Traumatic Brain Injury
Symptoms
Depending on the type and location of the injury, a person suffering from a traumatic brain injury can show the following symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness
- Feelings of depression
- Seizures
- Confusion and disorientation
- Memory loss / amnesia
- Sleep disturbances
- Dizziness/loss of balance
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Visual problems
- Poor attention / concentration
- Irritability / emotional disturbances
- Vomiting
If you or your child has received a blow to the head or body, that concerns you or has lead to any behavioral changes, then you should see a doctor immediately. Seek emergency medical care if there are signs or symptoms of traumatic brain injury after a recent blow or another traumatic injury to you or your child’s head.
Causes
Traumatic brain injury is caused due to a blow or other traumatic injury to your head or body. The degree of damage might depend on several factors, which include the nature of the injury as well as the force of impact.
Common events that generally lead to traumatic brain injury can include the following:
Falls- If you fall from your bed, a ladder, in the bath, or down the stairs, it can cause traumatic brain injury. It is the most common cause overall, among older adults as well as young children.
Violence- Gunshot wounds, domestic violence, child abuse, and such assaults are also common causes. A shaken baby syndrome is a traumatic brain injury that can happen to infants if they are shaken violently.
Sports Injuries- Sometimes a traumatic brain injury can also result from sports such as soccer, football, boxing, baseball, skateboarding, hockey, etc. These are common mostly among the youths.
Collisions- Collisions involving cars, motorcycles, bicycles, or pedestrians, can also lead to traumatic brain injury.
Explosive blasts or combat injuries- Among military personnel, explosive blasts are a common cause of traumatic brain injuries. It is still, however, not understood, how the damage occurs, but according to many researchers, the pressure waves passing through the brain can significantly disrupt brain function.
Traumatic brain injury can also be a result of penetrating wounds, severe blows to the head, or falls or bodily collisions with any objects following a blast.
Diagnosis
When a person is brought to the emergency room with a head injury, doctors try to learn as much as they can about the symptoms, as well as the cause and extent of the injury.
A GCS or Glasgow Coma Score is a 15-point test that is used to grade a patient’s level of consciousness. This test helps doctors assess how responsive and conscious a patient is.
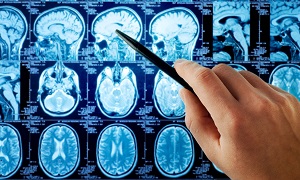
Next, diagnostic imaging tests are performed, which can include the following:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Computed Tomography (CT)
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
Treatment
In mild cases of traumatic brain injury, rest and medication might be enough to relieve headaches.
Medications can include anti-seizure drugs or coma-inducing drugs, etc.
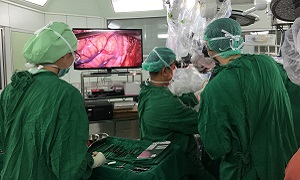
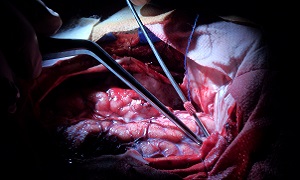
However, in severe cases, surgery may be required, to address the following problems:
Repairing skull fractures
Removing clotted blood (hematomas)
Bleeding in the brain
Opening a window in the skull
Surgery can also be used to relieve pressure inside the skull by draining accumulated cerebral spinal fluid or creating a window in the skull that helps to provide more room for swollen tissues.
Most people having a significant brain injury can require rehabilitation. They can relearn basic skills, such as walking or talking. This helps to improve their abilities while performing daily activities.
Complications
Immediately or soon after a traumatic brain injury, there might be several complications. The more severe the injury is, the higher the chances of greater complications.
A person can fall into a coma, where he/she is unaware of anything and unable to respond to any stimulus. A person can also fall into a vegetative state, where a person may open his or her eyes, though he/she is unaware of his/her surroundings. A vegetative state can also become permanent, though generally, individuals progress to a minimally conscious state. In a minimally conscious state, there are signs of self-awareness.
However, when there is no measurable activity in the brain and the brainstem, this is known as brain death. This condition is considered irreversible.
There might be physical complications as well, such as seizures, infection, hydrocephalus, blood vessel damage, headaches, or vertigo. These symptoms may last for a few weeks to a few months, after a traumatic brain injury.
Sometimes, traumatic brain injuries at the base of your skull can cause nerve damage to the nerves that emerge directly from one’s brain, i.e. the cranial nerves. If these nerves are damaged, it can result in:
- Paralysis of facial muscles or loss of sensation in the face
- Loss of or altered sense of taste
- Loss of vision or double vision
- Loss of or altered sense of smell
- Problems while swallowing
- Ringing in the ear
- Dizziness
- Hearing loss
Many people who suffer a significant brain injury can show cognitive problems, such as problems in memory and learning new things. Some people can problems while solving problems or multitasking.
Problems with communication are also common following a traumatic brain injury. Many people also experience changes in behavior and emotion.
According to research, it has also been suggested that repeated or severe traumatic brain injuries can increase the risk of degenerative brain diseases.
A degenerative brain disorder causes gradual loss of the functions of the brain. These disorders include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, etc.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of brain injury, follow these tips:
Seat belts and helmets- If you are driving or riding in a car, always remember a seatbelt. In case of a bicycle or motorcycle, remember to put on a helmet. Helmets are also important during certain sports such as baseball and snowboarding.
Alcohol and Drug Use- It is important not to drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Prescription medications can also impair one’s ability to drive.
To prevent falls around the house, follow the following tips:
- Install handrails in bathrooms
- Put a nonslip mat in the bathtub or shower
- Remove area rugs
- Install handrails on both sides of staircases
- Get regular vision checkups
- Get regular exercise
- Improve lighting in your house
- Keep stairs and floors clear of any clutter
The following tips can help your child avoid any head injuries:
- Install safety gates at the top of the stairways
- Install window guards to prevent falls
- Put a nonslip mat in the bathtub or shower
- Keep stairs clear of any clutter
- Use playgrounds that have shock-absorbing materials on the ground
- Make sure area rugs are secure
- Don’t allow your child to play on fire escapes or balconies