziness or fainting.

Subglottic stenosis is a narrowing of the airway below the vocal cords, often leading to breathing difficulties and stridor.
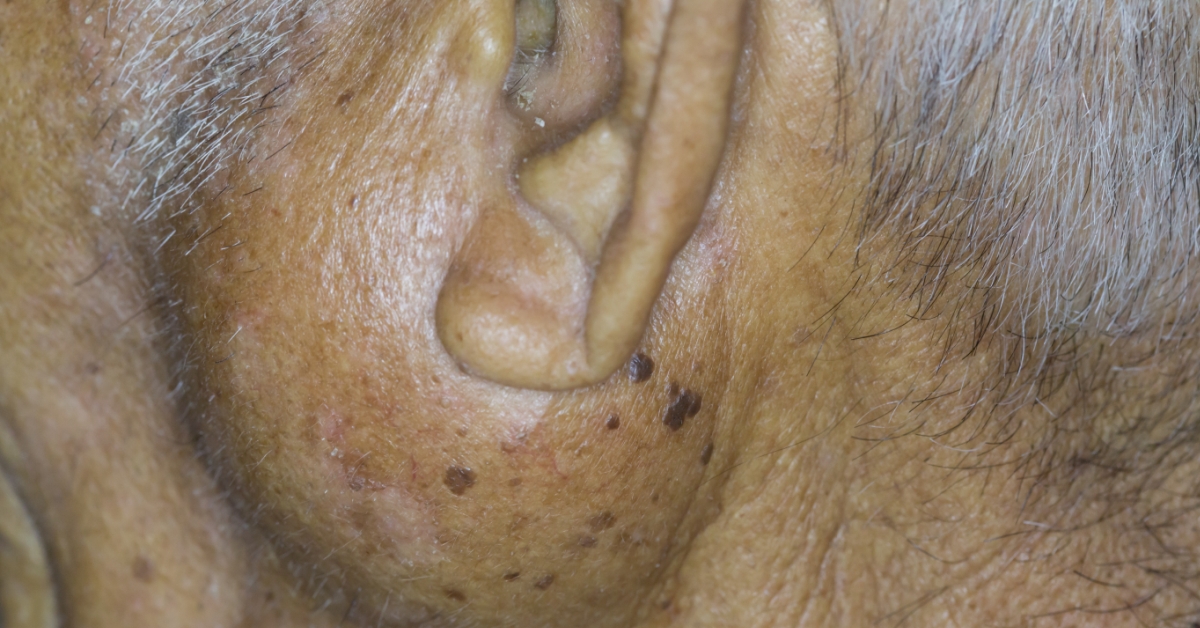
A parotid gland tumor is an abnormal growth that occurs in the largest salivary gland, located near the jaw and ear.

A colloid cyst is a benign, fluid-filled tumor typically located in the brain’s third ventricle, which can obstruct cerebrospinal fluid flow and lead to increased intracranial pressure.
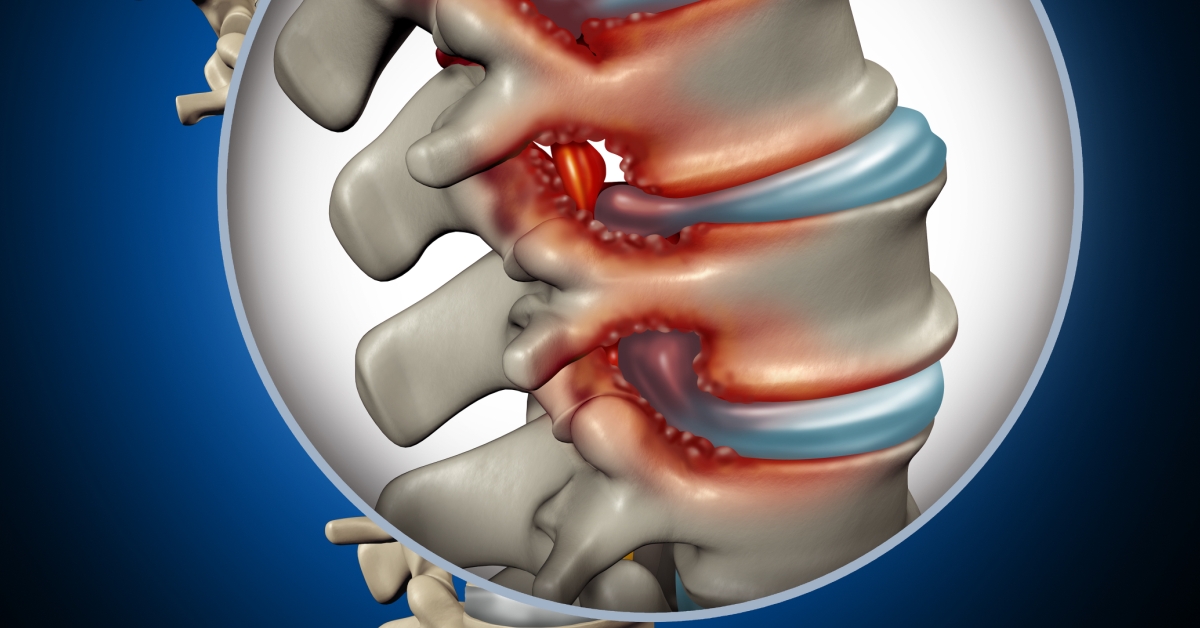
Cervical spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal in the neck, which can compress spinal nerves and lead to pain, numbness, and weakness.
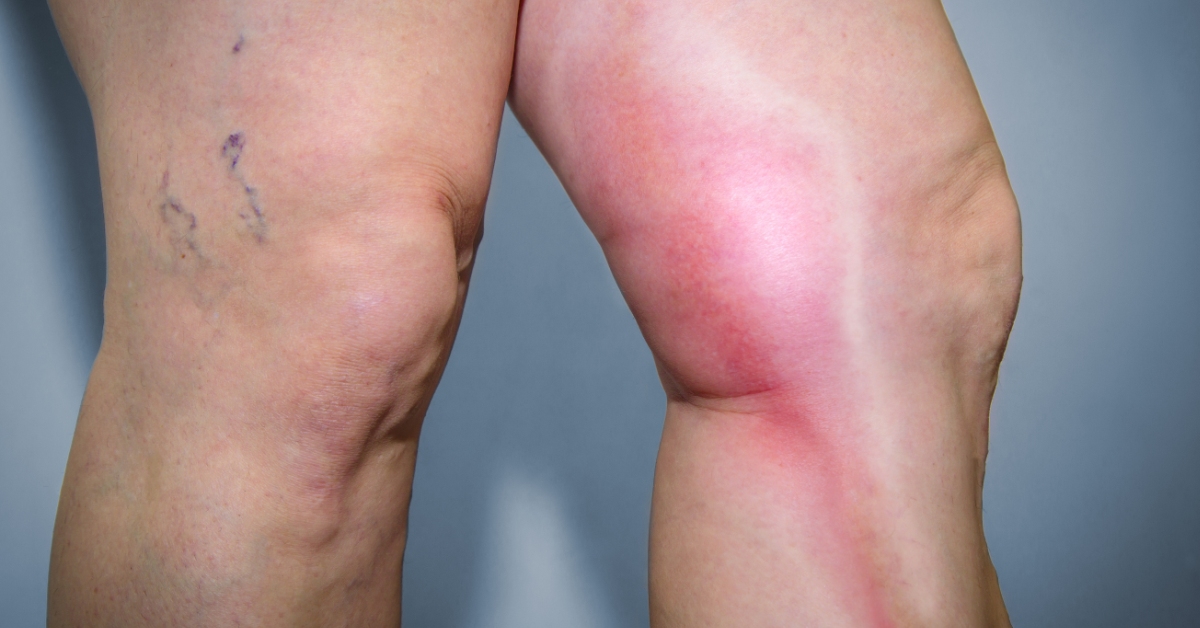
Venous thrombosis is a condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot within a vein, often occurring in the legs and potentially leading to serious complications.
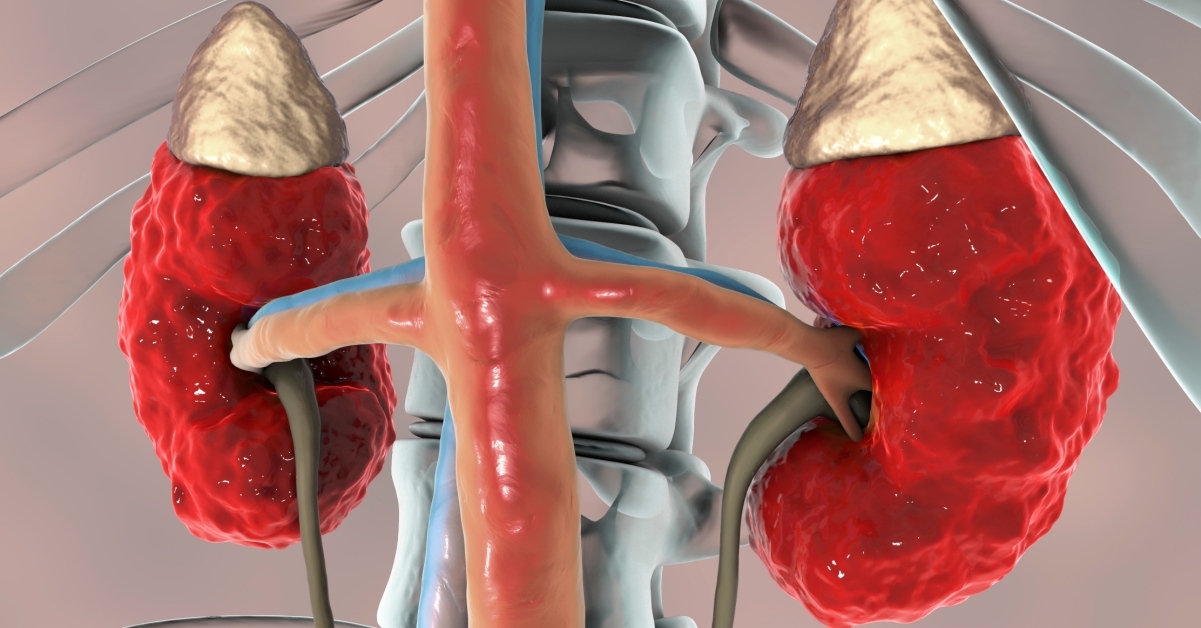
Minimal Change Disease is a kidney disorder characterized by a sudden onset of nephrotic syndrome, leading to significant protein loss in the urine and swelling.
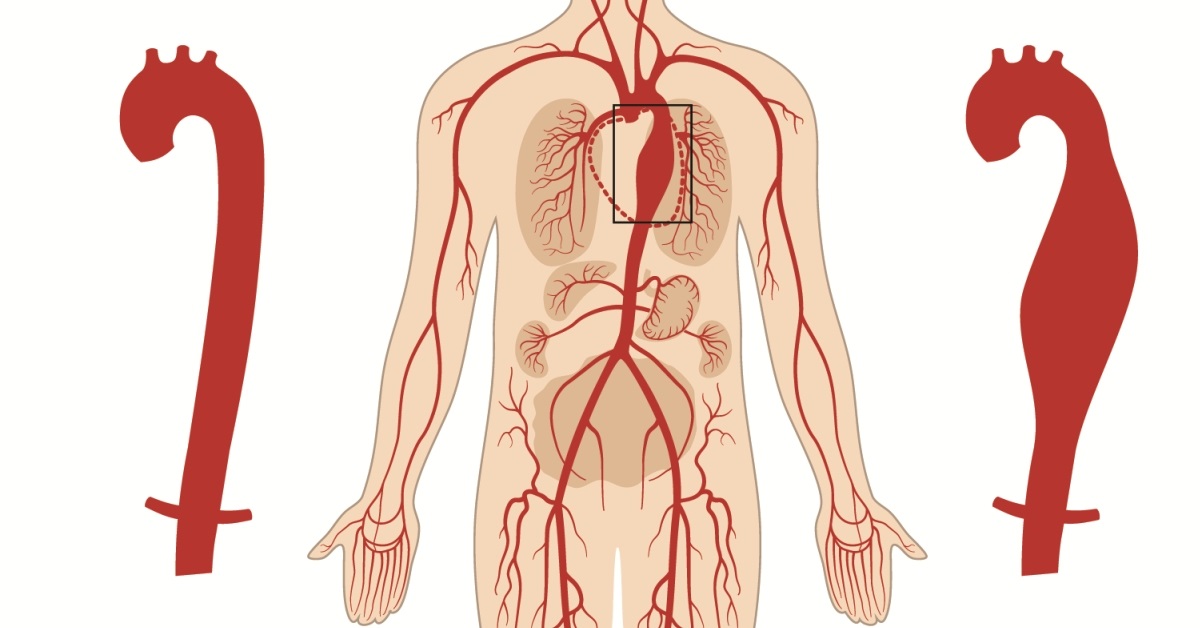
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of the aorta as it passes through the chest, potentially leading to serious complications if it ruptures.
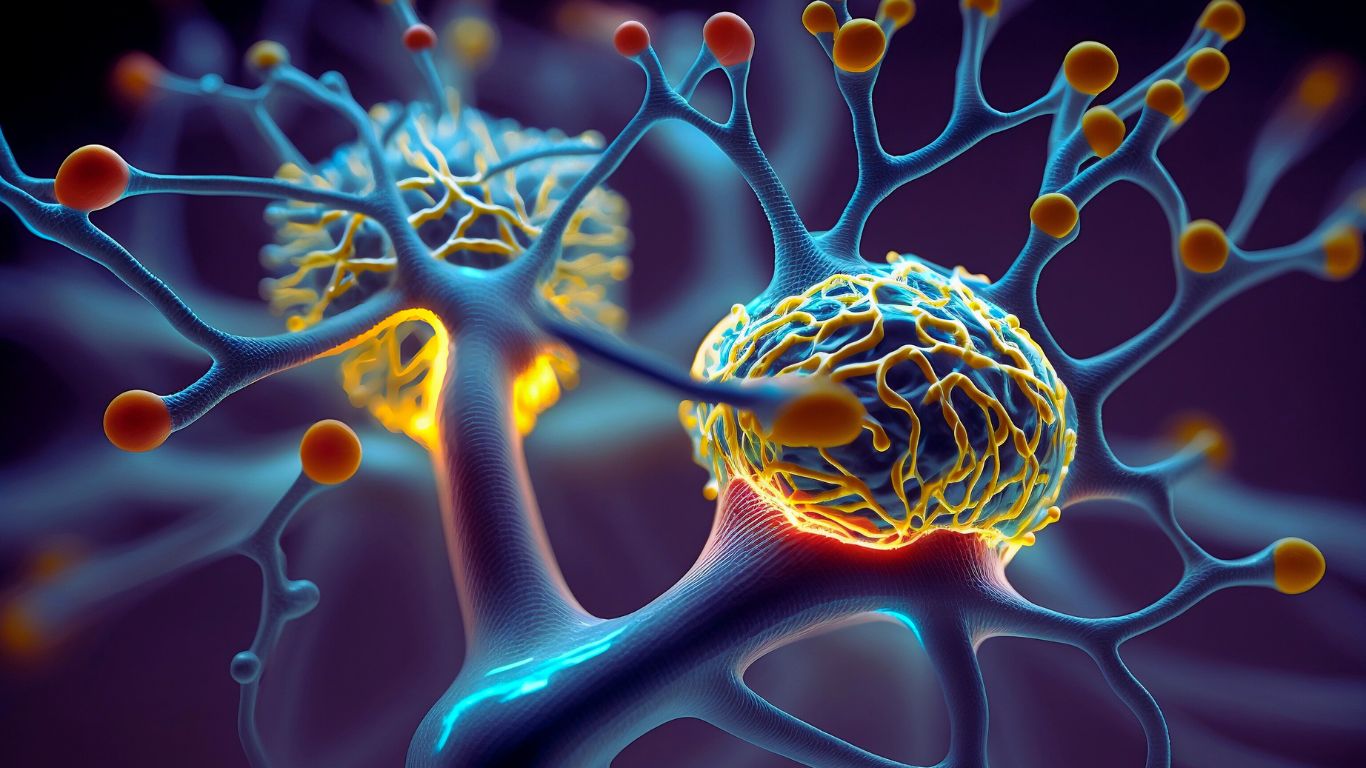
Motor neuron disease is a progressive condition that affects the nerve cells responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movements, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
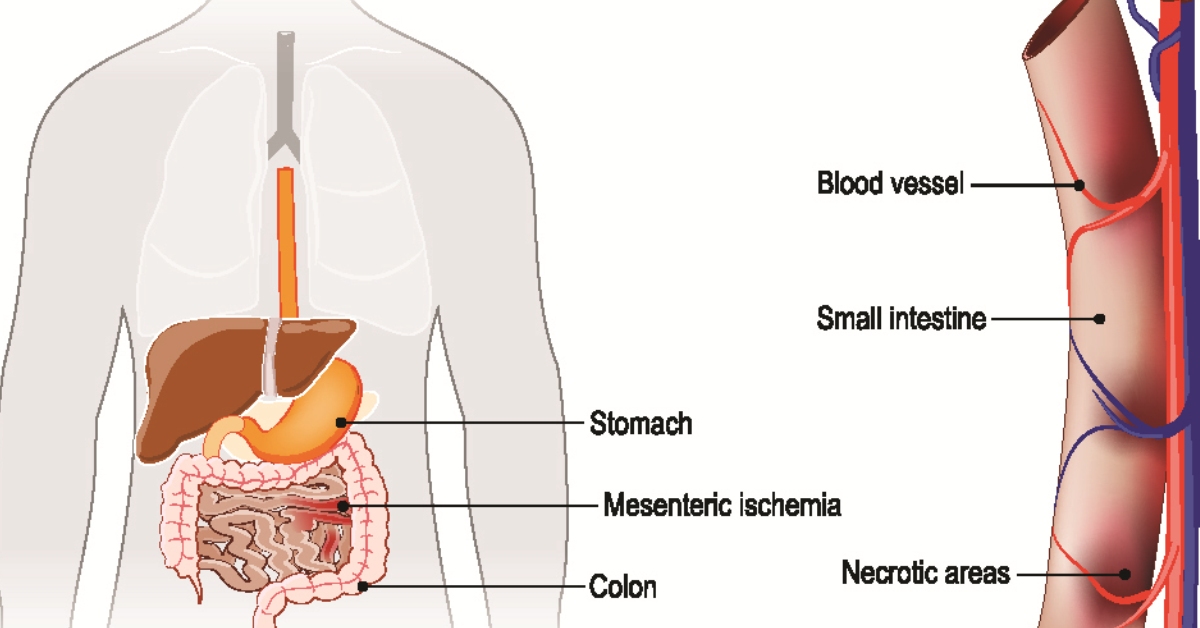
Mesenteric ischemia occurs when narrowed or blocked arteries reduce blood flow to the small intestine, potentially leading to serious complications.
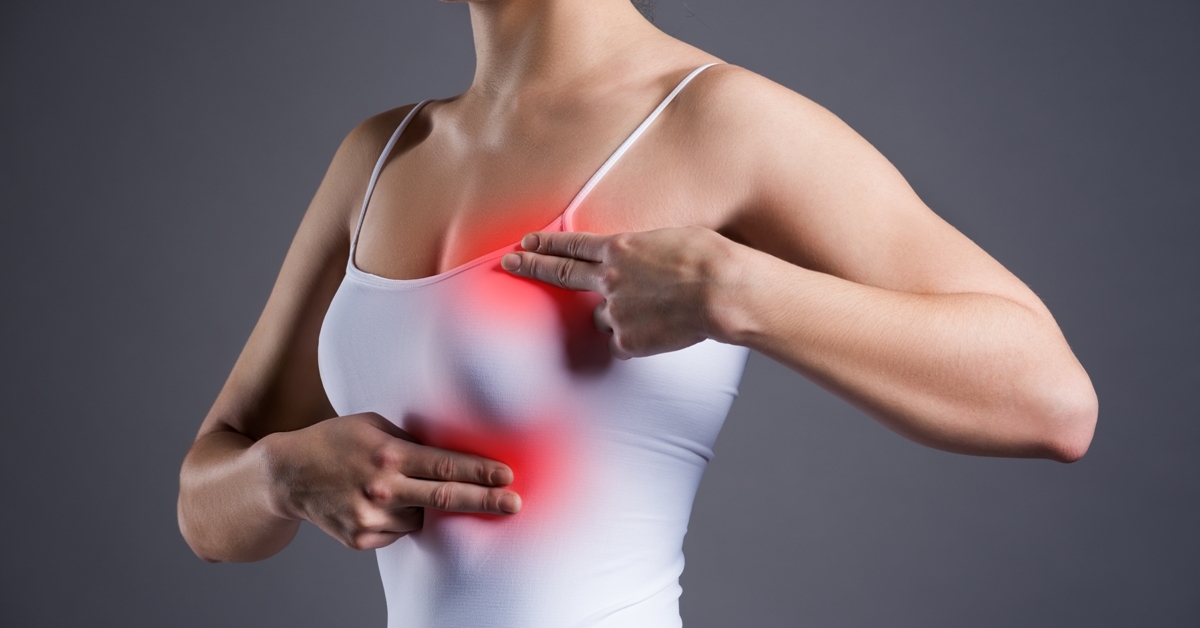
Fibrocystic breasts are characterized by lumpy or ropy breast tissue, often accompanied by discomfort or tenderness, particularly before menstruation.

A dislocated hip occurs when the ball at the top of the thigh bone slips out of its socket in the hip joint, often due to trauma or injury.
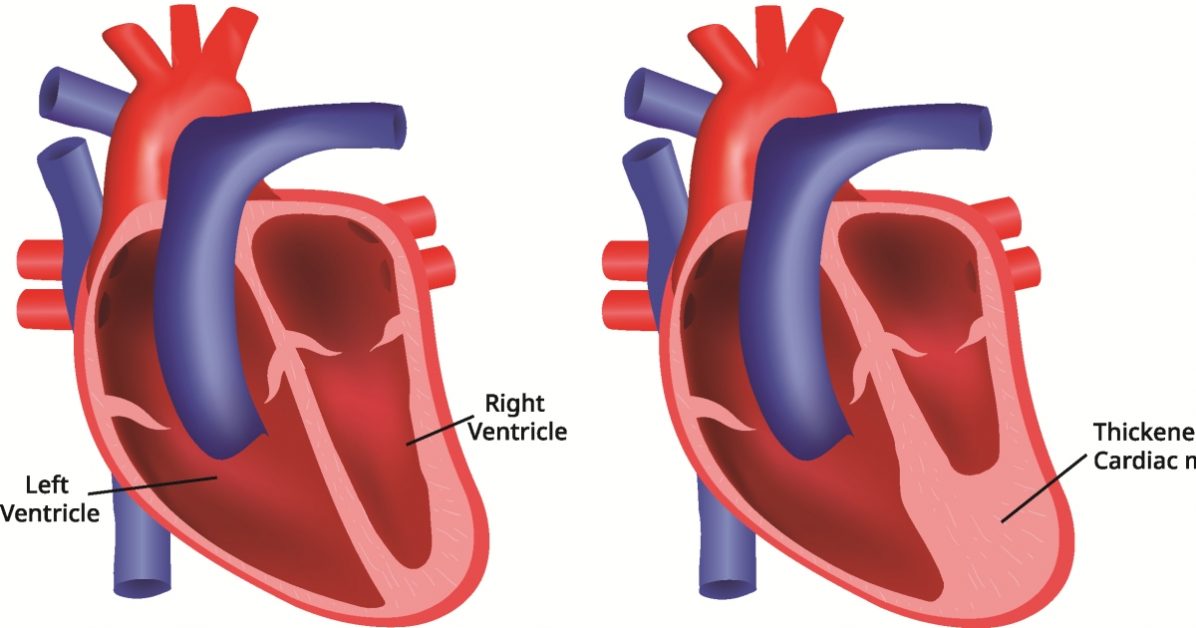
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a narrowing of the pulmonary valve that obstructs blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, potentially leading to heart strain.
Myeloproliferative disorders are a group of conditions where the bone marrow produces too many blood cells, leading to various complications.

Discitis is an infection of the intervertebral discs, often leading to back pain, fever, and mobility issues.
Osteoid osteoma is a benign bone tumor characterized by localized pain, often worse at night, typically affecting the long bones.
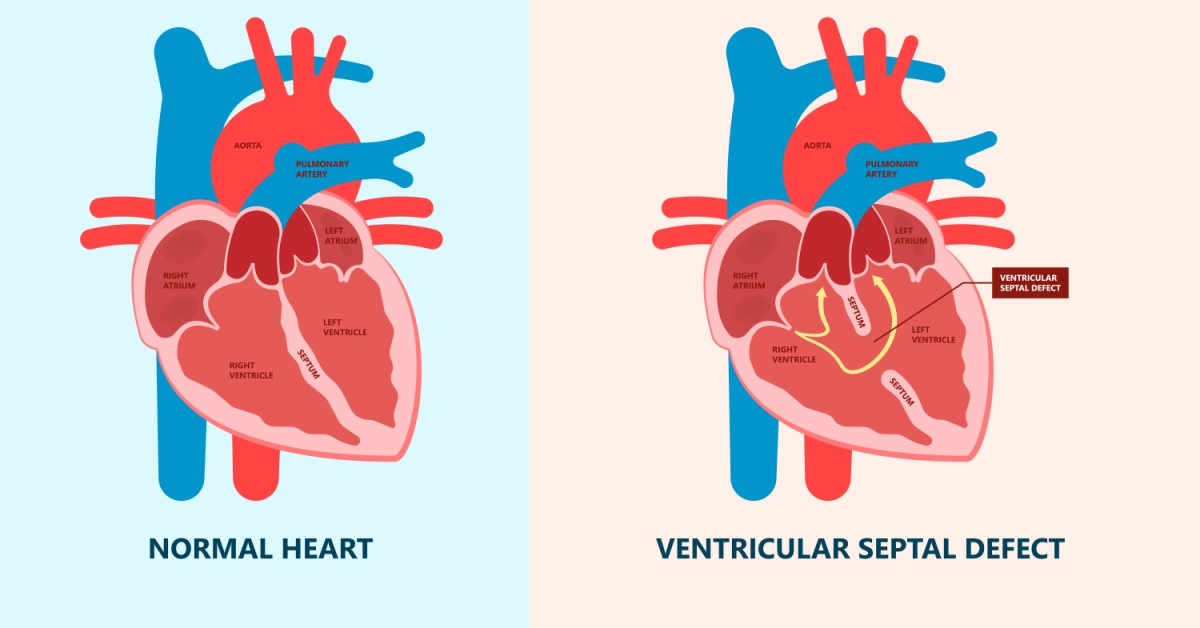
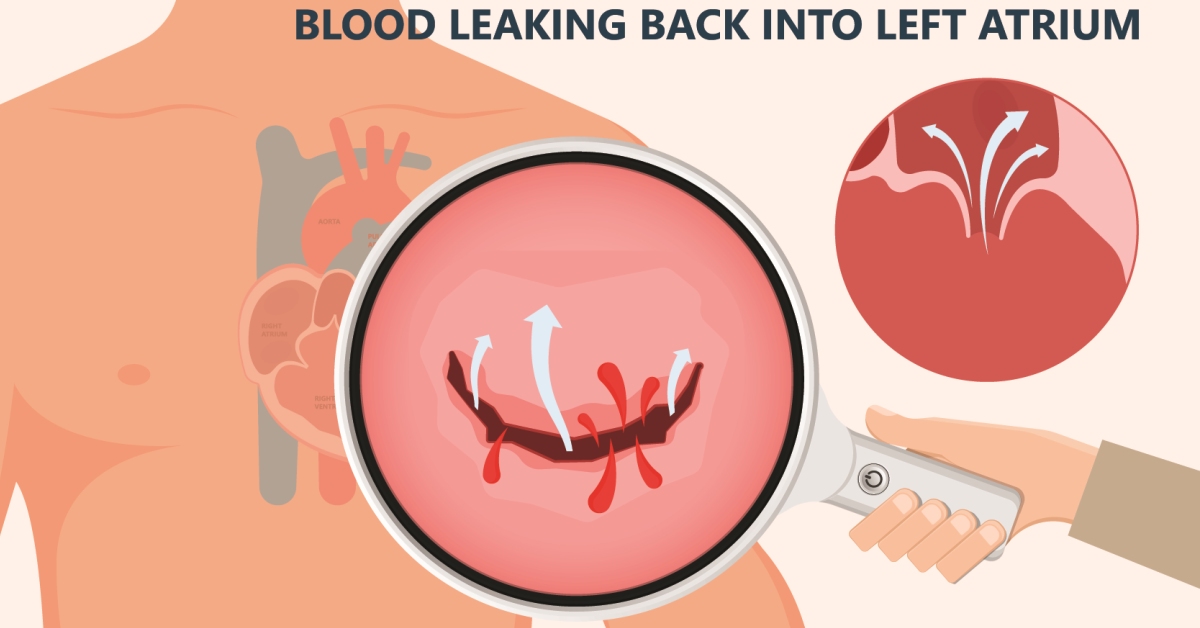
Mitral valve regurgitation is a heart condition where the mitral valve does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward into the left atrium during contraction.
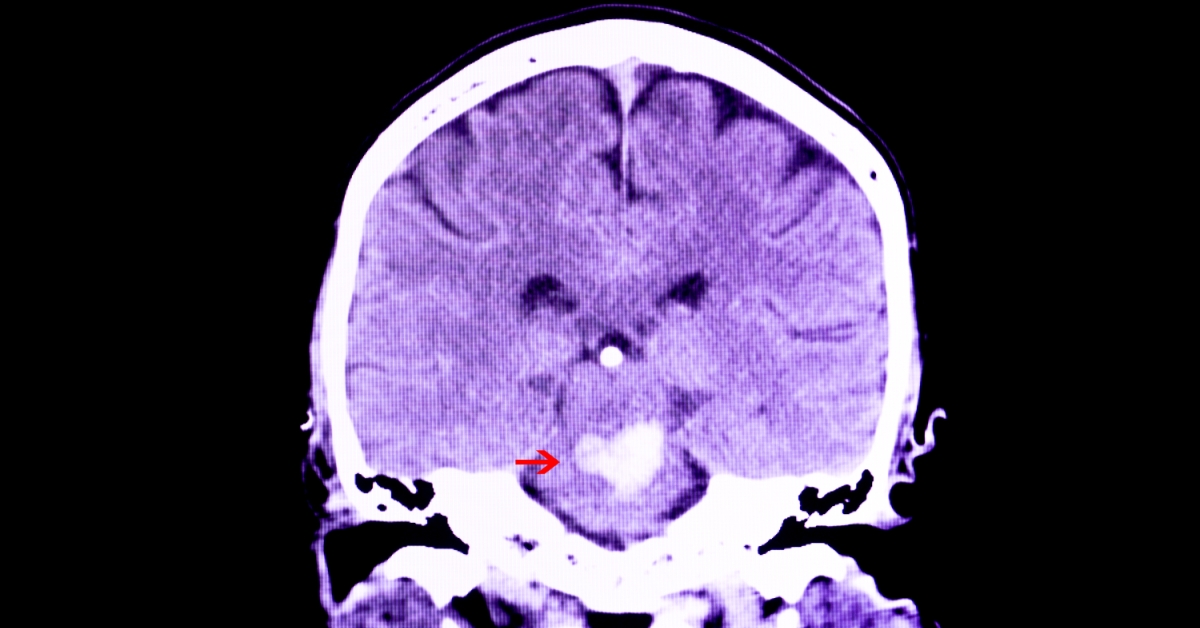
Intracranial hemorrhage is a condition characterized by bleeding within the skull, which can lead to increased pressure on the brain and serious complications.
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome is a congenital heart defect where the left side of the heart is underdeveloped, affecting normal blood flow.
Fibrous dysplasia is a bone disorder where normal bone is replaced with fibrous tissue, leading to weakened bones and deformities.
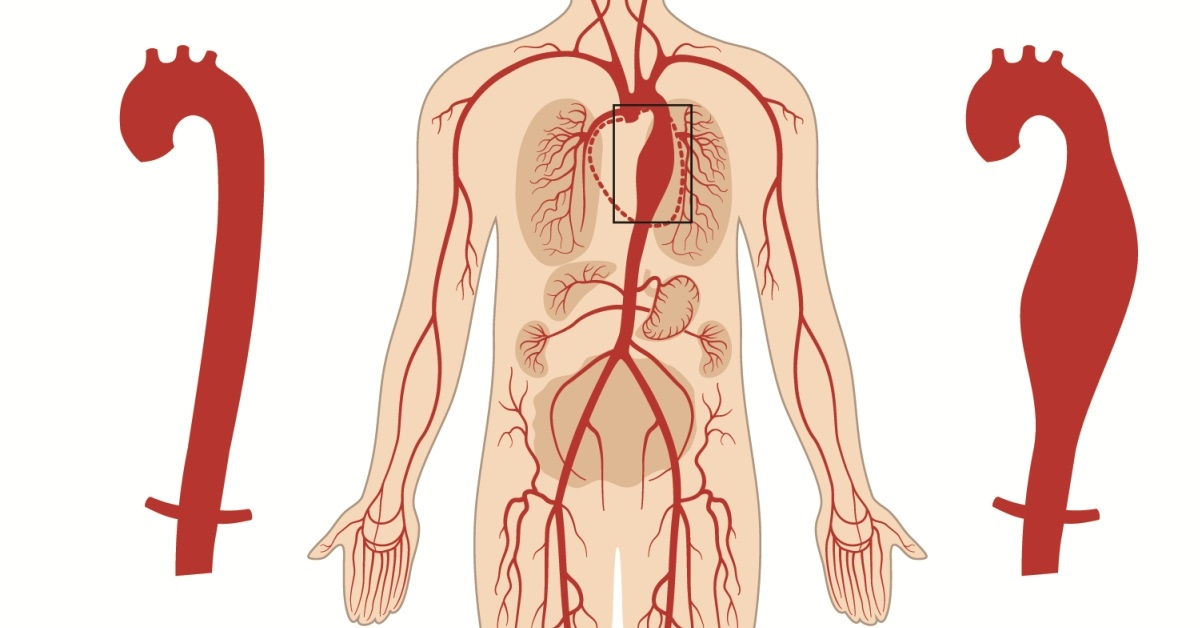
Fibromuscular dysplasia is a vascular condition characterized by abnormal growth in the walls of blood vessels, often leading to narrowing or blockages.
Esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing and discomfort.
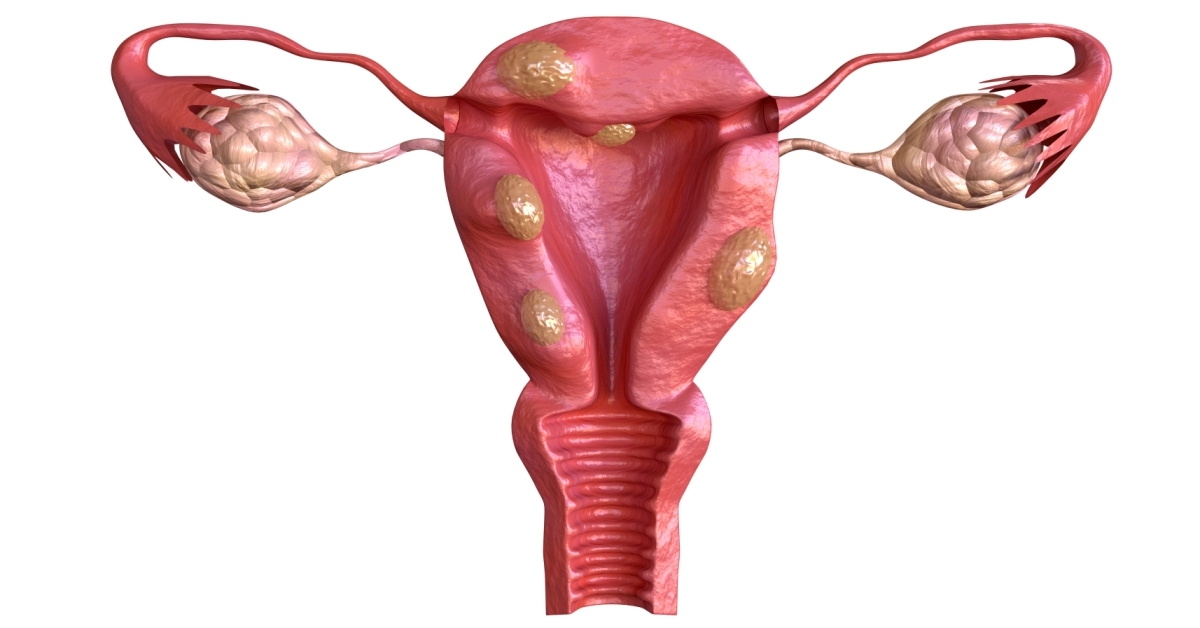
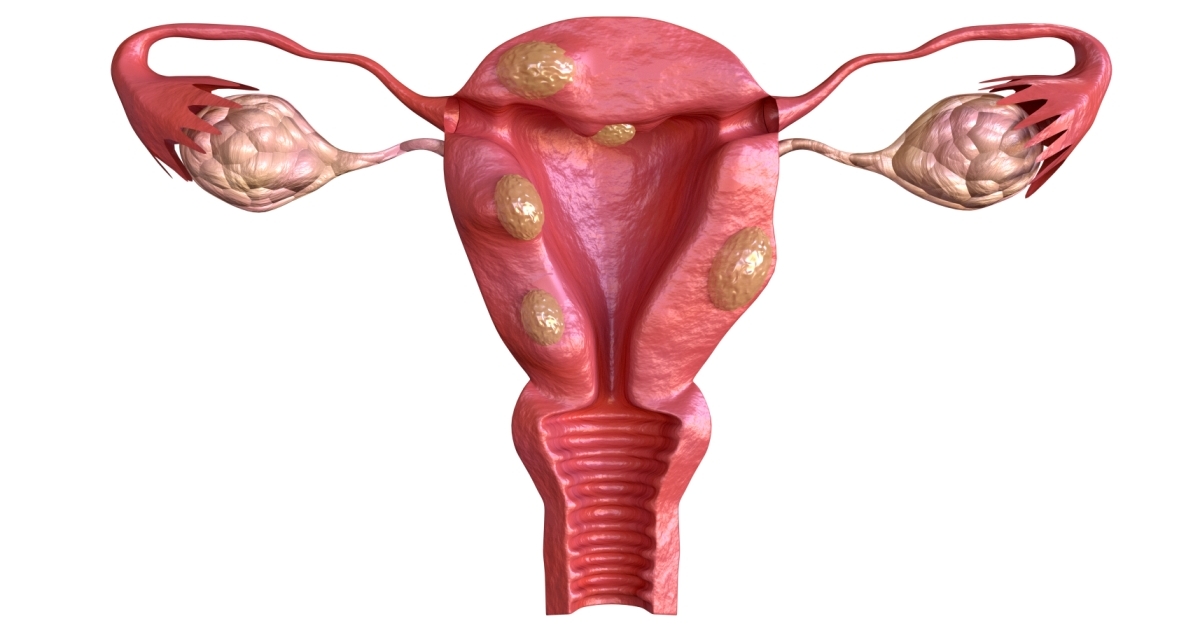
Uterine polyps are growths on the inner lining of the uterus, often caused by hormonal imbalances, and can lead to irregular bleeding or other symptoms.
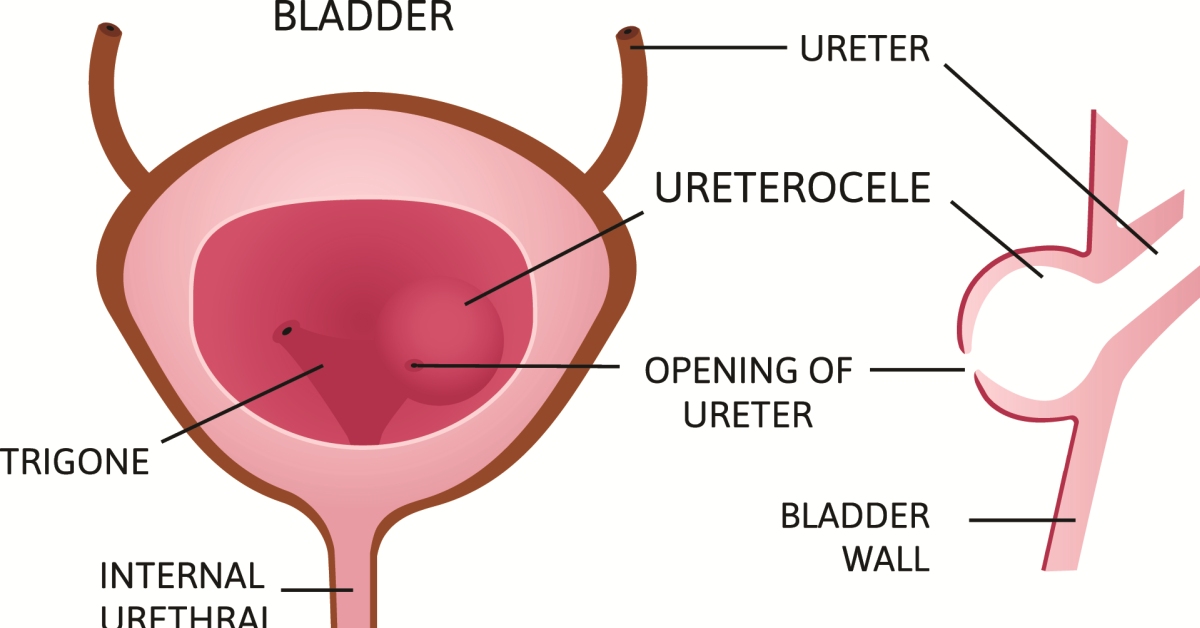
Ureterocele is a congenital condition characterized by a cystic dilation of the distal ureter, often leading to urinary obstruction and complications in the urinary tract.
Truncus arteriosus is a rare congenital heart defect where a single large blood vessel exits the heart, causing oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood to mix.
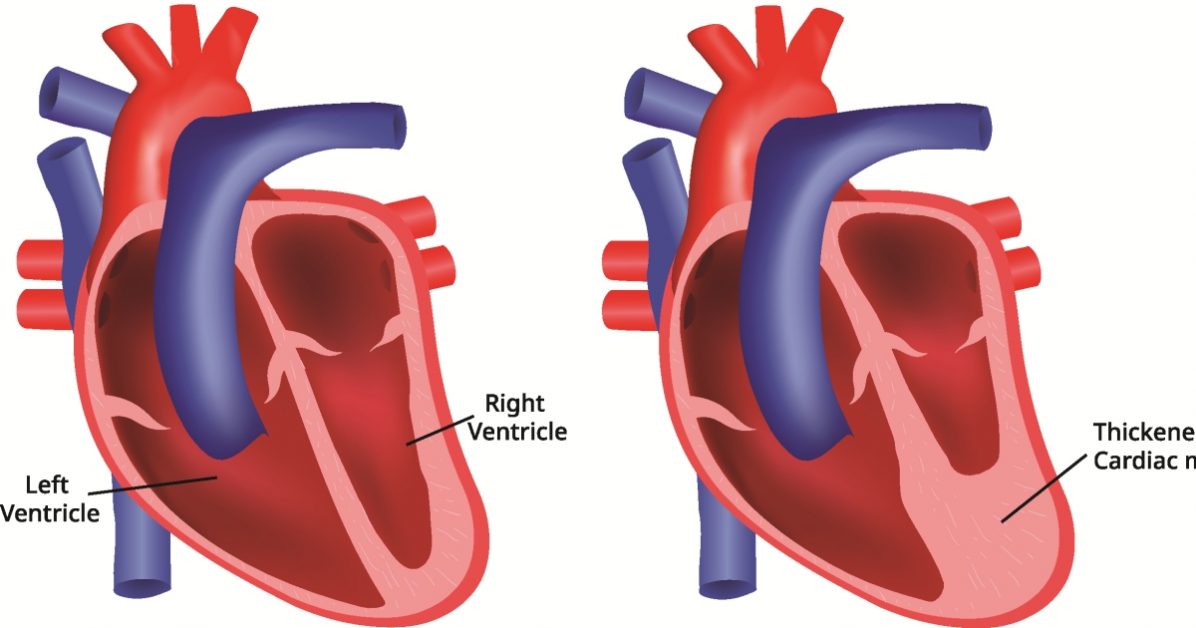
Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA) is a congenital heart defect where the two main arteries carrying blood away from the heart—the aorta and the pulmonary artery—are switched, leading to serious circulation issues.

Tracheoesophageal fistula is a congenital condition where an abnormal connection forms between the trachea and the esophagus, leading to significant swallowing and respiratory difficulties.
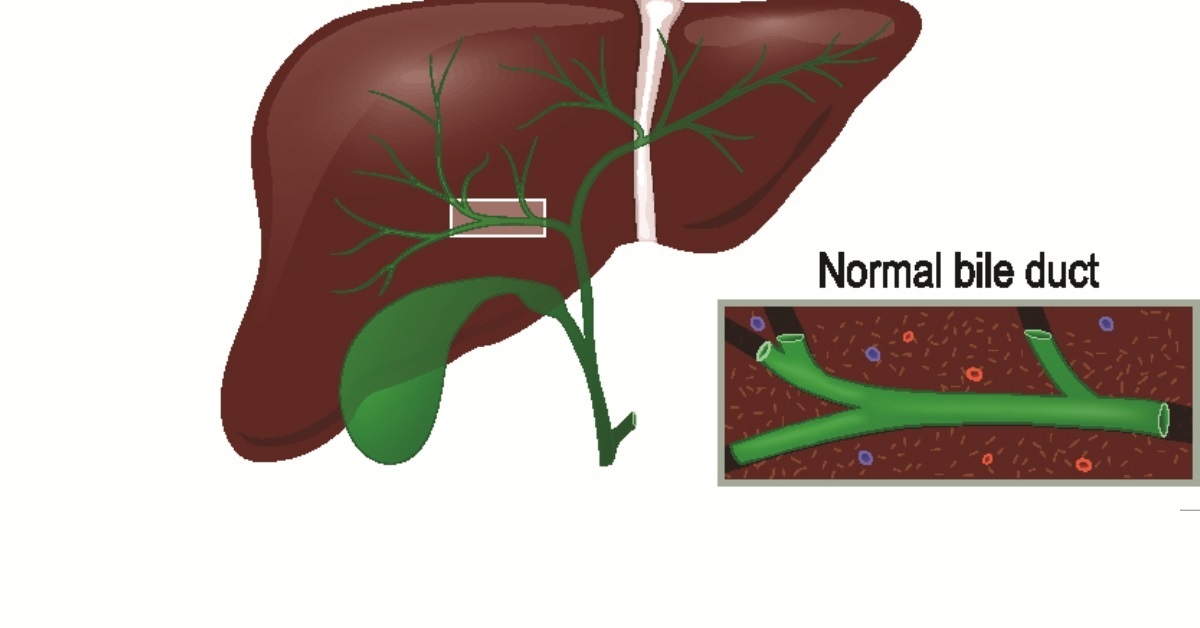
Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, leading to bile accumulation and potential liver damage.
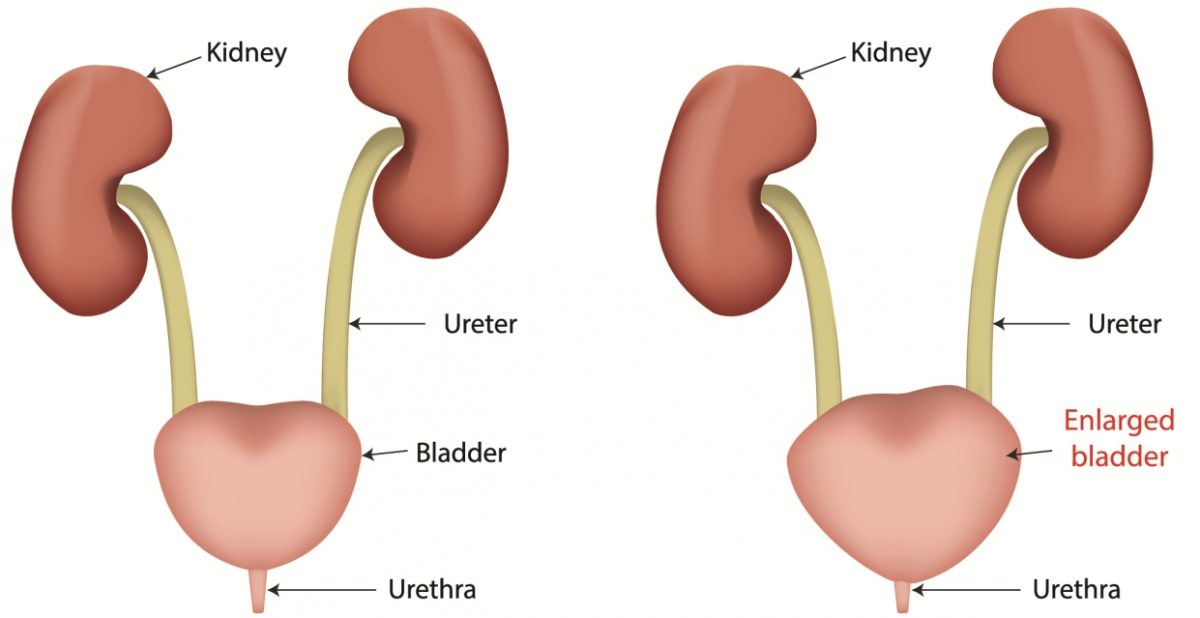
Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when pelvic organs, such as the bladder or uterus, descend into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic support tissues.
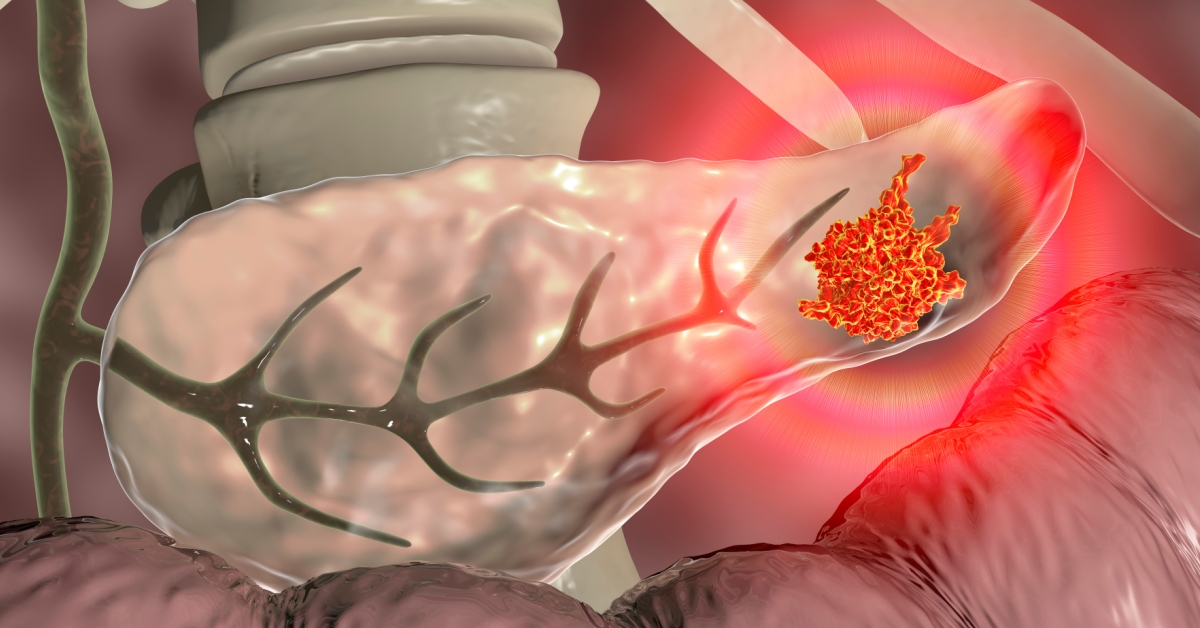
Insulinoma is a rare pancreatic tumor that produces excess insulin, leading to hypoglycemia and various symptoms related to low blood sugar.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare tumors that originate in the connective tissue of the gastrointestinal tract, often affecting the stomach and small intestine.
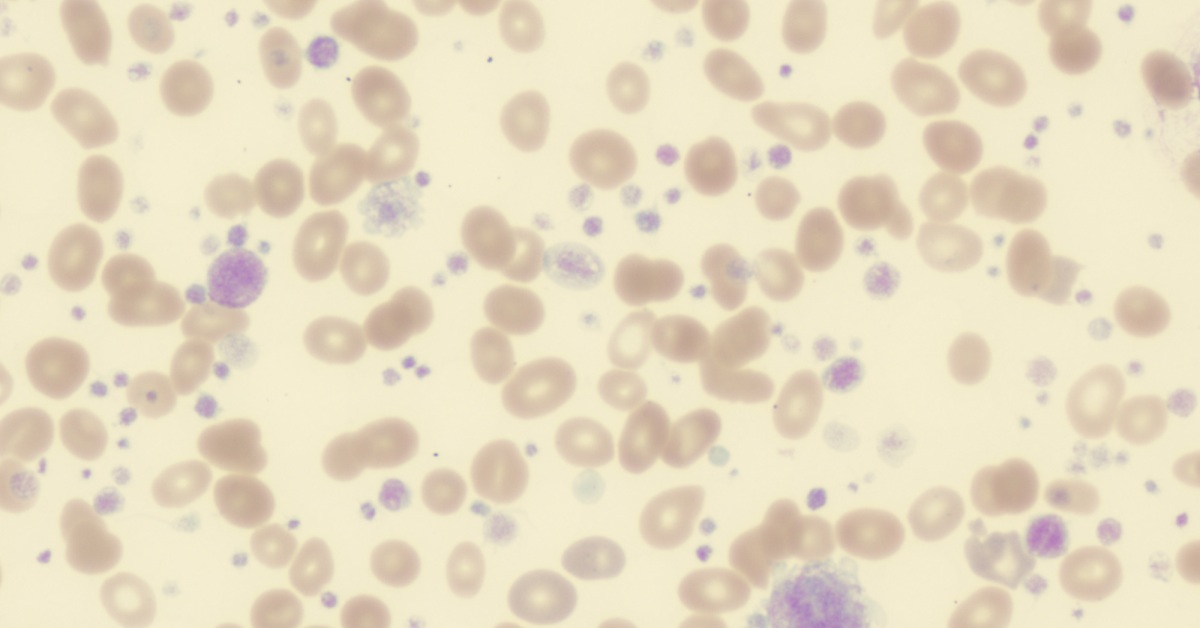
Essential thrombocythemia is a rare blood disorder characterized by an overproduction of platelets, leading to an increased risk of blood clots.

Ependymoma is a type of brain tumor that arises from ependymal cells lining the ventricles of the brain and the spinal cord.
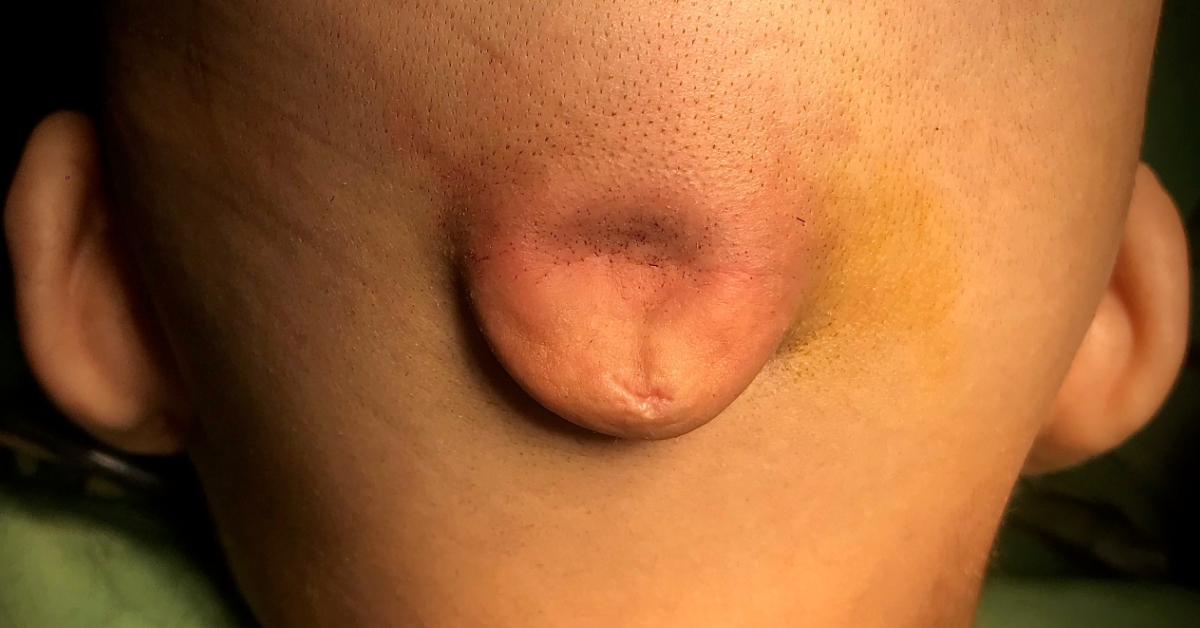
Encephalocele is a rare neural tube defect characterized by a protrusion of brain tissue through a defect in the skull, often accompanied by membranes.
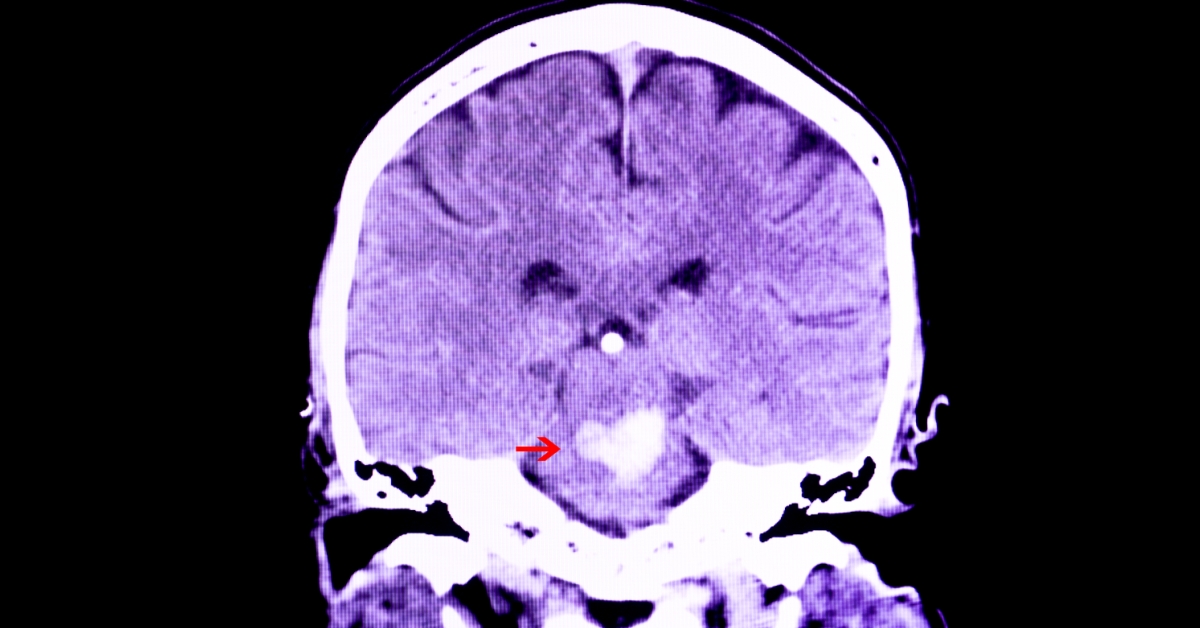
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, benign brain tumor that typically arises near the pituitary gland and can affect hormone regulation and vision.
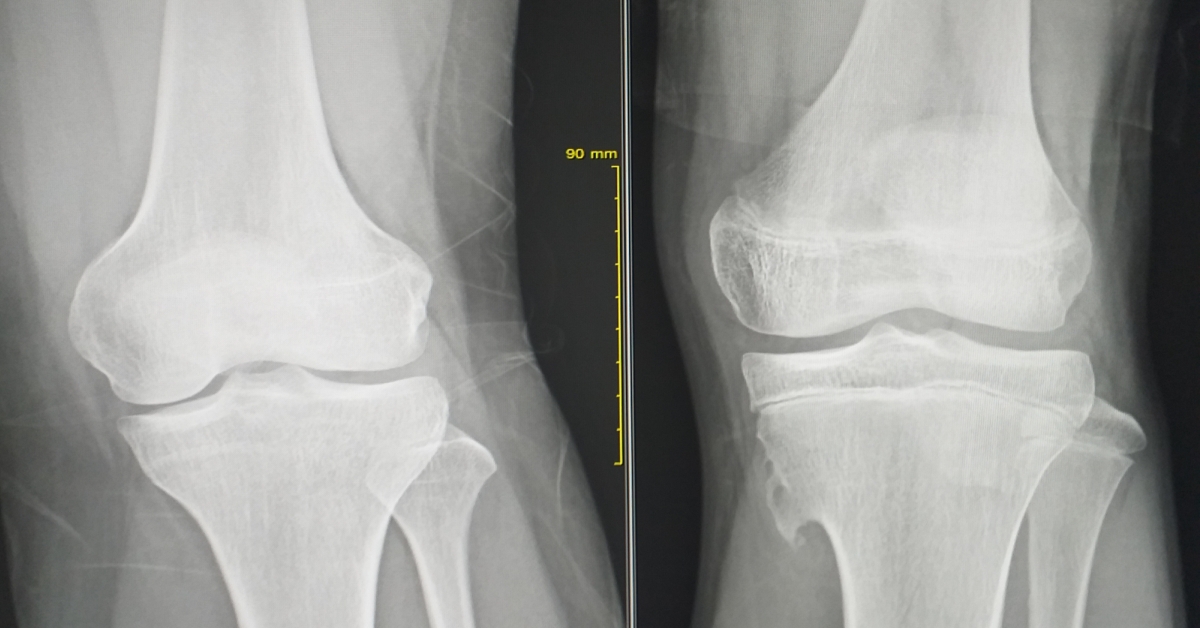
Chondrosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that arises from cartilage cells, typically affecting the bones of the pelvis, hips, and legs.
Urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra that can obstruct urine flow, often caused by trauma, infection, or inflammation.
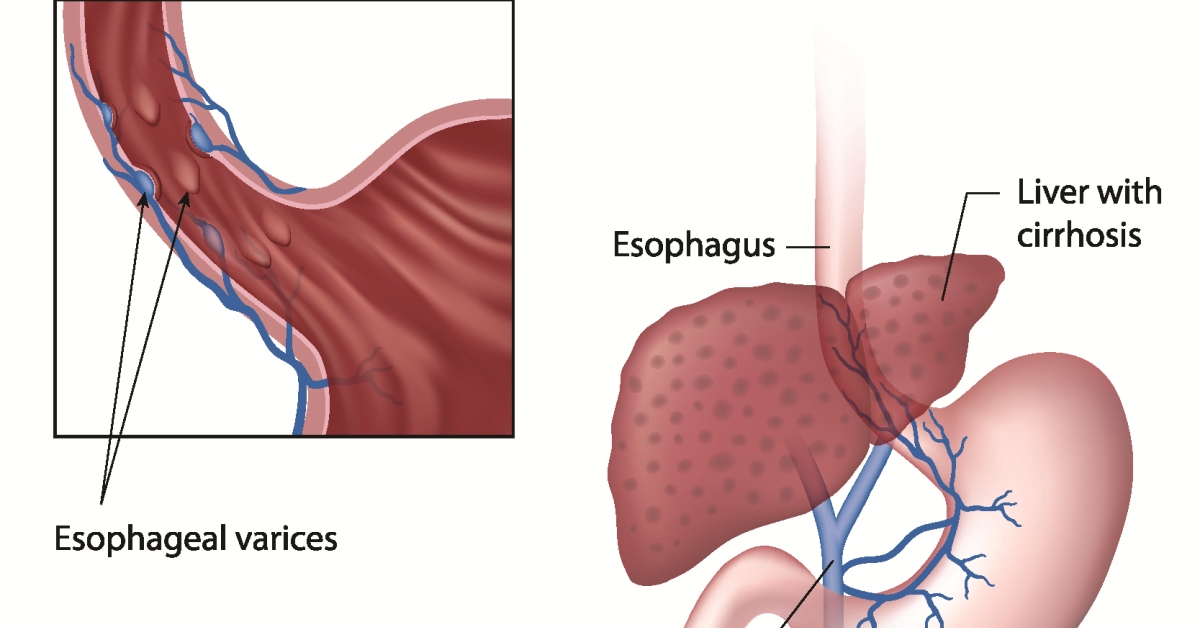
Portal hypertension is an increase in blood pressure within the portal venous system, often due to liver cirrhosis or thrombosis.
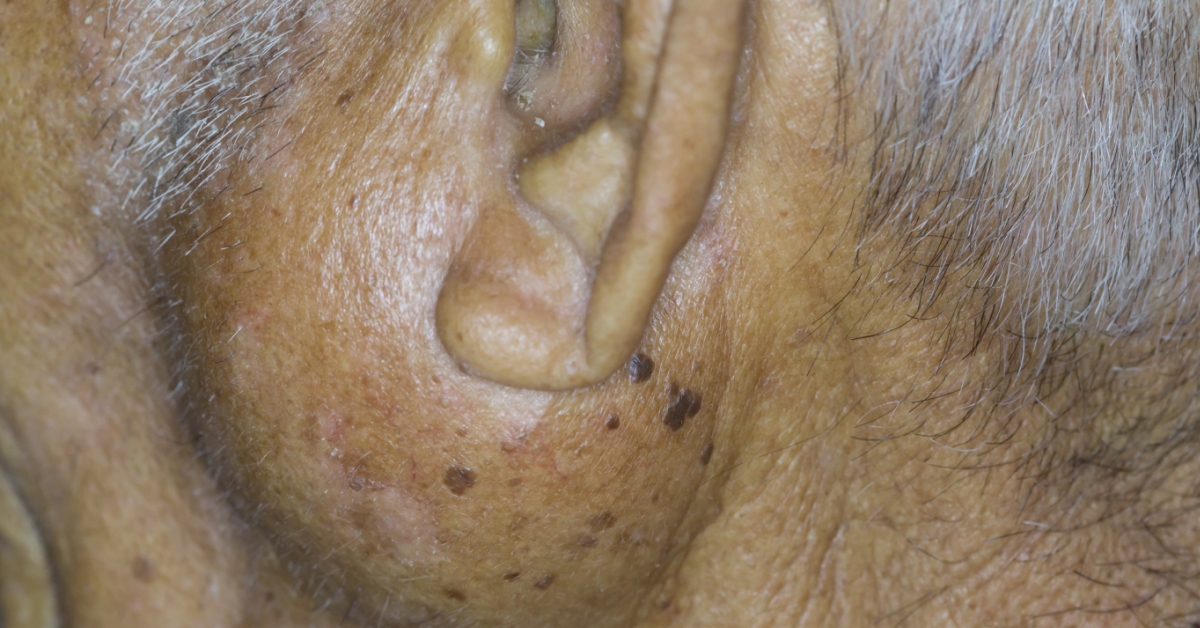
Pleomorphic adenoma is a benign tumor commonly found in the salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland.

Pelvic floor dysfunction refers to a range of conditions where the pelvic floor muscles are weakened or tightened, leading to issues such as incontinence, pain, or difficulty with bowel movements.

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a unique group of cancers that originate in specialized cells known as neuroendocrine cells.
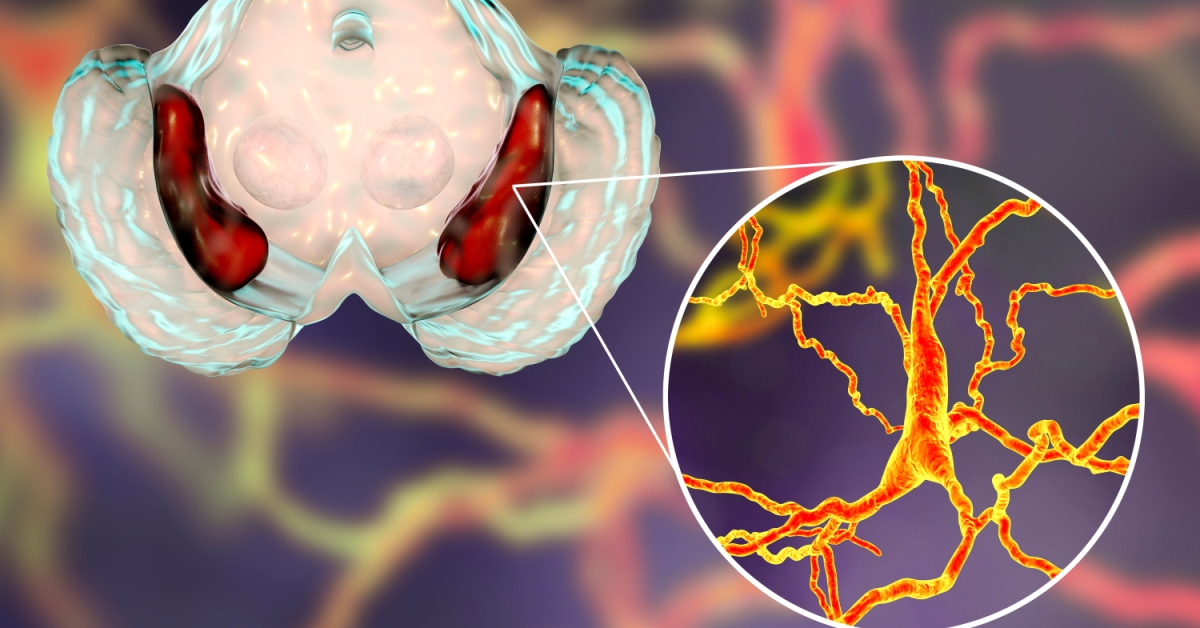
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a combination of motor, autonomic, and cognitive symptoms, leading to significant impairment in daily functioning.
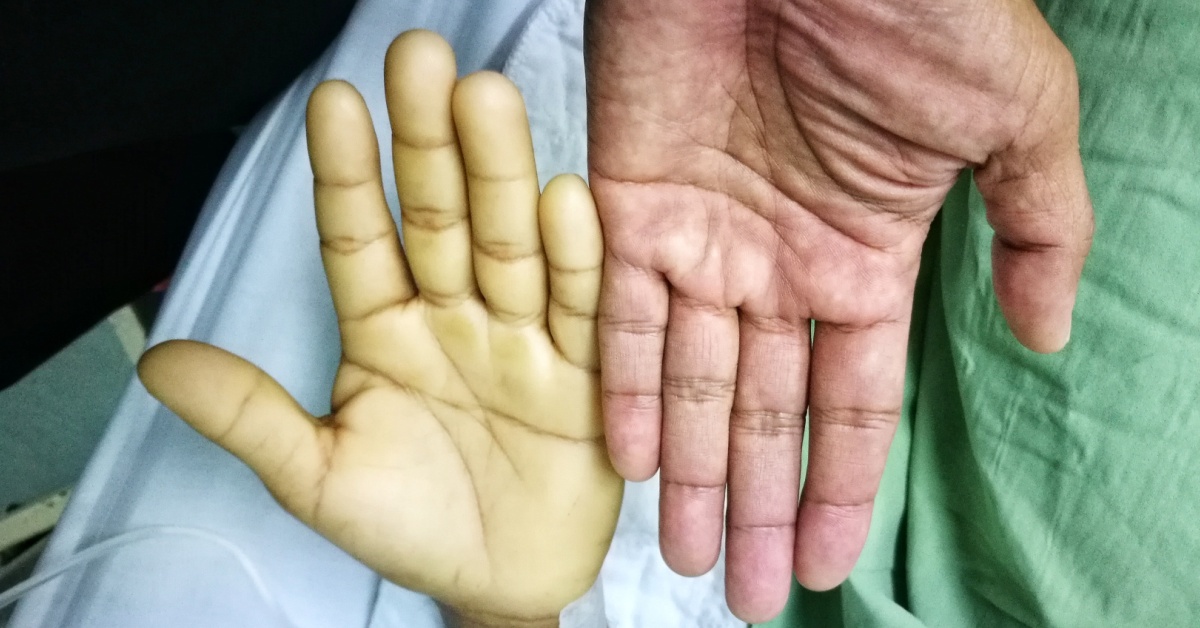
Fanconi Anemia is a rare genetic disorder characterized by bone marrow failure and increased risk of cancer, resulting from defects in DNA repair mechanisms.
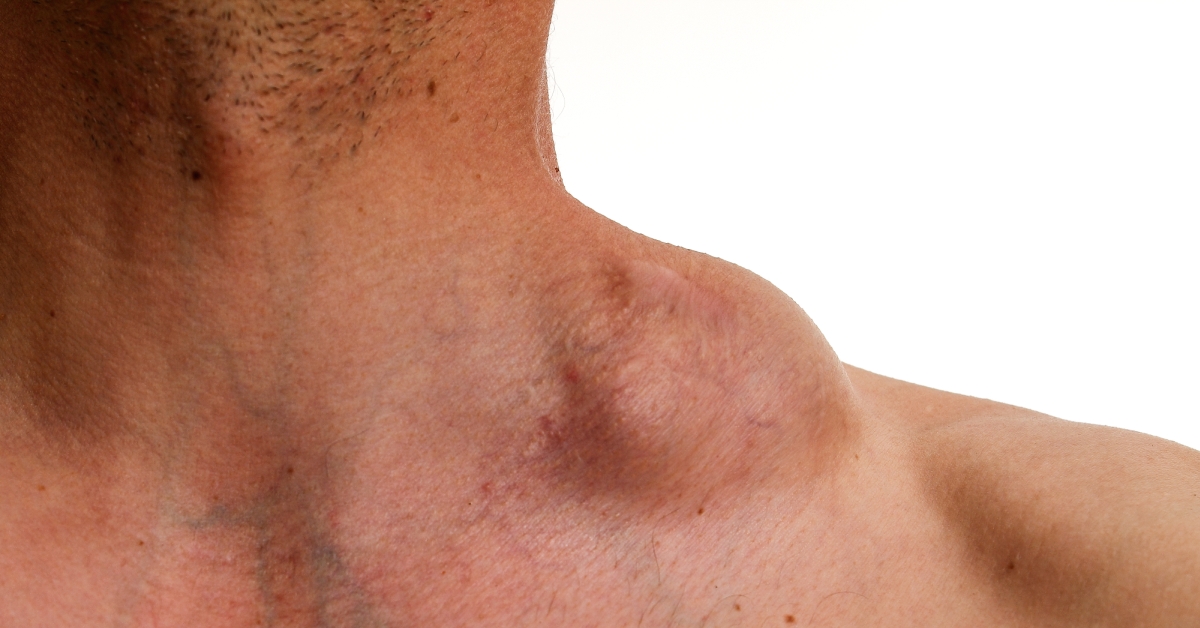
Desmoid tumors are rare, benign growths that arise from connective tissue, often found in the abdomen, limbs, or trunk.
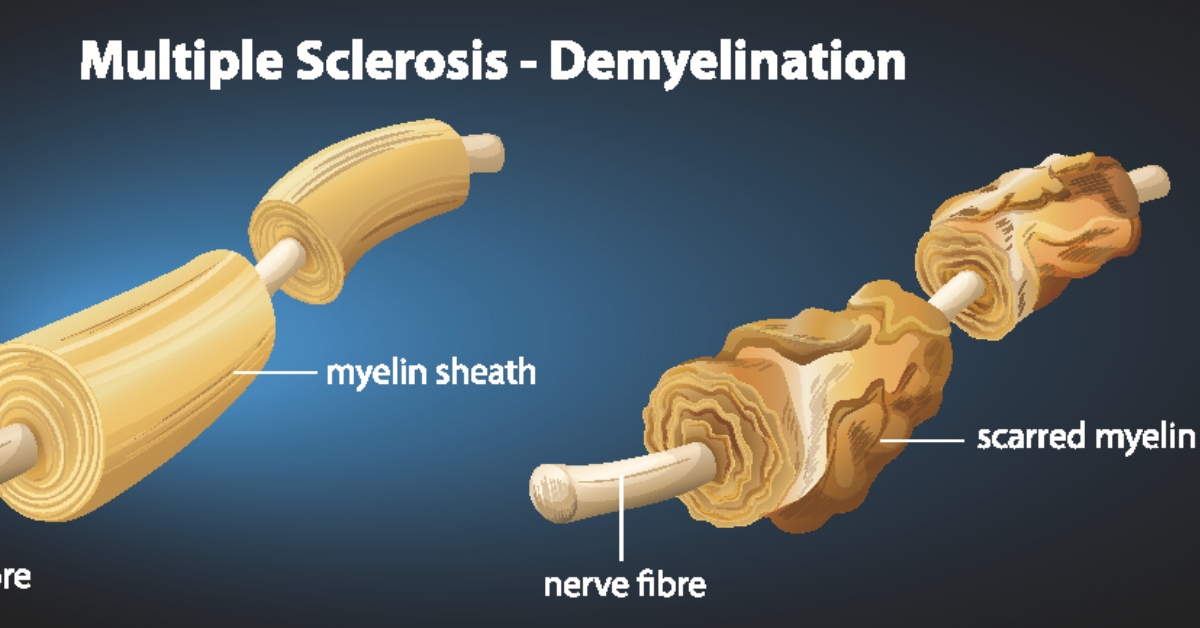
Demyelinating diseases are conditions that damage the protective covering (myelin) of nerve fibers in the central nervous system, leading to disrupted communication between the brain and the body.
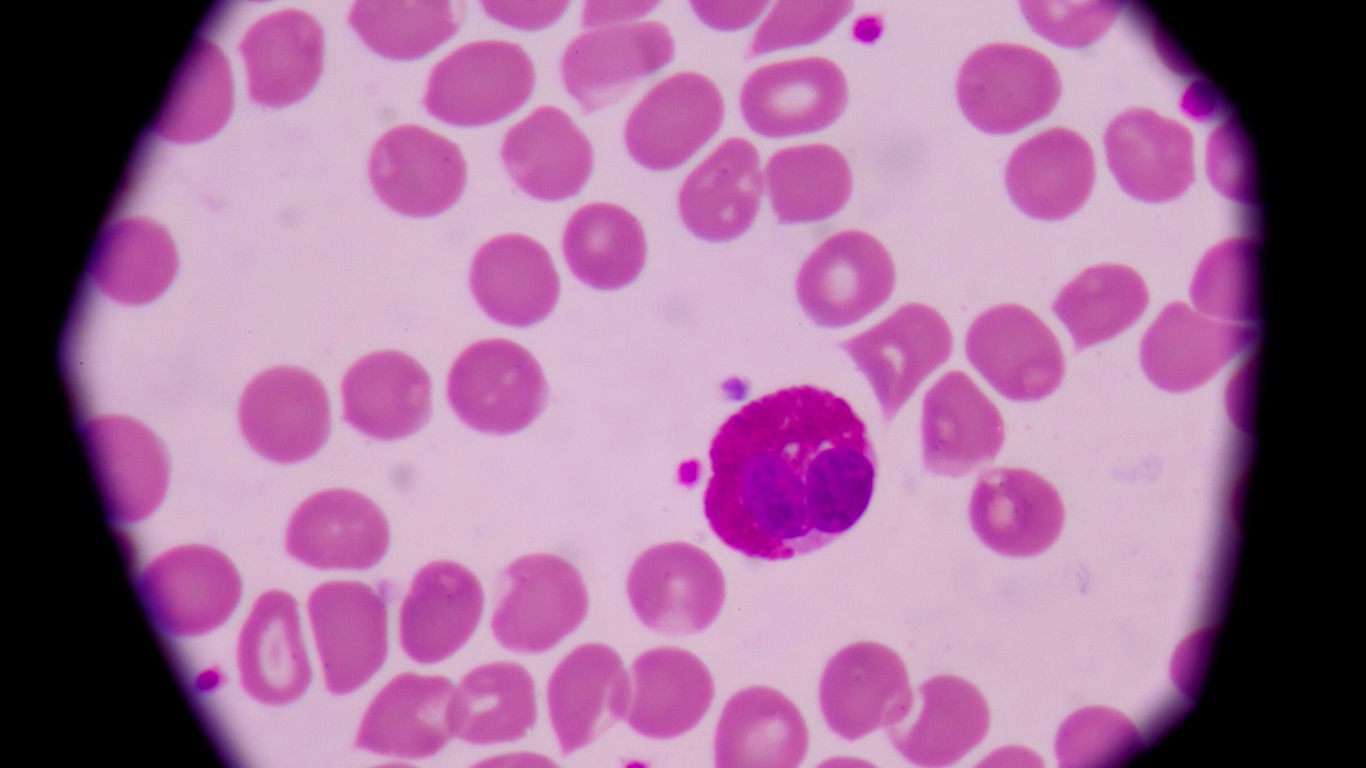
Churg-Strauss Syndrome, also known as Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis, is a rare autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels and high levels of eosinophils, often affecting the lungs and skin.
Chordoma is a rare type of cancer that occurs in the bones of the skull and spine, arising from remnants of the notochord.

Zenker’s diverticulum is a rare condition where a pouch forms in the upper esophagus, leading to difficulties in swallowing and potential food retention.
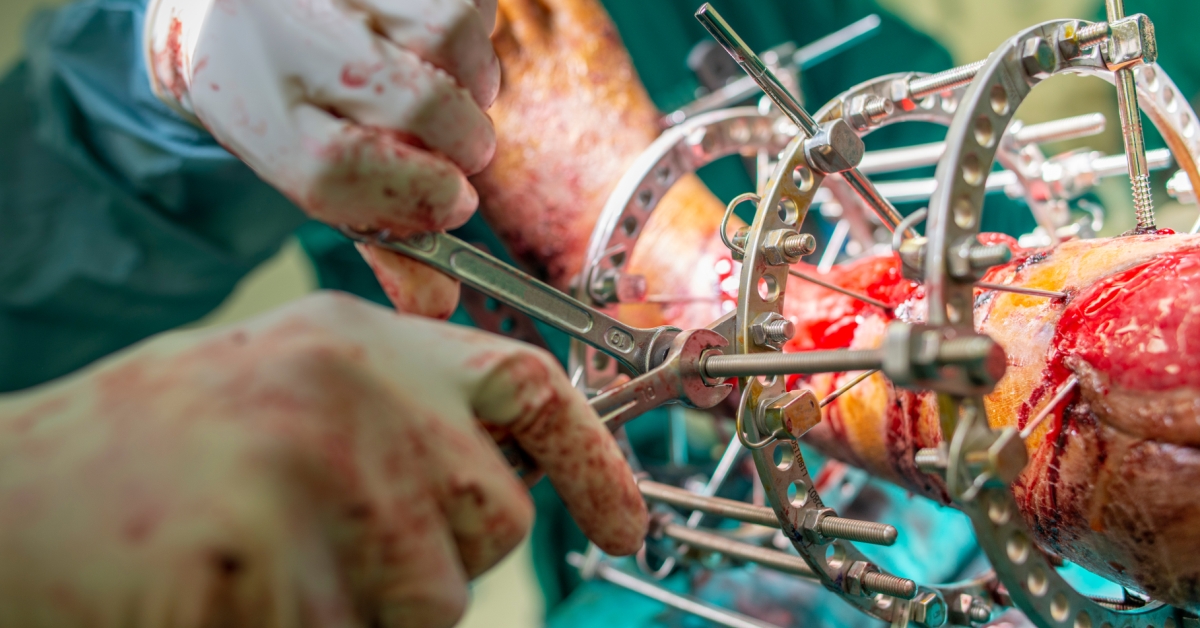
A tibial plateau fracture is a break in the upper part of the tibia (shinbone) that can affect the knee joint, often resulting from high-impact trauma or falls.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare and aggressive soft tissue cancer that typically arises near joints, particularly in the arms and legs, but can occur in other locations as well

Spinal cord injury (SCI) refers to damage to the spinal cord that results in loss of function, mobility, and sensation, potentially leading to paralysis.
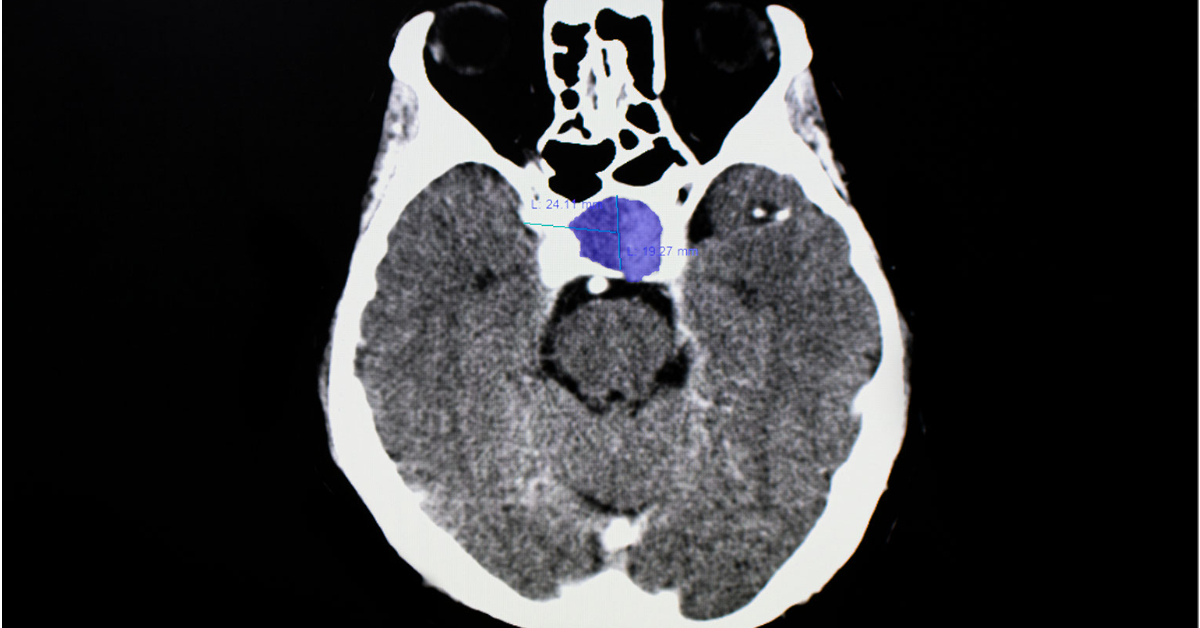
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland, which can disrupt hormonal balance and affect various bodily functions.

Muscle twitching, or fasciculation, refers to involuntary contractions of small groups of muscle fibers, often caused by fatigue, stress, or nerve irritation.
Long QT syndrome is a heart rhythm disorder that can lead to fast, chaotic heartbeats, increasing the risk of fainting or sudden cardiac arrest.
A Lisfranc injury involves damage to the midfoot ligaments or bones, often resulting from trauma or high-impact sports.
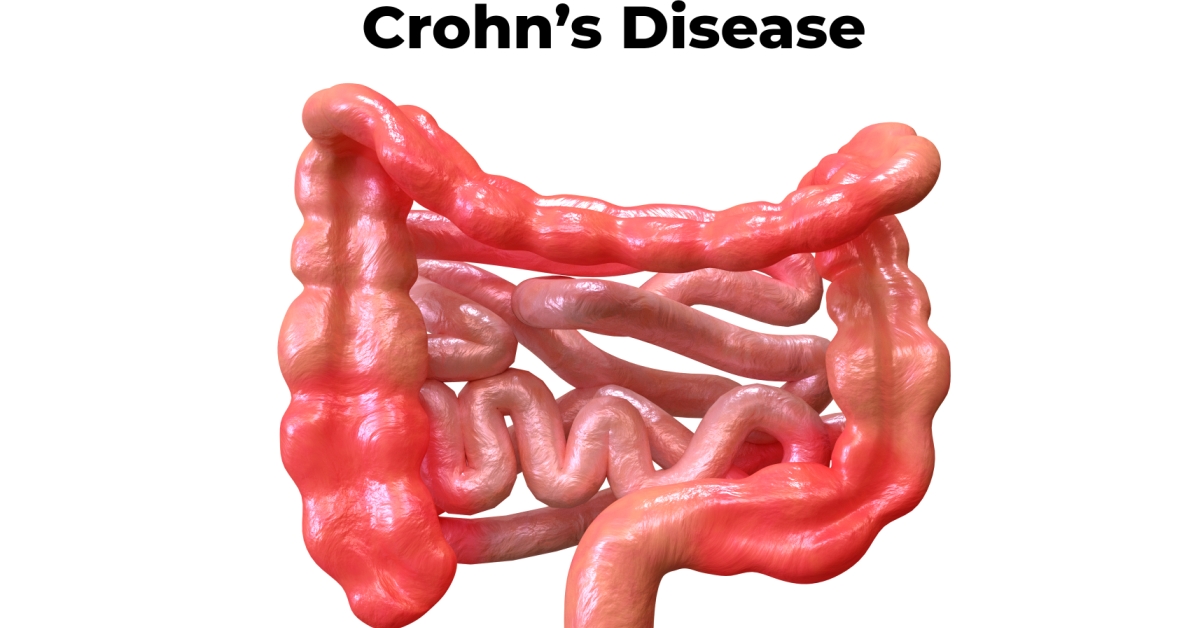
Intestinal obstruction is a condition where the intestines are blocked, preventing the normal passage of contents, which can lead to severe complications.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a primary liver cancer that typically arises in the context of chronic liver disease, particularly cirrhosis or hepatitis.

Dilated cardiomyopathy is a heart muscle disease characterized by the thinning and stretching of the heart’s chambers, particularly the left ventricle, leading to enlargement.
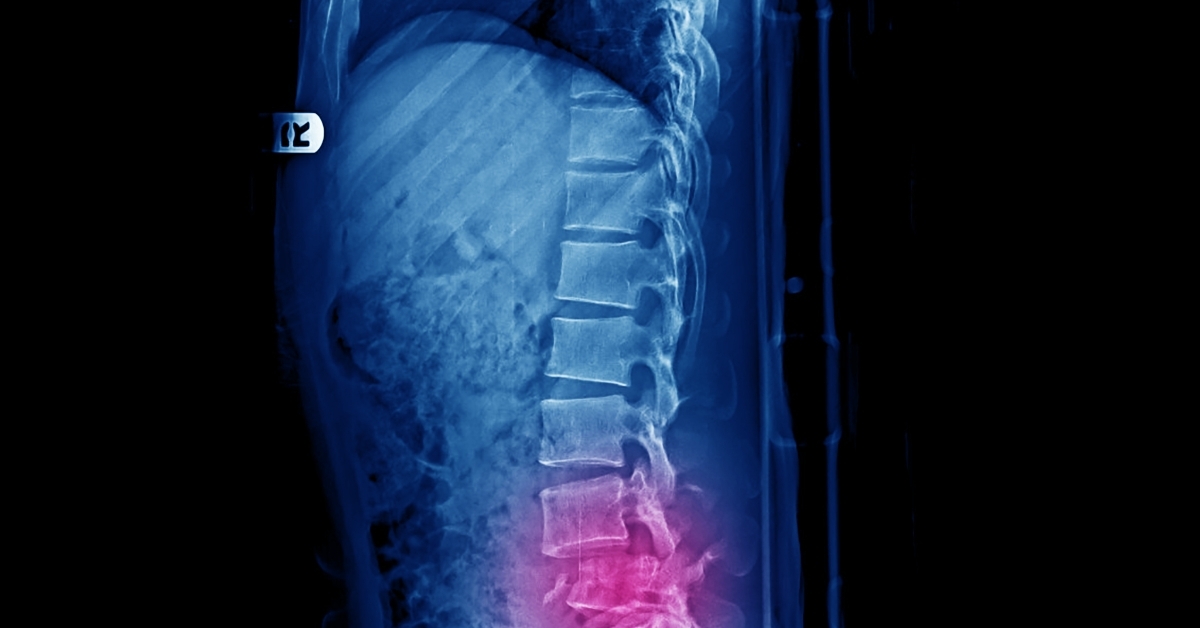
Syringomyelia is a rare neurological condition characterized by the formation of a fluid-filled cavity, or syrinx, within the spinal cord, leading to a variety of neurological symptoms.
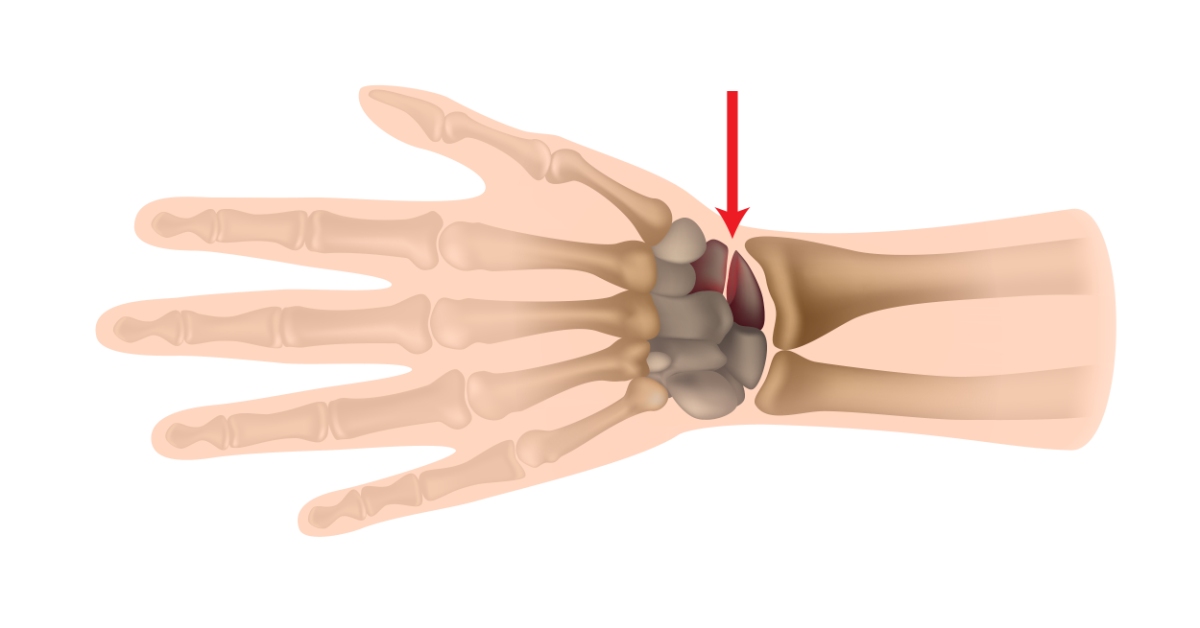
A scaphoid fracture is a common wrist injury that occurs when one of the small bones in the wrist, the scaphoid, breaks, often due to a fall on an outstretched hand.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that primarily affects soft tissues in children and adolescents, often presenting as a lump or swelling.

Otosclerosis is a condition characterized by abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, leading to hearing loss.
Muscle Atrophy refers to the progressive loss of muscle mass and strength, often resulting from disuse, aging, malnutrition, or certain medical conditions.
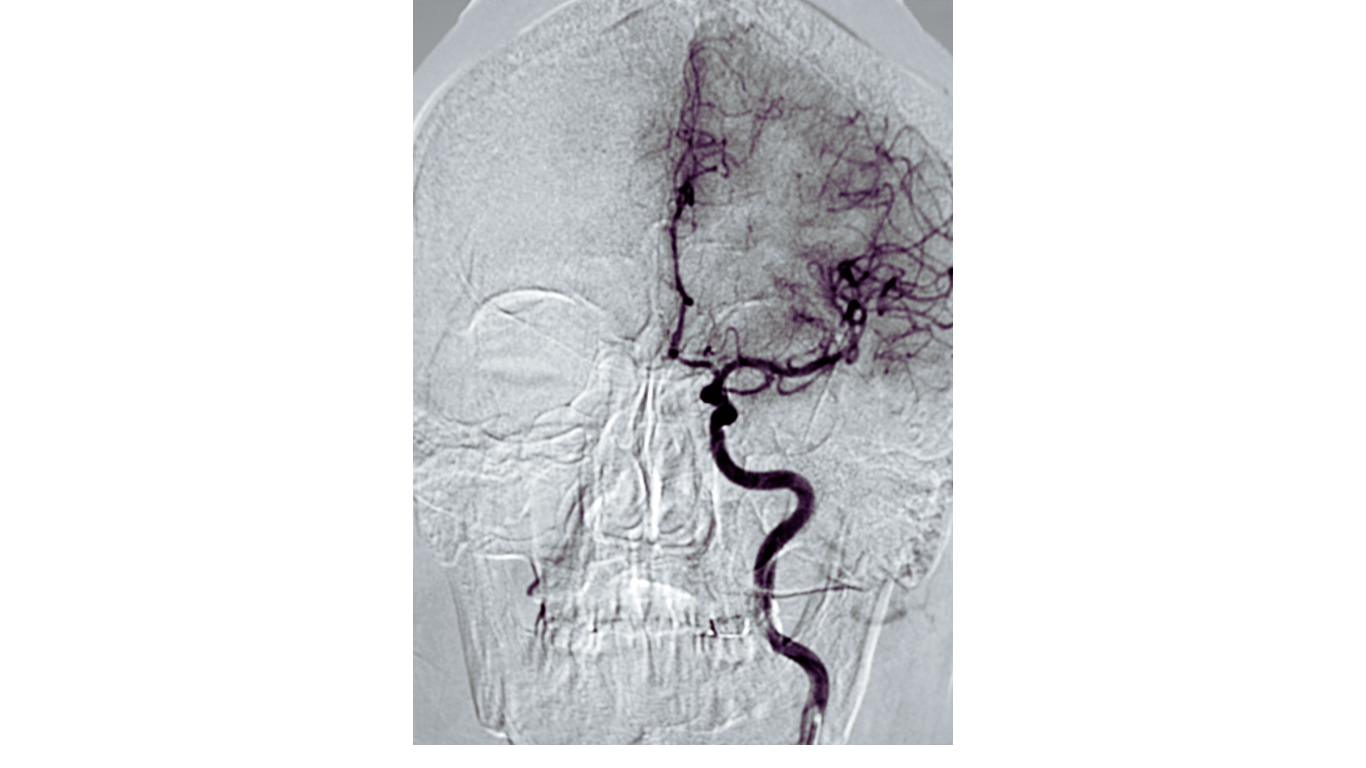
Moyamoya disease is a rare cerebrovascular disorder characterized by the progressive narrowing of the internal carotid arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the brain and increased risk of strokes.

Giant Cell Arteritis is an inflammatory condition affecting the blood vessels, particularly the large arteries in the head, and can lead to serious complications like vision loss.
Ebstein anomaly is a rare heart defect present at birth, characterized by abnormal formation of the tricuspid valve, leading to heart function issues.
Clubfoot is a congenital deformity where a baby’s foot appears twisted or rotated inward, often requiring early intervention for correction.

Wilms tumor, or nephroblastoma, is a rare kidney cancer primarily affecting children, characterized by the rapid growth of kidney cells.
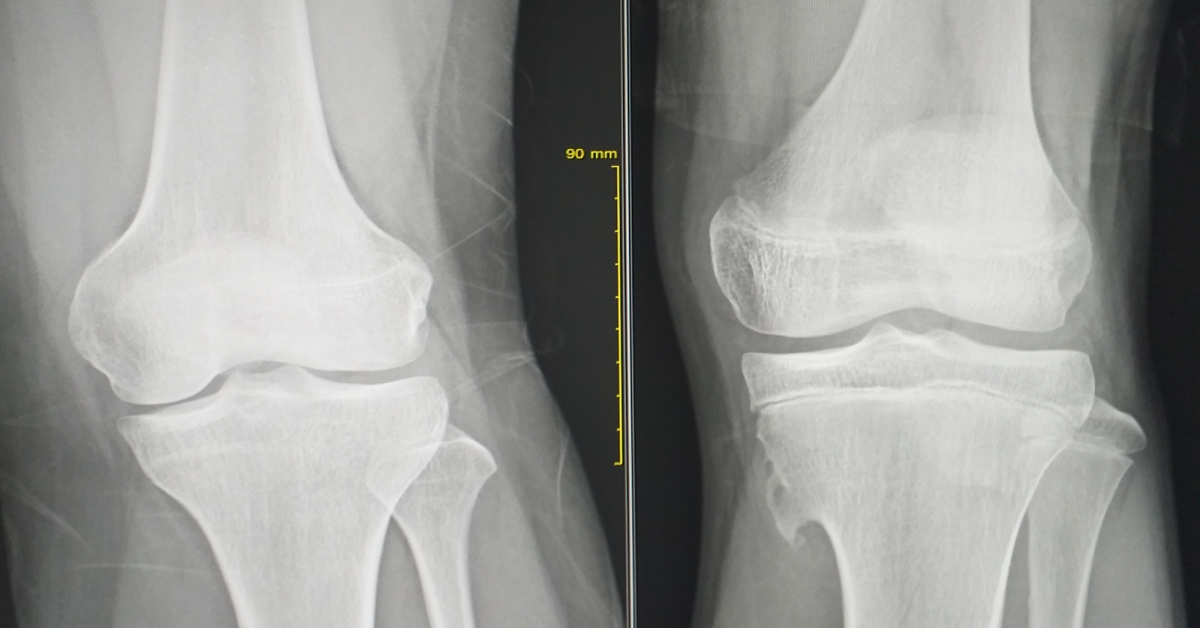
Osteochondroma is a benign bone tumor that typically develops during childhood or adolescence, characterized by an outgrowth of bone and cartilage.
Myelofibrosis is a rare bone marrow disorder characterized by the replacement of healthy marrow tissue with fibrous scar tissue, leading to anemia, weakness, and an enlarged spleen.
Mitral valve prolapse is a condition where the mitral valve does not close properly, potentially leading to blood regurgitation.

Medulloblastoma is a type of malignant brain tumor that primarily occurs in the cerebellum, most commonly in children, and can affect balance and coordination.
Glioma is a type of tumor that arises from glial cells in the brain and spinal cord, and it can vary in grade from benign to highly malignant.

Transverse myelitis is a neurological condition characterized by inflammation of both sides of the spinal cord, leading to symptoms like weakness, sensory changes, and bowel or bladder dysfunction.
Schwannoma is a benign tumor that arises from Schwann cells, which insulate nerves, often affecting peripheral nerves and leading to symptoms like pain or numbness.
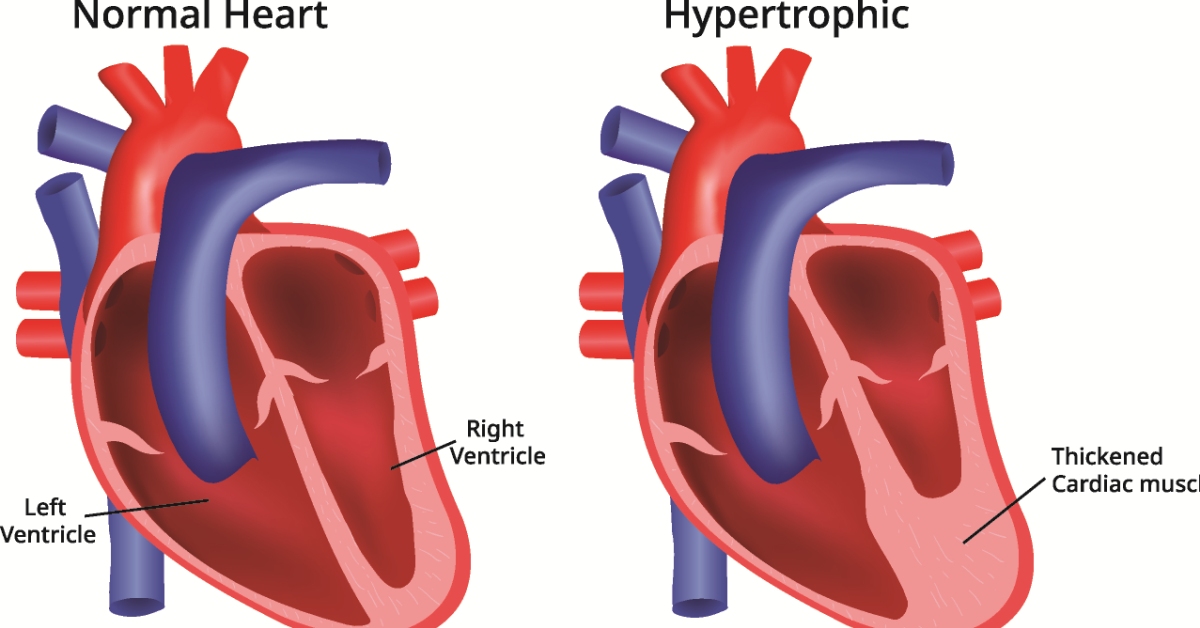
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetic condition characterized by the thickening of the heart muscle, which can lead to various complications, including heart failure and arrhythmias.

Essential tremor is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary, rhythmic shaking, often affecting the hands and arms, particularly during movement.
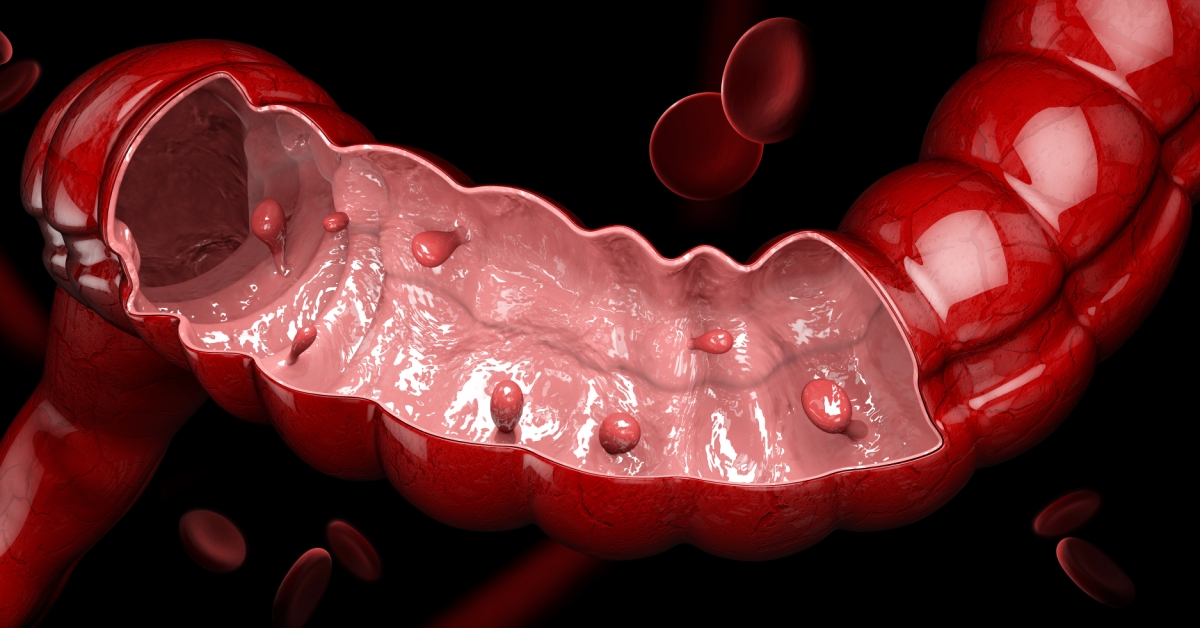
Colon polyps are growths on the lining of the colon that can vary in size and type, with some having the potential to develop into colorectal cancer.
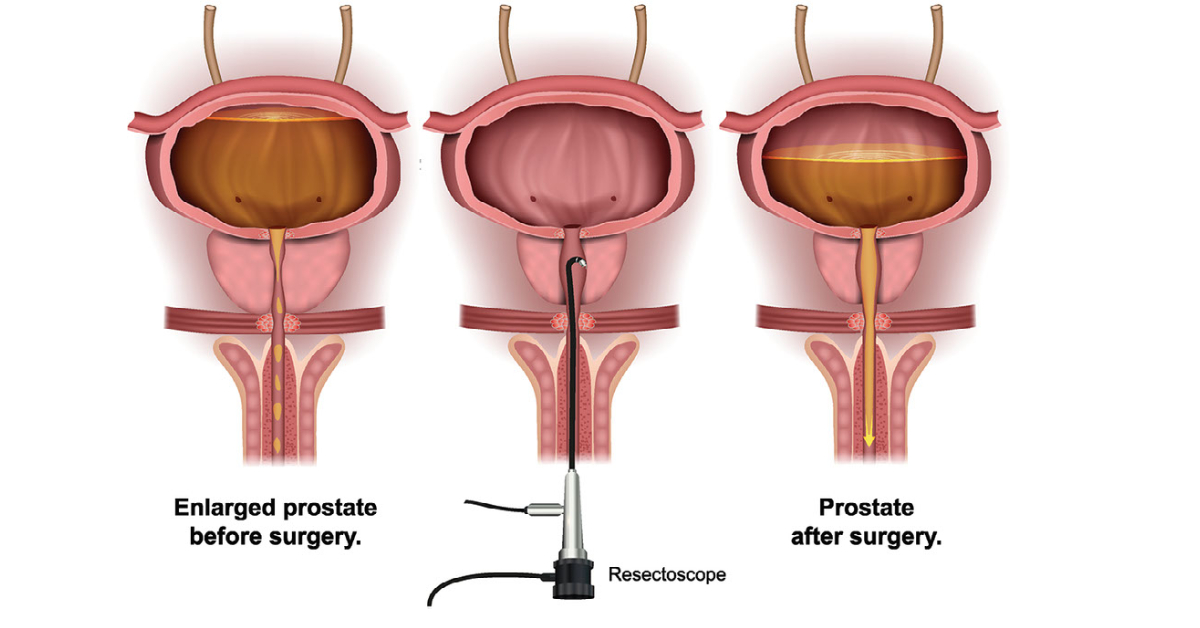
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine, which can result from various factors such as age, childbirth, or certain medical conditions.
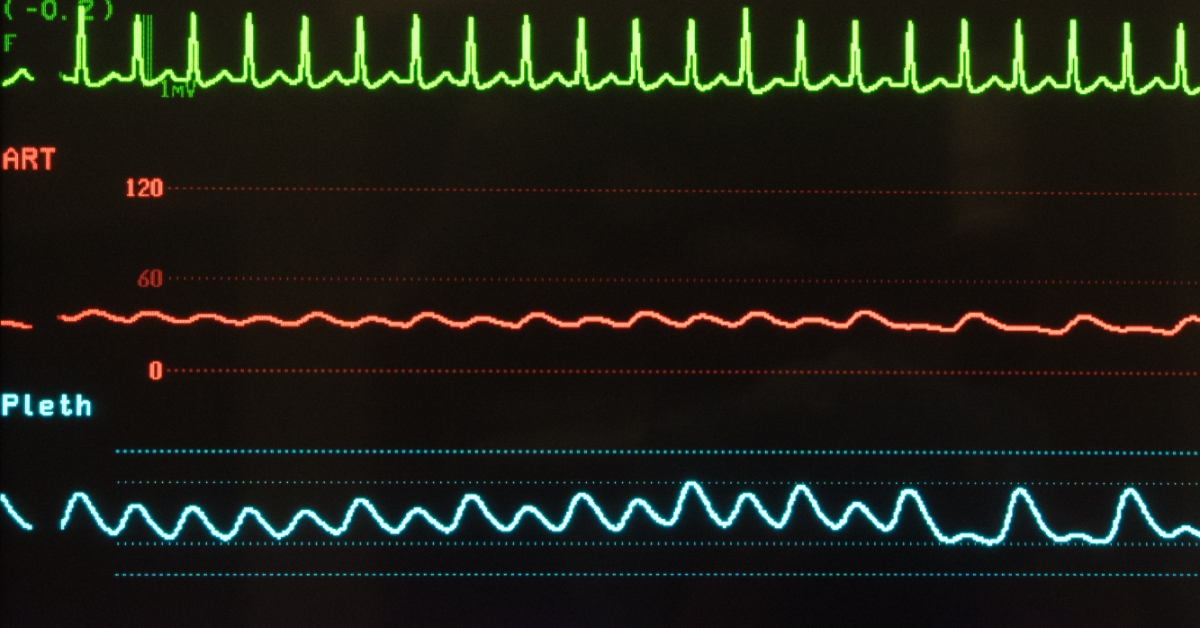
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heartbeat originating above the ventricles, often causing palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
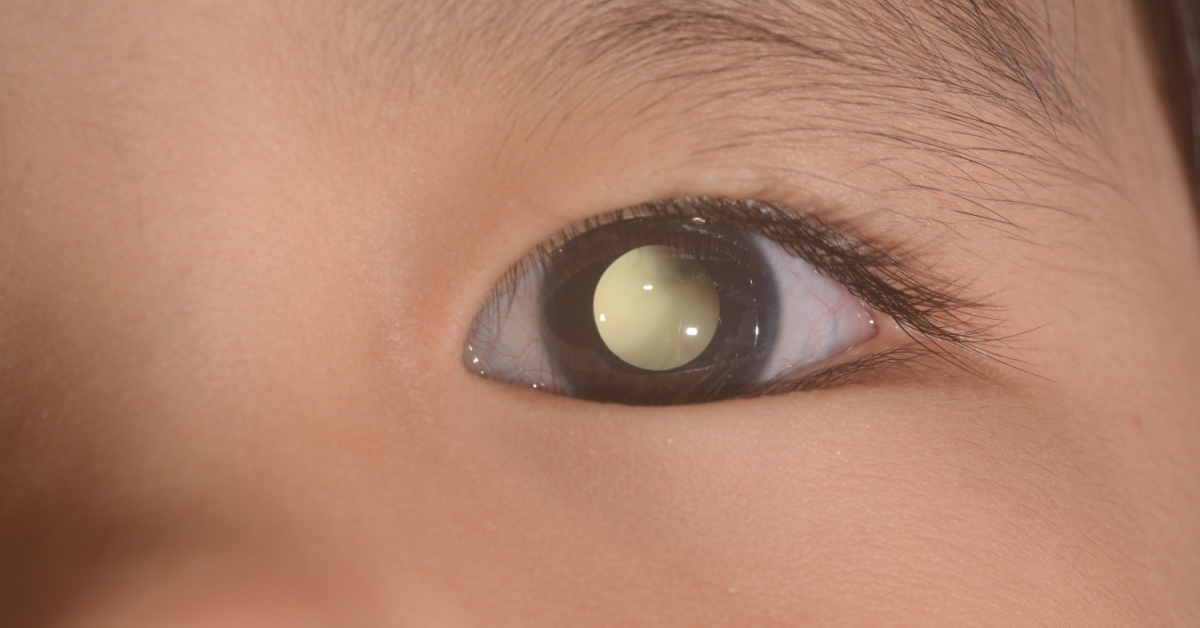
Retinoblastoma is a rare and aggressive eye cancer that primarily affects young children, arising from the retina.
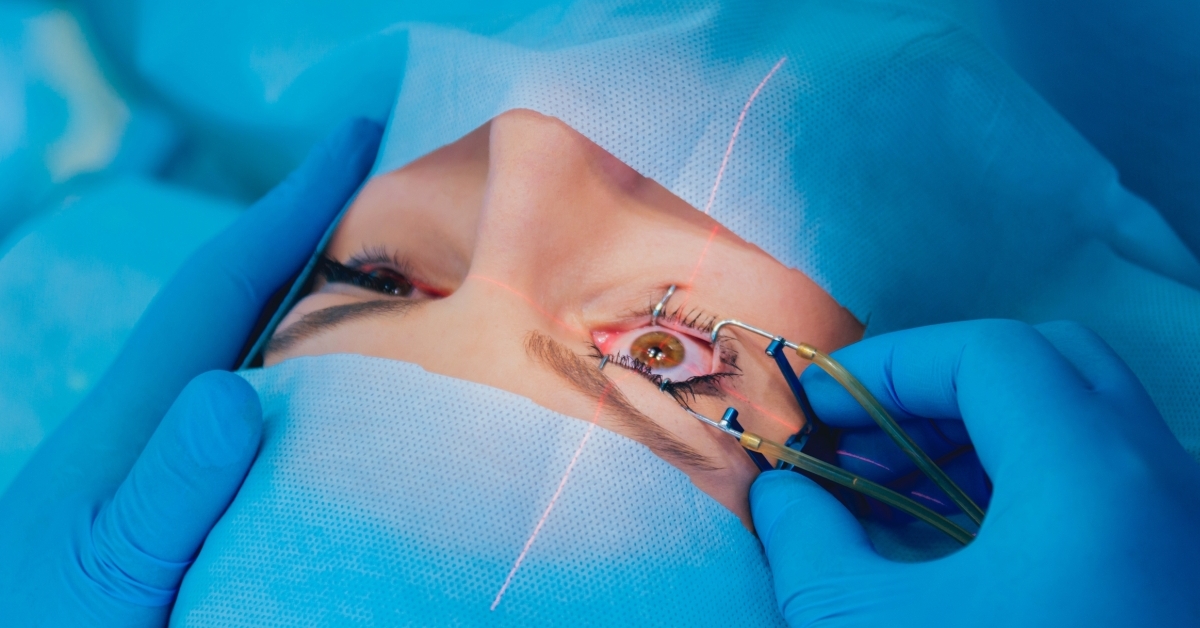
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition where the retina separates from its underlying tissue, potentially leading to vision loss if not treated promptly.
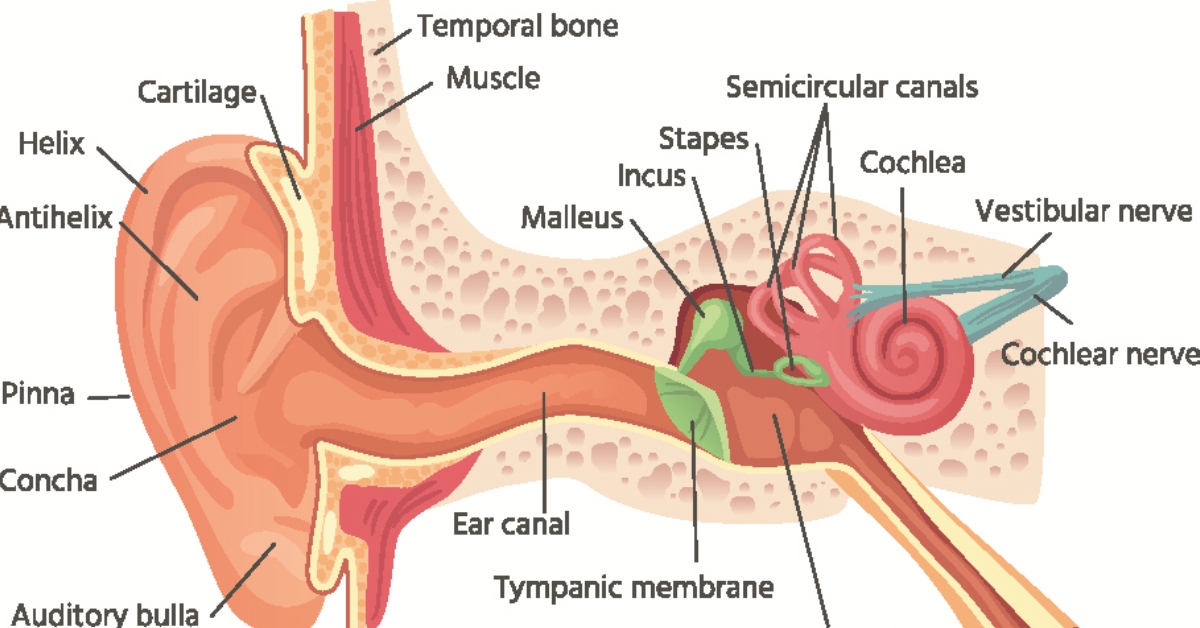
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) occurs when the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, fail to open properly, leading to feelings of fullness, discomfort, or hearing loss.

Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) is a rare and progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by prions—misfolded proteins that induce abnormal folding of normal proteins in the brain.
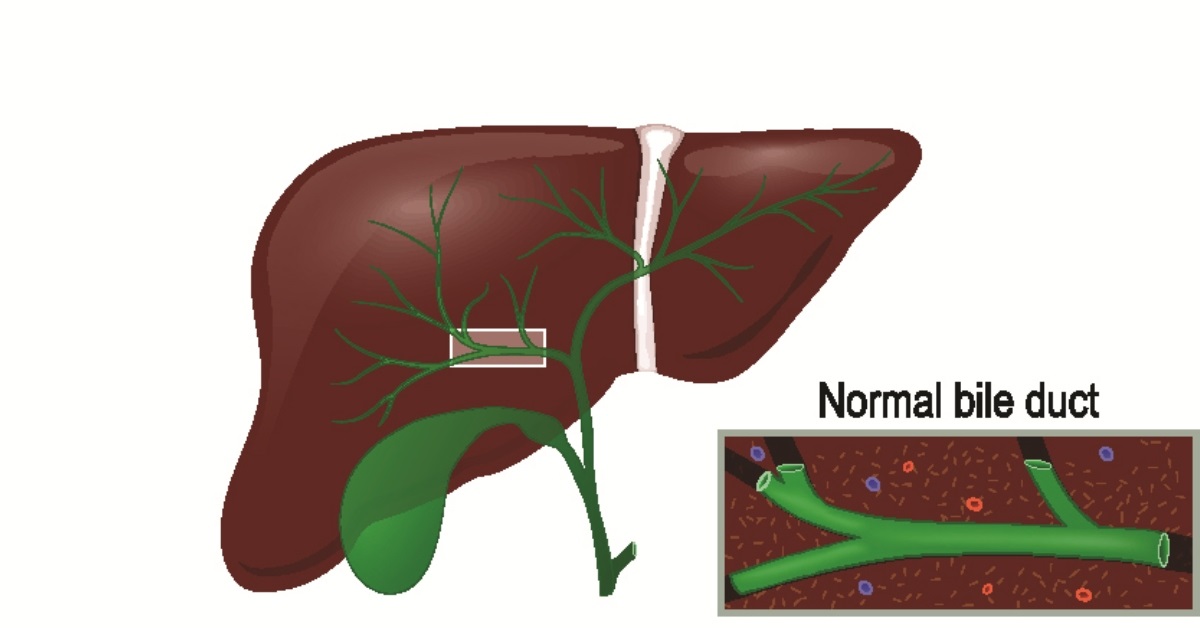
Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, often resulting from a blockage, leading to symptoms like jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain.
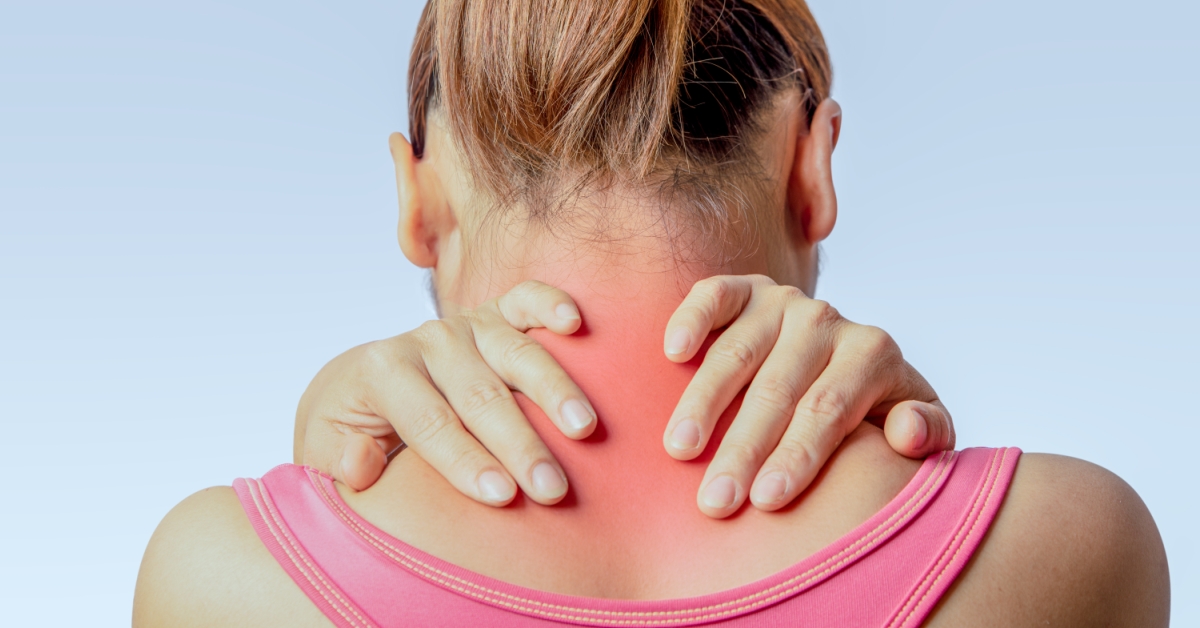
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition caused by compression or irritation of the nerves in the neck, leading to pain, weakness, or numbness radiating down the arms.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a congenital heart condition characterized by an extra electrical pathway, leading to episodes of rapid heart rate.
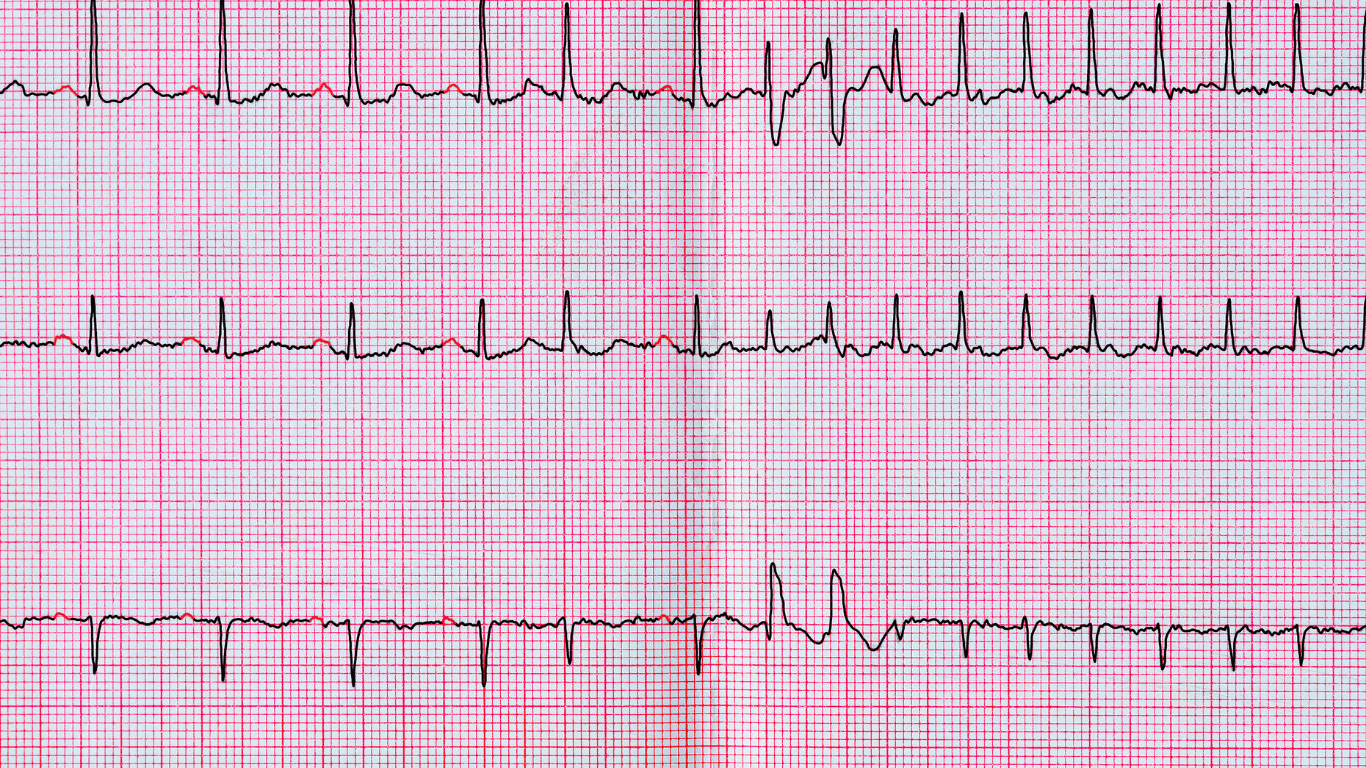
Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening heart rhythm disorder characterized by rapid, chaotic electrical activity in the ventricles, preventing the heart from pumping effectively.
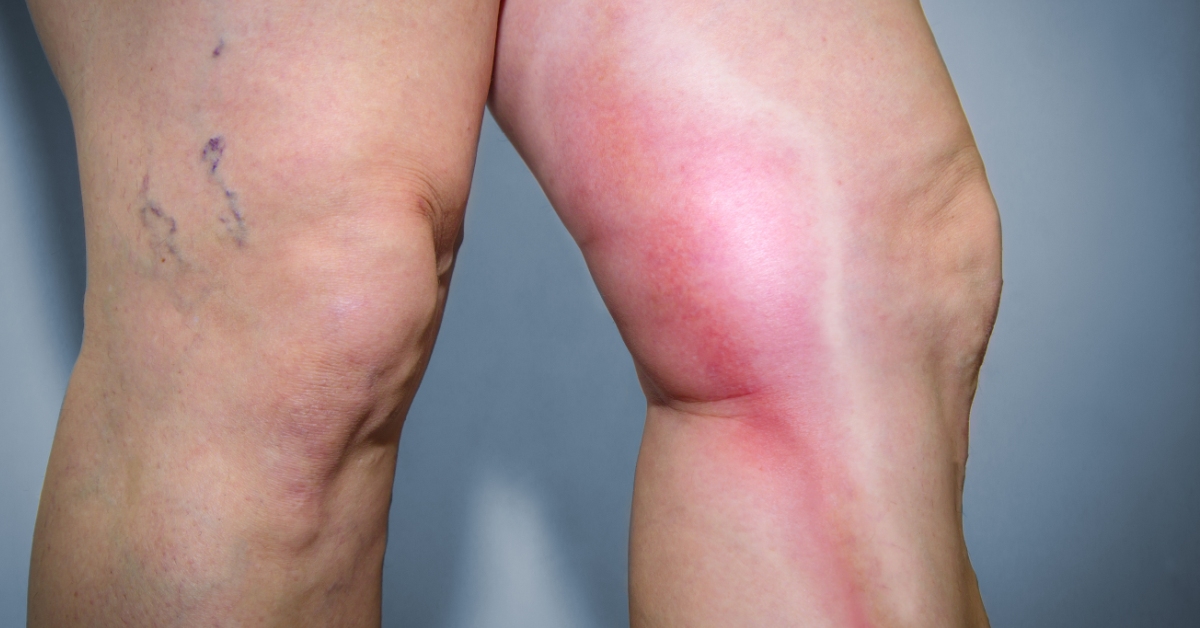
Thrombophlebitis is the inflammation of a vein caused by a blood clot, often resulting in pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
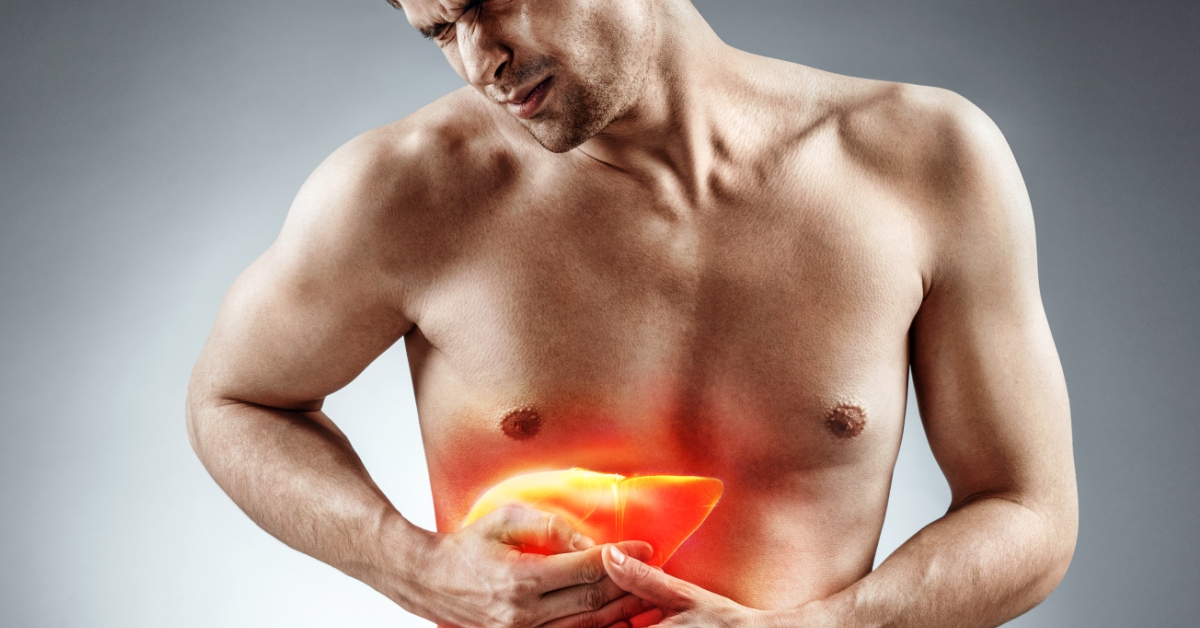
Primary Biliary Cholangitis is a chronic autoimmune disease that gradually damages the bile ducts in the liver, leading to bile buildup and potential liver failure.
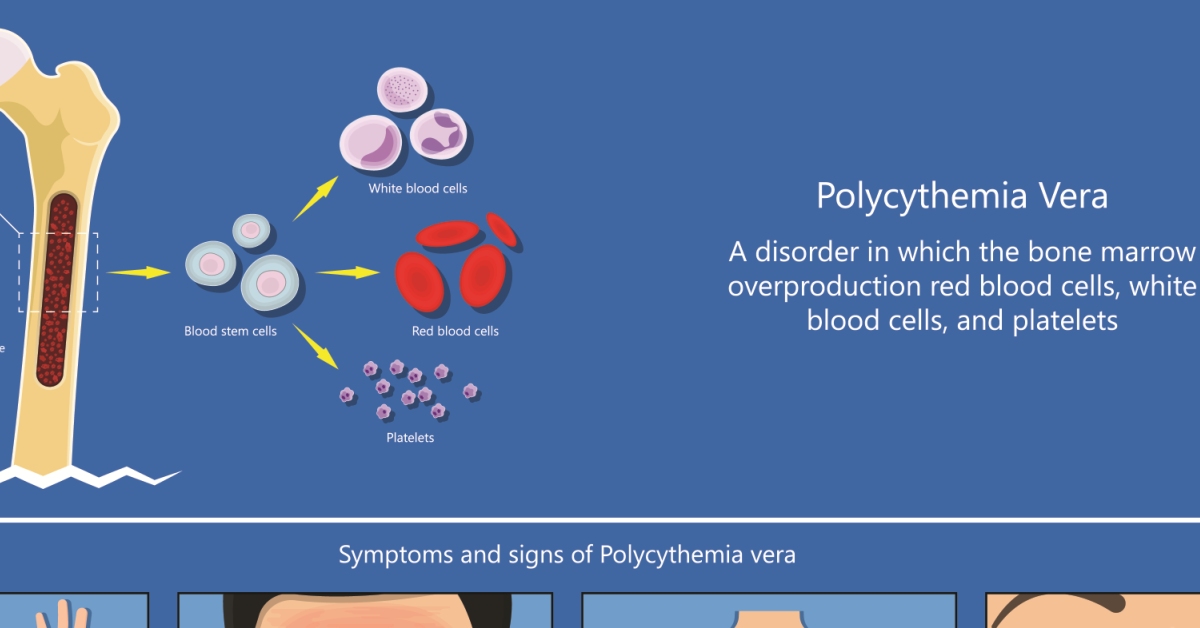
Polycythemia vera is a rare blood disorder characterized by the overproduction of red blood cells, leading to increased blood viscosity and a higher risk of clotting.
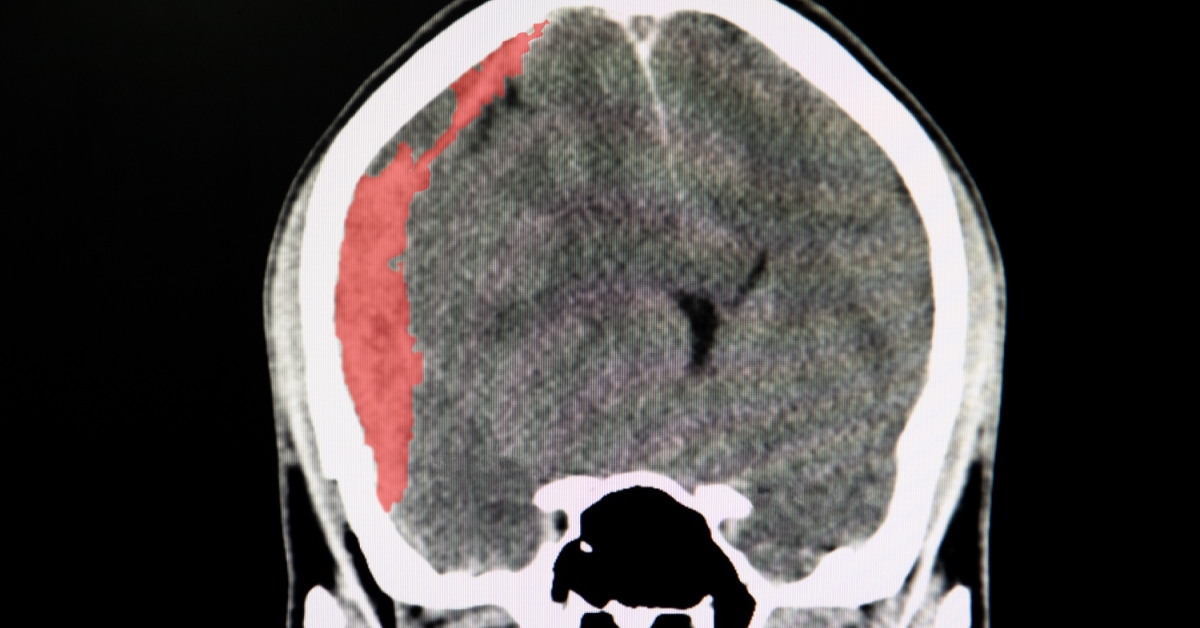
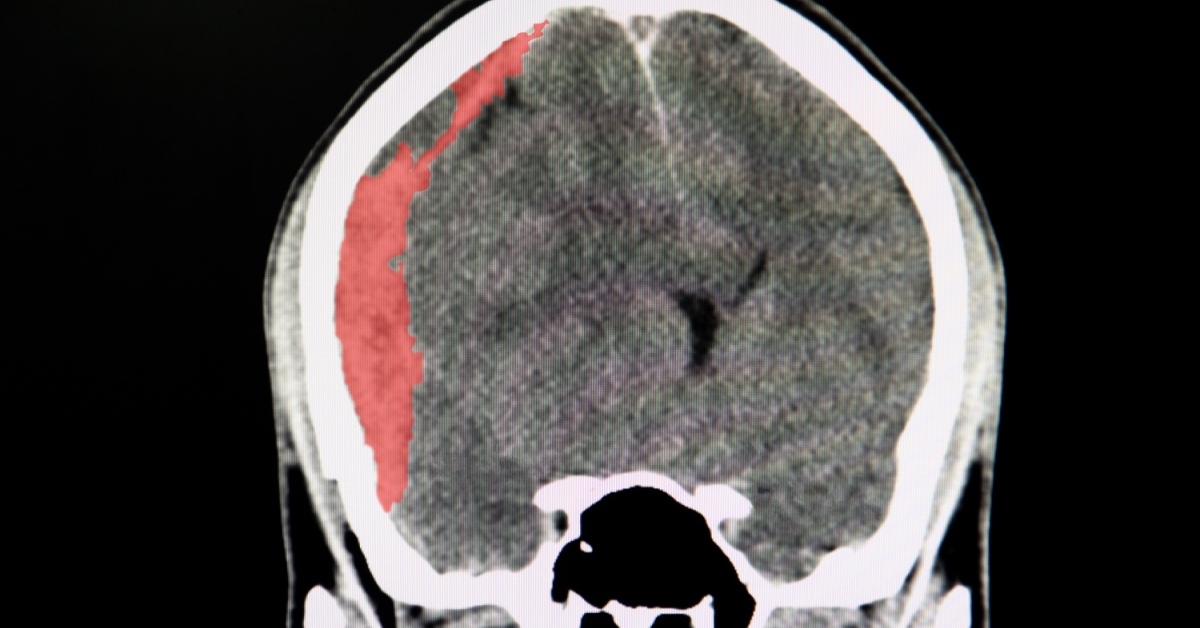
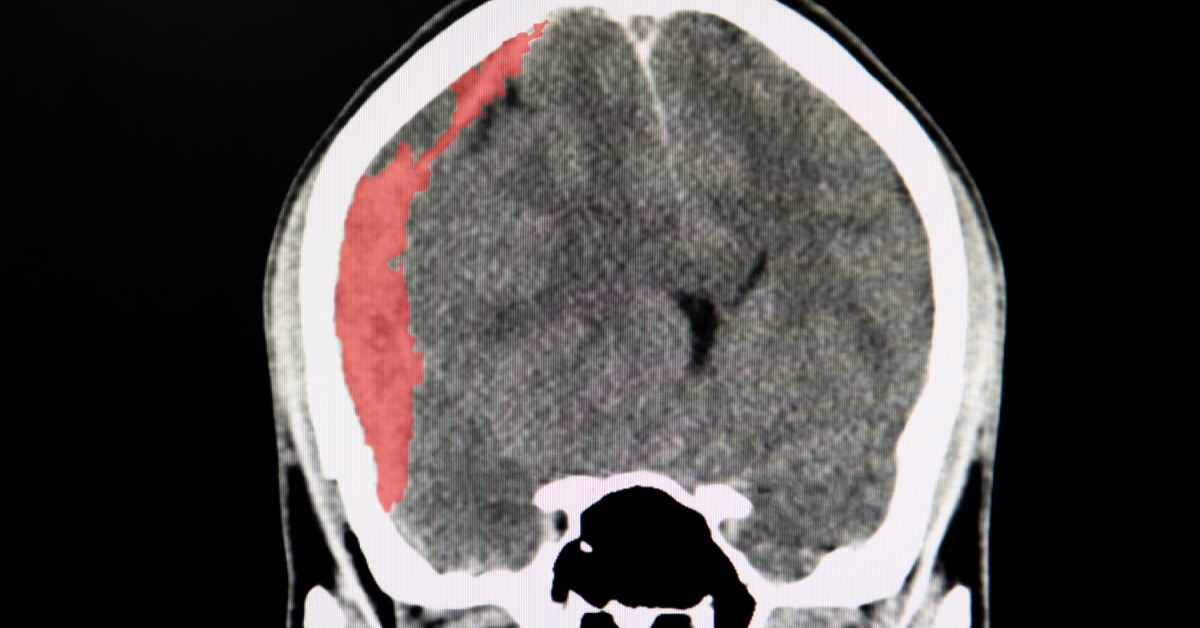
A subdural hematoma is a collection of blood between the brain’s surface and its outer covering, typically caused by head trauma.
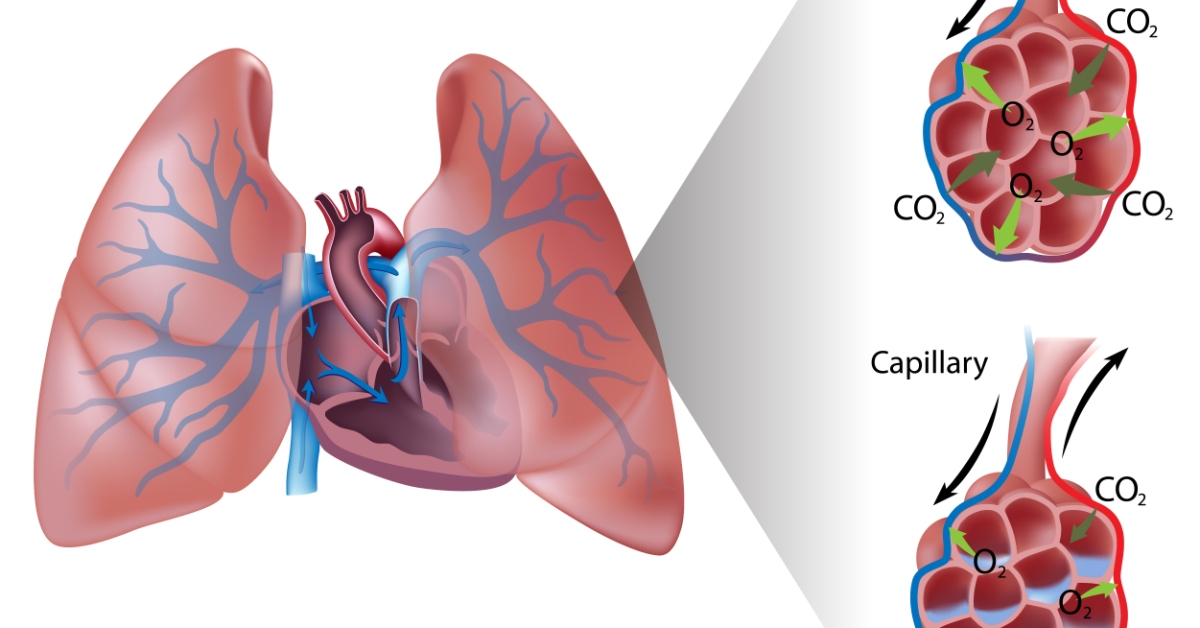
Pulmonary edema is a condition characterized by excess fluid accumulation in the lungs, leading to difficulty in breathing and reduced oxygen exchange.
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by excessive protein loss in urine, leading to symptoms such as swelling, high cholesterol, and low protein levels in the blood.
Chat on WhatsApp!
*Please note: As of now, we are only assisting international patients who plan to come to India for medical treatment.