Best Doctors in India for Rectal Cancer Treatment
- Liver Transplant Surgeon and HPB Surgeon, New Delhi, India
- Over 20 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- With over 20 years of experience in performing complex operations for cancer, and other diseases involving the pancreas, liver, and gall bladder, Dr. Anupam Saha has been the foremost gastro intestinal and Hepato-Pancreato-biliary surgeon of the Indian Armed Forces.
- He did a 1-year fellowship in Liver Transplantation as well, at King’s College Hospital, London.
- For his service, Dr. Anupam Saha has also been awarded the Vishist Sewa Medal by the Armed Forces.
- Liver Transplant Surgeon & HPB Surgeon, Noida, India
- Over 17 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. K R Vasudevan is a surgical gastroenterologist who has been trained at one of India’s best hospitals. Over a short span of 17 years, his career has progressed to the role of leading a team.
- He has established and sustained a liver transplant program at PSRI over the last few years. Due to his experience with over 1200 live donor liver transplants, he was selected for this role.
- HBP & Liver Transplant Surgeon, Bengaluru, India
- Over 35 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Sanjay Govil is an accomplished HBP & Transplant Surgeon. He completed FRCS from the Royal College of Surgeons in England.
- He has achieved a few major accomplishments throughout his life as well, which include the First Liver Resection in Karnataka, in 2007, First Laparoscopic Liver Resection in a Cirrhotic Liver in Karnataka in the year 2008, First Laparoscopic Pancreatic duodenectomy in Karnataka in 2008, First ALPPS procedure in India in 2012 and several more.
- He trained in liver surgery and transplantation at Kings College Hospital in London, Queen Mary’s Hospital in Hong Kong, and the Graduate School of Medicine in Tokyo.
- Hepatologist & Gastroenterologist, Chennai, India
- Over 18 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dinesh Jothimani is a Hepatologist and Gastroenterologist with over 18 years of experience.
- He completed his MRCP (UK) from the Royal College of Physicians, London in 2004.
- Dr. Dinesh Jothimani is a liver specialist trained in the UK and Australia. He cares for his patients who suffer from liver diseases and performs skillful liver transplants.
- Senior Consultant - Hepatology and Liver Transplant, Mumbai, India
- Over 13 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Uday Sanglodkar is a highly motivated and compassionate medical gastroenterologist with experience in hepatology/transplant hepatology.
- Dr. Uday Sanglodkar has vast experience in pre and post-liver transplant care, liver intensive care management, and evidence-based management of gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
- Dr. Sanglodkar is also an expert at diagnostic and therapeutic gastrointestinal endoscopy.
- Liver Transplant Surgeon, New Delhi, India
- Over 30 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Sanjiv Saigal is a trained Hepatologist who has spearheaded the medical team of liver transplantation in the largest liver transplant program in India for over a decade
- Dr. Saigal is a bright name in the field of Gastroenterology and a famous liver transplant specialist with over 3400 successful Liver Transplants in his career.
- Medical Gastroenterologist, New Delhi, India
- Over 54 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Sohan Lal Broor is a Gastroenterologist and has an experience of 54 years in this field. Dr. Broor practices at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals in New Delhi.
- He completed MBBS from Panjab University in 1967, MD – Medicine from PGIMER, Chandigarh in 1972, and DM – Gastroenterology from PGIMER, Chandigarh in 1974.
- Dr. Sohan Lal Broor is a member of the 2-Year Fellowship in Gastroenterology at Medical College Of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, USA.
- Some of the services provided by Dr. Broor are Irritable Bowel Syndrome ( IBS ) Treatment, Peptic/ Gastric Ulcer Treatment, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treatment, Hemorrhoids Treatment, and Gastritis Treatment.
- Surgical Gastroenterologist, Chennai, India
- Over 22 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Jameel is an internationally acclaimed GI and Minimal Access Surgeon from India with more than 22 years of experience.
- He underwent higher surgical training and Oncology research in Yorkshire. Dr. Jameel also did Robotic Surgical training at the University College Hospitals, London.
- Following his successful completion of training and obtaining CCT, he practiced at MidYorkshire Hospitals. In addition to consultation, he was an educational supervisor and provided surgical training to many surgeons.
- Surgical Gastroenterologist, Chennai, India
- Over 41 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Bala Chandran T G is a veteran gastroenterologist with over 41 years of experience.
- Apart from completing his MBBS, MS, and MCh, he has done a fellowship from the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, the UK.
- He obtained training in laparoscopic techniques from Ethicon Endosurgery Institute, Mumbai.
- Dr. Bala Chandran T G has done much research, authored, and published several articles in many publications.
- Surgical Gastroenterologist, Chennai, India
- Over 48 years’ experience
Profile Highlights:
- Dr. Prasanna Kumar Reddy is a veteran gastroenterologist in Chennai.
- Along with MBBS and DNB in surgery, he has a Diploma in Laparoscopy from Strasbourg.
- Over the years, Dr. Prasanna Kumar Reddy has gained enough recognition and appraisals for his treatment methods and has become one of the most preferred doctors.
Best Hospitals in India for Rectal Cancer Treatment
CK Birla Hospital, Gurugram
- City: Gurugram, India
Hospital Highlights:
- The CK Birla Hospital in Gurugram is a NABH-accredited multi-specialty hospital.
- The hospital strives to increase the quality of healthcare by focusing on UK NHS nurse and midwife training requirements. Policies and practices derived from the National Institute for Health and Treatment Excellence (NICE) recommendations in the United Kingdom ensuring that a strong focus on safety, high-quality clinical care, and sanitation is maintained.
- The hospital’s cutting-edge technology and facilities allow for real-time communication and seamless collaboration among caregivers, ensuring accuracy and the best possible results. Those with foreign experience and accreditations make up part of the hospital’s team of clinicians.
KIMS Hospital, Hyderabad
- City: Hyderabad, India
Hospital Highlights:
- KIMS Hospital (a brand name of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences) is one of the largest and best multi-speciality hospitals in Hyderabad. The hospital provides various treatments to an enormous number of patients.
- The hospital has a capacity of more than 3000 beds. KIMS Hospitals offers different healthcare services in more than 25 specialities and super specialities.
- The hospital is equipped with modern medical equipment and technology. It has robotic equipment to provide minimal invasive techniques for patients.
- The hospital is aimed at providing world-class healthcare facilities and services at an affordable cost for patients.
- The various specialities and departments of the hospital include neurosciences, gastroenterology & hepatology, robotic science, reproductive sciences, dental science, oncological sciences, organ transplantation, heart and lung transplantation and mother and child care.
Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh
- City: New Delhi, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Fortis Hospital in Shalimar Bagh is a multi-super specialty hospital that strives to provide world-class patient care by leaving no stone unturned.
- Fortis, Shalimar Bagh, with 262 beds and a 7.34-acre footprint, provides the best level of medical care through its team of doctors, nurses, technicians, and management professionals.
Reliance Hospital, Mumbai
- City: Mumbai, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Reliance Hospital is one of the best super-specialty care hospitals in Navi Mumbai.
- The main purpose of this hospital is to become a trustworthy place for the best health and hope for society. The hospital is well connected to the suburbs of Mumbai and Navi Mumbai.
- The hospital has various specialty departments, viz., Accident & Emergency, Anesthesiology, Dental Services, Dermatology, Diabetology, Dietetics Nutrition, Endocrinology, ENT, Gastroenterology, General Surgery, Gynaecology And Obstetrics, Hepato Pancreato Biliary Surgery, Infectious Disease, Internal Medicine, Interventional Radiology, Laboratory Medicine, Minimal Access Laparoscopic Surgery, Nephrology, Neurosciences, Opthalmology, Orthopaedics, Paediatrics, Pain Management Palliative Care, Physical Medicine Rehabilitation, Plastic And Reconstructive Surgery, Psychiatry, Pulmonary Medicine, Radiology, Rheumatology, Transplant, Urology Andrology, Vascular Surgery
Lilavati Hospital & Research Centre, Mumbai
- City: Mumbai, India
Hospital Highlights:
- Lilavati Hospital & Research Centre is India’s premier multi-speciality tertiary care hospital and has been recognised as a global medical excellence centre.
- Lilavati Hospital & Research Centre has built an unrivalled level of trust with its patients over the years, thanks to a solid foundation that comprises cutting-edge facilities, the best medical competence, research, education, and charity endeavours.
- The hospital is quite proud of the fact that it now serves patients from all kinds of backgrounds, not just from the United States but from all around the world.
- The hospital has a total of 323 beds, one of the largest Intensive Care Units (ICUs), 12 Operation Theatres with modern amenities, over 300 consultants, and almost 1,800 personnel.
Rectal Cancer
Rectal Cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the cells of the rectum. Your rectum is located below the sigmoid colon, above your anus. Cancer inside the rectum (known as rectal cancer) and inside the colon (known as colon cancer) are usually referred to together as colorectal cancer. Across, the world, colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer among females and the third most common among males.
Although in the past, people with rectal cancer mostly did not survive for the long-term, thanks to advanced treatment in the past few decades, the survival rates among people having rectal cancer have improved drastically.
Symptoms
In the early stages, rectal cancer might show no obvious symptoms. As the disease continues to develop, symptoms can include changes in bowel movement, rectal bleeding, as well as a thin stool. There might be other signs and symptoms as well, such as:
- Fatigue
- Weight Loss
- Blood in the stool
- Diarrhea and/or constipation
- Bloating
- Abdominal Pain
- A feeling of being unable to empty the bowels
If your cancer metastasizes or spreads to other body parts, then symptoms can vary depending on where in the body your cancer is located. Some of the symptoms of metastatic rectal cancer include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Jaundice
- Swelling in the hands and feet
- Changes in vision or speech
Causes
Rectal cancer begins when your body’s healthy cells in the rectum develop changes or mutations in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains all instructions that instruct it what to do.
These changes instruct the cells to grow uncontrollably and to continue living, whereas healthy cells would die normally. These accumulating cells can become a tumor. Within time, the cancer cells might grow to invade and destroy any healthy tissue nearby. And cancerous cells can break away and travel i.e. metastasize to any other parts of the body.
Generally, for most rectal cancers, it is unclear what leads to the mutations that cause cancer to form.
There are some inherited gene mutations as well, which can increase the risk of this cancer. One of these is known as Lynch syndrome. This disorder can raise the risk of colon and other cancers, especially before the age of 50.
Another such syndrome that increases the risk of rectal cancer is familial adenomatous polyposis. This disorder that can cause polyps in the lining of the colon and rectum is usually rare. Without treatment, it may increase the risk of colon or rectal cancer, especially before the age of 40.
Other risk factors for rectal cancer are:
- Age- Diagnosis usually occurs after the age of 50, although rates are increasing among younger people.
- Family history- Personal or family history of colorectal cancer can also increase risk.
- Race- African Americans are at a higher risk than other ethnicities of developing rectal cancer.
- Radiation therapy– If you have undergone radiation therapy in the abdominal area, it might increase risk.
Other conditions that may increase risk include:
- Ovarian cancer
- Obesity
- Polyps
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Type 2 diabetes that’s not well managed
Some lifestyle factors can sometimes play a role in colorectal cancer as well:
- Diet with too few vegetables and too much red meat
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Consuming over three alcoholic drinks a week
Diagnosis
Your doctor is most likely going to begin by first taking your medical history. Then he/she will need to perform a physical examination.
Sigmoidoscopy
Next, a fecal immunochemical test or a sigmoidoscopy might also be recommended. If these steps are positive for cancer, the next step is going to be a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy
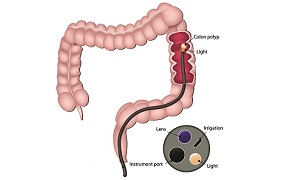
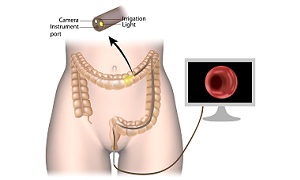
A colonoscopy involves your doctor using a thin tube with a light and a camera at the end to view the inside of your rectum and colon. They are usually able to remove any polyps they can find at this time. During this test, your doctor can also collect tissue samples for later examination in a lab. These samples can be viewed under a microscope to determine if they are cancerous. They may also be tested for genetic mutations that are associated with colorectal cancer.
Blood test
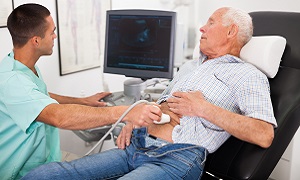
Ultrasound
Once your doctor is able to confirm the diagnosis, the next step is going to involve determining how far it might have spread.
Your doctor might use an endorectal ultrasound in order to examine your rectum and its surrounding area. For this, your doctor will need to insert a probe into your rectum to produce a sonogram, a type of image.
Imaging tests
Your doctor might need to use other imaging tests as well, such as an X-ray or an MRI, to look for any signs of cancer throughout the body.
Treatment
Treatment for rectal cancer generally involves a combination of therapies. When possible, surgery is used to remove or cut away the cancer cells. Other treatments such as chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, might be used after the surgery, to kill any cancer cells that remain as well as reduce the risk that the cancer is going to return.
If the surgeons are concerned that your cancer is not removable completely, without hurting any nearby organs, then a combination of radiation therapy and chemotherapy might be recommended initially. These kinds of treatments can help in shrinking the cancer cells and make them easier to remove during the operation.
Surgery
Surgery is generally the most common and preferred method for removing the cancer cells. There are various kinds of surgeries that may be performed, depending on the location and stage of cancer, how aggressive the cells are, as well as your overall health, and your preferences.
The surgery can be of various types, including any of the following:
Removing very small cancers from the inside of the rectum
Very small rectal cancers can be removed with the help of a colonoscope or a specialized type of scope inserted through the anus. Surgical tools can be passed through the scope for cutting away cancer and some of the healthy tissue around it.
If your cancer is small and unlikely to spread to any nearby lymph nodes, then this procedure is an option. If a lab analysis indicates that your cancer cells are aggressive or more likely to spread to the lymph nodes, then it is likely that your doctor is going to recommend additional surgery.
Removing all or part of the rectum
This might be required for larger rectal cancers that are far enough away from the anal canal. It involves the removal of any nearby tissue and lymph nodes as well. This procedure can help in preserving the anus so that the waste is able to leave the body normally.
How this procedure will be performed, is going to depend on the location of the cancer. If your cancer is affecting the upper portion of the rectum, then this part of the rectum is removed, after which the colon is attached to the remaining rectum. All of the rectum might require removal as well if the cancer is located in the lower portion of the rectum. Then the colon is shaped into a pouch after which it is attached to the anus.
Removing the rectum and anus
If your rectal cancer is located near the anus, it might be not possible to remove cancer completely without damaging the muscles that control the bowel movements. In these situations, surgeons may recommend an operation which is termed abdominoperineal resection (APR). This involves removing the rectum, anus as well as some of the colon, and its nearby tissue and lymph nodes.
The surgeon then creates an opening in the abdomen and attaches the remaining colon to it. Waste is able to leave your body through this opening and collects in a bag attached to the abdomen.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy involves using powerful energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill the cancer cells. In people who are suffering from rectal cancer, radiation therapy can also be combined with chemotherapy as it can make the cancer cells more likely to be damaged by radiation. It may be used after surgery as well, to kill any cancer cells that are remaining. It can be used before surgery as well, to shrink cancer, making it easier to remove.
Radiation therapy can also help in relieving symptoms like pain.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells. For rectal cancer, chemotherapy might also be recommended after surgery in order to kill any cancer cells that are remaining.
Chemotherapy can also be combined with radiation therapy might before an operation to shrink large cancer so that it becomes easy removing it with surgery.
Chemotherapy may also be used to relieve symptoms of rectal cancer which is not removable with surgery.
Targeted drug therapy
Targeted drug treatments are meant to focus on specific abnormalities that exist within cancer cells. When these abnormalities are blocked, targeted drug treatments can lead to the death of the other cancer cells.
Targeted drugs are generally combined with chemotherapy. Generally, they are reserved for people having advanced rectal cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that strengthens your immune system to fight cancer. Your body’s immune system might not attack your cancer as the cancer cells produce proteins and these hide them from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy can help to interfere with that process.
Immunotherapy is also generally reserved for advanced rectal cancer.
Prevention
Exercising for at least 30 minutes a day can help to increase the risk of rectal cancer. Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and maintaining a healthy weight, can also help.
If you are a smoker, it is important to stop. If you choose to drink alcohol, drink it in moderation. For women, it should not exceed one drink a day, and for men, it shouldn’t exceed two.